-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 13
Python plotting
Current dependencies: numpy, matplotlib, scipy, h5py, pycuda, pyshtools (version < 4.5), psutil
The mjolnir (THOR/mjolnir/) plotting scripts are written for Python 3 (compatibility with Python 2 still needs to be tested). Most dependencies are pretty standard for science: numpy, matplotlib, and scipy. Additionally, you'll need to install h5py:
$ pip3 install h5py
or
$ conda install h5py
h5py is simply a Python package that allows easy interaction with hdf5 files (THOR's standard output format).
Before running mjolnir.py itself, it is necessary to run pgrid.py on the results folder like
$ ./pgrid -i 0 -l 10 awesome_results
mjolnir.py is set up as an executable for command line, but you'll need to add the path to your environment file. In bash, add the line
export PATH="$PATH:<path to thor>/mjolnir"
to your ~/.bashrc or ~/.bash_profile file, replacing <path to thor> with the actual path to the repository on your system. Probably not the smartest or most pythonic way of setting this up but one thing at a time please. Once that is done, the command to make a plot looks like
$ mjolnir <options> <type of plot>
For example,
$ mjolnir -i 0 -l 10 -f awesome_results -s coolest_planet Tver
where -i, -l, -f, and -s are options flags and Tver is a plot type. The available options flags are
-i / --initial_file <N> number of first output file to open
-l / --last_file <N> number of last output file to open
-f / --file <string> folder containing results
-s / --simulation_ID <string> name of planet (used in naming of output files)
-lev / --horizontal_lev <N> pressure level to use in horizontal plots (mbar units)
-pmin / --pressure_min <N> pressure minimum for vertical plots (mbar units)
-slay / --split_layer <N> splits conservation data into "weather" and "deep" layers at this pressure (mbar units)mjolnir averages the data over time for the entire range of files read in. So with -i 0 and -l 10, files 0-10 will all be read in, and the plotted quantities will be averaged over all 11 snapshots in time. If you want to plot one instant in time, just set -i and -l to the same value. The averaging process can get quite long because the data is interpolated in many ways before averaging. Be careful if you are passing mjolnir more than ~50 output files.
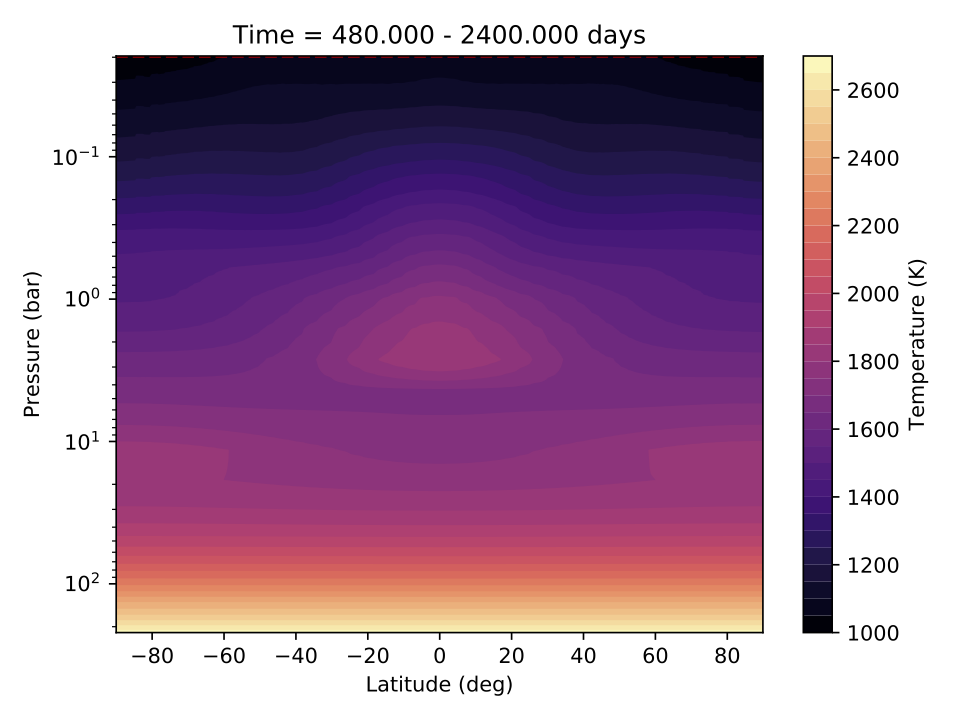
There are three basic types of plot mjolnir can make (plus a few other special ones): vertical, horizontal, and profile. Vertical plots are averaged zonally and temporally, resulting in contours on a latitude vs pressure grid. Horizontal plots are averaged only temporally, and plotted at a given pressure level on a latitude vs longitude grid. Profile plots show quantities along single columns or average columns, as a function of pressure.
The -p option is used only by the horizontal plot types and is simply the desired pressure level to be viewed. The -pmin option is used only by the vertical plot types and is just the lowest pressure level to be plotted. For vertical plots, mjolnir will plot a dashed line representing the maximum pressure at the top of the model--thus data plotted above this line requires some extrapolation and should be viewed skeptically.
Current vertical plot types are
Tver time- and zonally-averaged temperature
uver time- and zonally-averaged zonal wind speed
wver time- and zonally-averaged vertical wind speed
PTver time- and zonally-averaged potential temperature
PVver time- and zonally-averaged potential vorticity
stream time- and zonally-averaged mass streaming functionAn example of time- and zonally-averaged vertical plots are below. These show the temperature and zonal wind for the deep hot jupiter benchmark:

Current horizontal plot types are
Tulev time-averaged temperature and horizontal wind along a pressure surface
ulev time-averaged zonal and meridional winds along a pressure surface
PVlev time-averaged potential vorticity along a pressure surface
RVlev time-averaged relative vorticity along a pressure surface
tracer time-averaged molecular abundances along a pressure surface
Current profile plot types are
TP temperature-pressure profiles drawn from all over the grid
wprof vertical wind vs pressure averaged over 4 quadrants (useful for synchronous rotation) 