A command line tool to download Android applications directly from the Google Play Store.
PlaystoreDownloader is a tool for downloading Android applications directly from the Google Play Store. After an initial (one-time) configuration, applications can be downloaded by specifying their package name.
This project is intended for learning purposes only and is not affiliated with Google in any way.
| Command Line Interface |
|---|
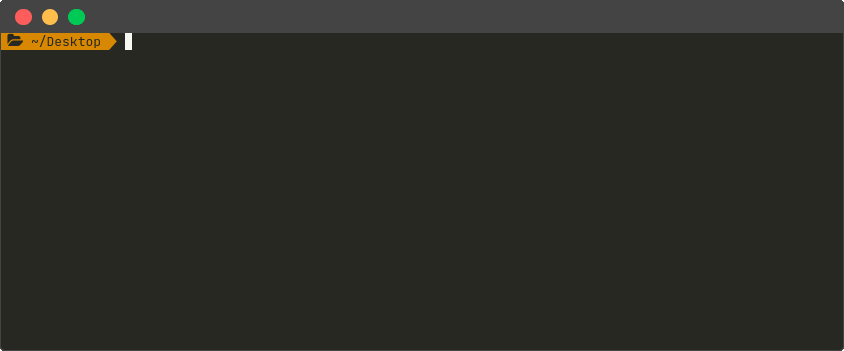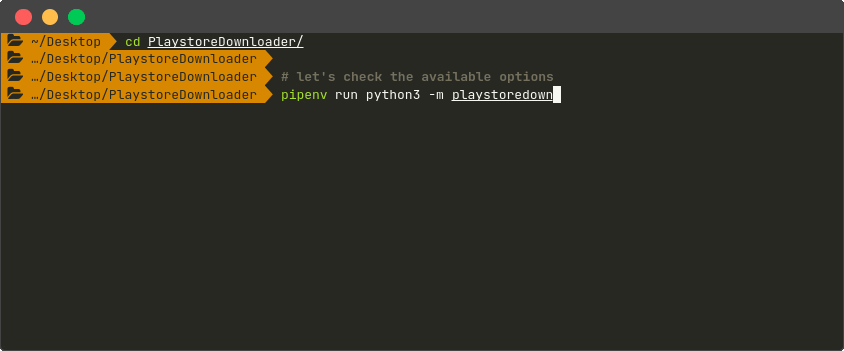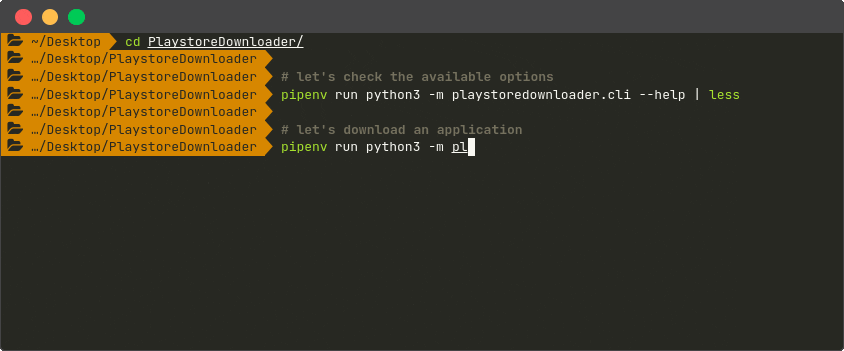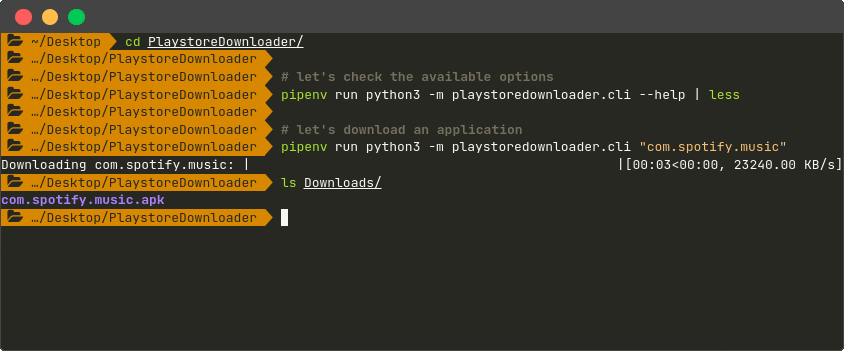 |
| Web Interface |
|---|
 |
There are two ways of getting a working copy of PlaystoreDownloader on your own
computer: either by using Docker or by
using directly the source code in a Python 3 environment. In both
cases, the first thing to do is to get a local copy of this repository, so open up a
terminal in the directory where you want to save the project and clone the repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/ClaudiuGeorgiu/PlaystoreDownloader.gitThis is the suggested way of installing PlaystoreDownloader, since the only requirement is to have a recent version of Docker installed:
$ docker --version
Docker version 19.03.0, build aeac949The official PlaystoreDownloader Docker image is available on Docker Hub (automatically built from this repository):
$ # Download the Docker image.
$ docker pull claudiugeorgiu/playstore-downloader
$ # Give it a shorter name.
$ docker tag claudiugeorgiu/playstore-downloader downloaderIf you downloaded the official image from Docker Hub, you are ready to use the tool so
go ahead and check the usage instructions, otherwise execute the
following command in the previously created PlaystoreDownloader/ directory (the folder
containing the Dockerfile) in order to build the Docker image:
$ # Make sure to run the command in PlaystoreDownloader/ directory.
$ # It will take some time to download and install all the dependencies.
$ docker build -t downloader .When the Docker image is ready, make a quick test to check that everything was installed correctly:
$ docker run --rm -it downloader --help
usage: download.py [-h] [-b] [-s] [-c CREDENTIALS] [-o FILE] [-t TAG] package
...PlaystoreDownloader is now ready to be used, see the usage instructions for more information.
Apart from valid Google Play Store credentials, the only requirement of this project is
a working Python 3 (at least 3.6) installation and
pipenv (for dependency management).
Run the following commands in the main directory of the project (PlaystoreDownloader/)
to install the needed dependencies:
$ # Make sure to run the commands in PlaystoreDownloader/ directory.
$ # This project uses pipenv (https://pipenv.pypa.io/) for dependency management.
$ # It can be installed with the following command:
$ # python3 -m pip install pipenv
$ # Install PlaystoreDownloader's requirements (a virtual environment will be created).
$ pipenv install --deployAfter everything is installed, make a quick test to check that everything works correctly:
$ pipenv run python download.py --help
usage: download.py [-h] [-b] [-s] [-c CREDENTIALS] [-o FILE] [-t TAG] package
...PlaystoreDownloader is now ready to be used, see the usage instructions for more information.
Before interacting with the Google Play Store you have to provide valid credentials and an ANDROID ID associated to your account. Please modify the credentials.json file and insert the required information before trying to use this tool:
-
Enter your Google email and password in the
USERNAMEandPASSWORDfields of the credentials.json file. This information is needed to authenticate with Google's servers. In case you have 2-Step Verification activated, you will need to generate an App Password for thePASSWORDfield. -
Use the above credentials on an Android device (real or emulated) and download at least one application using the official Google Play Store on the device. This step is necessary in order to associate the ANDROID ID of the device to your account, so that you will be able to download applications as if you were directly using your device. Do not remove the account from the device or its ANDROID ID won't be valid anymore.
-
Get the ANDROID ID of the device and fill the
ANDROID_IDfield of the credentials.json file. You can obtain the ANDROID ID by installing the Device ID application on your device, then copy the string corresponding toGoogle Service Framework (GSF)(use this string instead of theAndroid Device IDpresented by the application). -
In case of errors related to the authentication after the above steps, consider the following actions (visit the links while you are logged in with the account used to download the applications):
-
allow less secure apps to access your account (https://myaccount.google.com/lesssecureapps)
-
temporarily unlock access to your account (https://accounts.google.com/DisplayUnlockCaptcha)
-
Note that you will be able to download only the applications compatible with the device corresponding to the aforementioned ANDROID ID and further limitations may influence the total number of applications available for download.
After configuring the Google Play Store credentials as described in the
configuration, you should have a valid credentials.json file ready
to be used. The usage instructions depend on how you installed the tool.
The file with the credentials is not included in the Docker image, so it has to be
mounted into the container. A download directory has to be mounted too, otherwise the
downloaded application won't be accessible to the host machine. If the current
directory (${PWD}) contains the credentials.json file and an output/ folder, the
command to download an application with package name com.application.example becomes:
$ docker run \
-u $(id -u):$(id -g) \
-v "${PWD}/credentials.json":"/app/credentials.json" \
-v "${PWD}/output/":"/app/Downloads/" \
--rm -it downloader "com.application.example"If the download is successful, the resulting .apk file will be saved in the output/
folder contained in the directory where the command was run (type
$ docker run --rm -it downloader --help or check the
available parameters for more information).
A simple web interface is also available:
$ docker run \
-u $(id -u):$(id -g) \
-v "${PWD}/credentials.json":"/app/credentials.json" \
-v "${PWD}/output/":"/app/Downloads/" \
-p 5000:5000 \
--entrypoint=python \
--rm -it downloader flask_app.py
$ # Navigate to http://localhost:5000/ to use the web interface.In the main directory of the project (PlaystoreDownloader/), call the following
instruction using the package name of the app to be downloaded:
$ pipenv run python download.py "com.application.example"If the download is successful, the resulting .apk file will be saved in the
PlaystoreDownloader/Downloads/ directory. You can change the name and the location
of the downloaded .apk file by providing an additional -o "path/to/downloaded.apk"
argument to
download.py
(type $ pipenv run python download.py --help or check the
available parameters for more information).
A simple web interface is also available:
$ pipenv run python flask_app.py
$ # Navigate to http://localhost:5000/ to use the web interface.All the parameters are described in the help message:
$ # With Docker.
$ docker run --rm -it downloader --help
$ # With source.
$ pipenv run python download.py --help
usage: download.py [-h] [-b] [-s] [-c CREDENTIALS] [-o FILE] [-t TAG] package
...The only mandatory parameter is the package name of the application to be downloaded,
as it appears in the Google Play Store (e.g., com.spotify.music or com.whatsapp).
The other optional arguments are as follows:
-
-bis a flag for downloading the additional.obbfiles along with the application (if there are any). See Expansion Files for more information. The additional files will be saved in the same directory as the downloaded application. -
-sis a flag for downloading the additional split.apkfiles along with the application (if there are any). See Dynamic Delivery for more information. The additional files will be saved in the same directory as the downloaded application. Note: this feature used to work but currently seems broken. -
-c CREDENTIALSis used to set the path to the JSON configuration file containing the Google Play Store credentials. If not specified, by default the tool will try to use a file namedcredentials.jsonlocated in the directory where the command is run. -
-o FILEis used to set the path (relative or absolute) of the downloaded.apkfile (e.g.,-o /home/user/Desktop/downloaded.apk). If the path contains missing directories, they will be created automatically. If not specified, by default the file will be saved in aDownloads/directory created where the tool is run. -
-t TAGcan be used to set a tag that will be prepended to the file name, e.g., by using-t "LABEL"the final name of the downloaded application will look like[LABEL] filename.apk. Note: the tag is applied only to the main application, the additional files won't have any tag added to the file name.
Note that currently only the command line interface is configurable with the above arguments, the web interface will ask only for a package name and will use the default values for all the other parameters.
Questions, bug reports and pull requests are welcome on GitHub at https://github.com/ClaudiuGeorgiu/PlaystoreDownloader (see contributing).
You are free to use this code under the MIT License.

