Welcome to use this project.
This project is based on the mongodb driver package development, which greatly simplifies the native API and enables developers to focus on the business itself. The project uses an annotation style pattern that simplifies configuration like XML.
1: Simple document mapping
2: nested document mapping
3: asynchronous storage. Batch storage
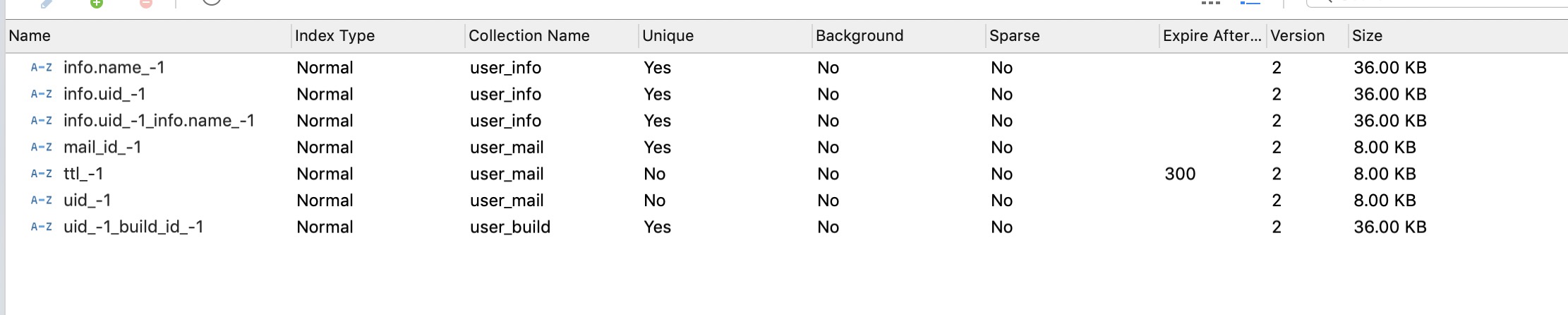
4: index
Simple and combined indexes can be automatically created and maintained by annotating @Indexed and @compoundIndexed, simplifying the use and maintenance of mongodb indexes
/**
* compound indexed:Multiple field combination index composition
*
*/
@Inherited
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
public @interface CompoundIndexed {
Indexed[] value();
int order() default -1;
boolean unique() default true;
}
/**
* Normal index: Creates an index for a field
*/
@Target({ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE, ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Indexed {
boolean unique() default false;
String name();
int order() default -1;
}
/**
* Expiration time index: This document is time-sensitive
*/
@Target({ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE, ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ExpireIndex {
boolean unique() default false;
String name() default "";
int order() default -1;
}
The detailed use of IndexTest is shown in IndexTest, where the index is created when the index is marked on the Po class or field of each document.
Simple document: The document structure is simple, and the field type is basic data type field.
Use steps:
/**
* A simple document
*/
@MongoDocument(table = "user_build")
@CompoundIndexed(value = {@Indexed(name = "uid"), @Indexed(name = "build_id")})
public class BuildPo extends AbstractMongoPo {
@MongoId(name = "uid")
private long uid;
@MongoId(name = "build_id", tick = true)
@BsonProperty("build_id")
private long buildId;
private int x;
private int y;
private String type;
private String name; MongoDocument annotation @mongoDocument database name to specify the table name, @compoundIndex to specify which fields to use as the joint index. You can also use @indexed to specify a separate index and @mongoid to specify a primary key. Since mongodb can't implement mysql customization, indexes use this annotation to specify primary key customization
public static void addBuild() throws MException {
BuildPo buildPo = new BuildPo();
buildPo.setY(6);
buildPo.setX(7);
buildPo.setUid(1);
buildPo.setName("北京SOHO大厦");
buildPo.setType("高端建筑");
MongoManager.getInstance().add(buildPo);
} private static void addManyBuild() throws MException {
List<BuildPo> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
BuildPo po = new BuildPo();
po.setUid(2049);
po.setX(i);
po.setY(i);
list.add(po);
}
MongoManager.getInstance().addMany(list);
}For example, the added data can be queried in mongodb

Query can be divided into two ways, one is to use the @mongoid annotation 'get' primary key to query, and the other is to use a field to 'find' query
/**
* 主键查询
*/
public static void get() throws MException {
BuildPo b = MongoManager.getInstance().get(BuildPo.class, PrimaryKey.builder("uid", 1), PrimaryKey.builder("build_id", 7));
System.out.println(b.getBuildId());
}
public static void getAll() throws MException {
List<BuildPo> bs = MongoManager.getInstance().getAll(BuildPo.class, PrimaryKey.builder("uid", 1));
System.out.println("getAll size=" + bs.size());
}
public static void findOne() throws MException {
BuildPo b = MongoManager.getInstance().findOne(BuildPo.class, Query.builder().and("uid", 1).and("build_id", 7));
System.out.println(b.getX() + "|" + b.getY());
}
public static void findAll() throws MException {
List<BuildPo> bs = MongoManager.getInstance().findAll(BuildPo.class, Query.builder().and("uid", 1).and("y", 6), QueryOptions.builder().limit(100));
System.out.println("findAll size=" + bs.size());
}Modify a field in a document by, for example, modifying the query 'build' name
public static void update() throws MException {
BuildPo b = MongoManager.getInstance().get(BuildPo.class, PrimaryKey.builder("uid", 1), PrimaryKey.builder("build_id", 2));
b.setName("new name build");
MongoManager.getInstance().update(b);
}The system supports asynchronous operations. Encapsulate the operation as a task and add it to an asynchronous queue, from which the database execution thread retrieves the operation task.
private static void init() {
mongoManager = new MongoManager("127.0.0.1:27017", true);
} private void execute() {
if (pool.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
pool.forEach((k, v) -> collectionManager.getCollection(k).bulkWrite(v));
pool.clear();
}Thank you for your support of this project. If you find any problems, please feel free to issue. Welcome to star 🌟 🌟 🌟 🌟.
author:wenjiang.tang
gmail:[email protected]