-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 4
Working with User Search Strings
Allowing a user to search a database for certain strings is a common operation. Creating a SQL query based on a string entered by the user can be a bit of work, however. SQL Yoga comes to the rescue with some helper commands that can parse strings for you automatically and convert them into search conditions for a SQL Query object.
When working with SQL Query objects you can use sqlquery_setConditionsFromUserSearchString to set the conditions property of a SQL Query based on text a user enters.
In the following examples you will see results based on various search strings that were entered. The code to perform the search looks like this:
put sqlquery_createObject("todo_items") into tQueryA
put the text of field "Search" into tSearchString
put "todo_items.name contains :1" into tSearchCondition
sqlquery_setConditionsFromUserSearchString tQueryA, tSearchString, tSearchCondition
Basically the text that the user enters in the "Search" field will be parsed by SQL Yoga and inserted into the search condition that has been defined.
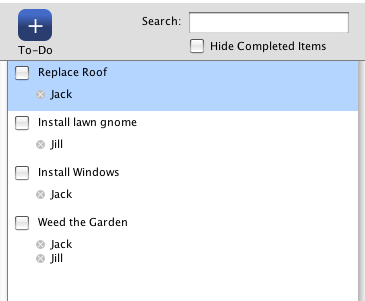
Here is what the results look like when no search term has been entered in the Search field.
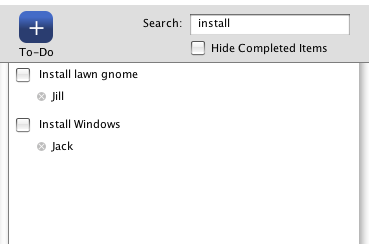
If a single word is entered then any record that contains that word will be returned. Here you can see that two to-do items contain the word install. The where clause looks like this:
WHERE (todo_items.name LIKE '%install%')
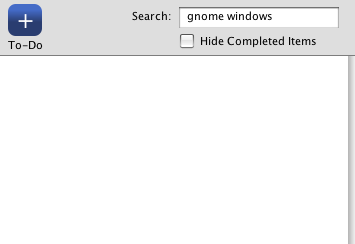
If more than one word is used then the words are split up and results that contain all of the words are returned. Here you can see that no records contain both the word gnome AND the word windows. The where clause looks like this:
WHERE (todo_items.name LIKE '%gnome%') AND (todo_items.name LIKE '%windows%')
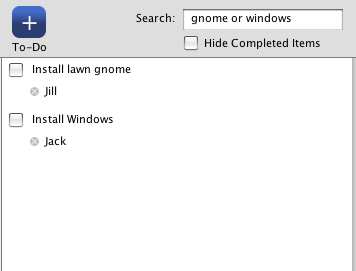
If the search term enters the words AND or OR then the search takes that into account. Here you can see that records that contain the word gnome OR the word windows are returned. The where clause looks like this:
WHERE (todo_items.name LIKE '%gnome%') OR (todo_items.name LIKE '%windows%')
If the search term is wrapped in quotes then an exact match is searched for rather than both words. Here you can see that there are no records that contain the phrase install gnome. The where clause looks like this:
WHERE (todo_items.name LIKE '%install gnome%')
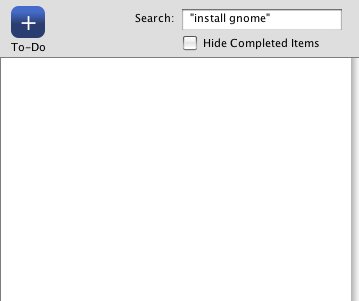
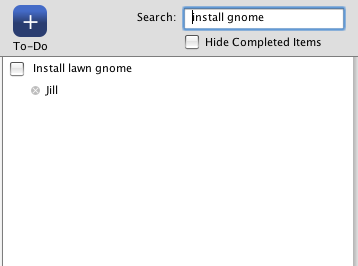
If the quotes are removed then a result is returned as there is one record that contains the word install and the word gnome. The where clause looks like this:
WHERE (todo_items.name LIKE '%install%') AND (todo_items.name LIKE '%gnome%')
If you are using Scope objects then you you can use sqlyoga_splitUserSearchString. It is similiar to sqlquery_setConditionsFromUserSearchString except that it is used when adding a scope to a SQL Query object. For example:
if the text of field "Search" is not empty then
sqlquery_addScope theQueryA, "name contains", \
sqlyoga_splitUserSearchString(the text of field "Search")
end if
SQL Yoga USER GUIDE
- Home
- SQL Yoga Objects
- Database Objects
- Connection Objects
- SQL Query Objects
- SQL Record Objects
- Table Objects
- Table Object Behaviors
- Relationships
- Scopes
- Schema
- Working with User Search Strings
- SQL Query Template Objects
- Error Handling
- Migrating from SQL Yoga 1.x
- Integrating with the Levure Application Framework