什么是GraphQL? 官方的解释:GraphQL是一门为API和运行时而生的查询语言。是一个由Facebook提出的应用层查询语言.通俗点来说,可以理解为基于RESTful的一种封装,一种新的api标准。
为什么要使用GraphQL?
- 所见即所得,相对RESTful API依赖于后端隐式的被动的数据约定,GraphQL更加显式,在获取数据和更新数据时更加主动。
- 减少网络请求的使用,GraphQL可以实现对多个数据源的调用,合并成一份完整的数据给前端使用。
- 参数类型强校验,GraphQL提供了强类型的schema机制,从而确保了参数类型的合法性。
准备 Prerequisites(先决条件):nodeV6或以上的版本,es6的一些语法糖。(官网上说,这些事例在nodeV6之前的版本还是可以使用。目前node稳定版本都在10.16以上了,所以...)
- 新建项目
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\graphql>npm init
This utility will walk you through creating a package.json file.
It only covers the most common items, and tries to guess sensible defaults.
See `npm help json` for definitive documentation on these fields
and exactly what they do.
Use `npm install <pkg>` afterwards to install a package and
save it as a dependency in the package.json file.
Press ^C at any time to quit.
package name: (graphql) u-test1
version: (1.0.0)
description: graphql test
entry point: (index.js)
test command:
git repository:
keywords:
author: onsen
license: (ISC)
About to write to C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\graphql\package.json:
{
"name": "u-test1",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "graphql test",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "onsen",
"license": "ISC"
}
Is this OK? (yes)
安装graphql
npm install graphql --save
编写代码,在根目录新建test-hello.js文件,输入:
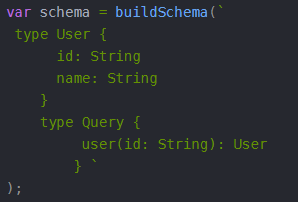
var { graphql, buildSchema } = require('graphql');
// Construct a schema, using GraphQL schema language
var schema = buildSchema(`
type Query {
hello: String
}
`);
// The root provides a resolver function for each API endpoint
var root = { hello: () => 'Hello world!' };
// Run the GraphQL query '{ hello }' and print out the response
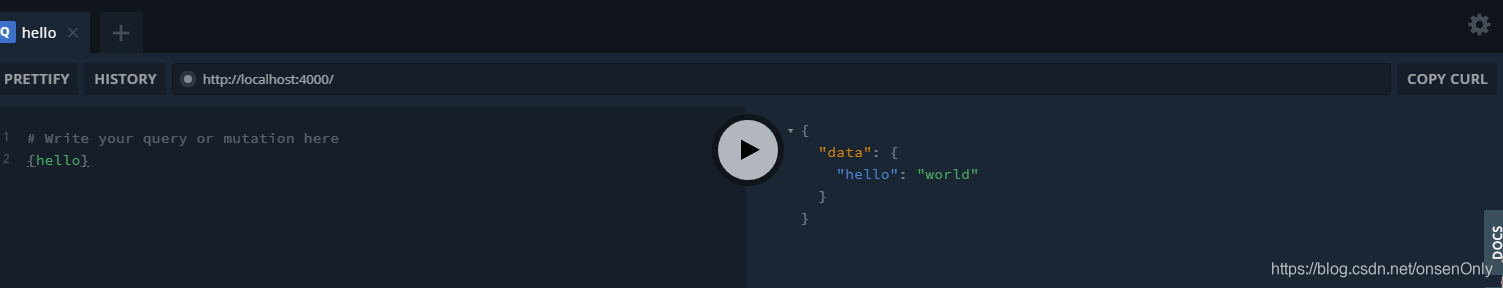
graphql(schema, '{ hello }', root).then((response) => {
console.log(response);
});运行
node test-hello.js
结果:
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\graphql>node index.js
{ data: { hello: 'Hello world!' } }
过程分析:
- 创建一个 schema 来定义查询语句和类型,buildSchema() 方法需要传入的参数是字符串类型;
- 创建一个 root 处理器,处理对应的查询;
- 联合处理器和模型。
Express作为一个流行的Node.js Web应用程序框架,为此搭建Express GraphQL服务器是学习GraphQL挺必要的一个东西。
基于Express GraphQL服务器的hello world
安装包模块:
npm install express express-graphql graphql
新建文件test2-express.js,输入:
var express = require('express');
var graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
var { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
var schema = buildSchema(`
type Query {
hello: String
}
`);
var root = { hello: () => 'Hello world!' };
var app = express();
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true,
}));
app.listen(4000, () => console.log('Now browse to localhost:4000/graphql'));运行
node test2-express.js
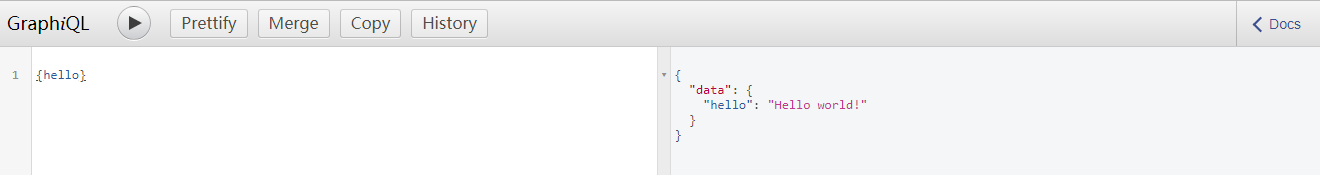
打开浏览器,输入:http://localhost:4000/graphql 由于aphqlHTTP带着graphiql: true,此时打开上面的地址之后,会进入到GraphiQL工具输入查询的界面。然后在界面上输入:{ hello },点击运行,可以看到给出的一个结果,如下图所示:
使用客户端发送请求 在访问http://localhost:4000/graphql后,可以使用图形用户界面发送测试查询。如果要使用客户端发送请求则应当如何使用呢?
- 创建一个 schema 来定义查询语句和类型,buildSchema() 方法需要传入的参数是字符串类型;
- 创建一个 root 处理器,处理对应的查询;
- 实例化 express ,并且将路由转发给 graphqlHTTP 处理。
graphqlHTTP 中的三个参数介绍: schema:定义的查询语句和类型 rootValue:处理对应查询的处理器 graphiql:是否开启调试窗口,开发阶段开启,生产阶段关闭
apollo-server是一套可以用于各种node.js框架(Express, Connect, Hapi, Koa etc)的GraphQL服务器的包。
安装包模块: npm install apollo-server graphql
新建文件test2-apollo.js,输入:
const { ApolloServer, gql } = require('apollo-server');
var typeDefs = gql
` type Query {
hello: String
}
schema {
query: Query
}`
;
var resolvers = {
Query: {
hello(root) {
return 'world';
}
}
};
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });
server.listen().then(({ url }) => {
console.log(`🚀 Server ready at ${url}`);
});运行
node test2-apollo.js
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\graphql>node index.js
� Server ready at http://localhost:4000/打开浏览器,输入:http://localhost:4000/
然后在界面上输入:{ hello },点击运行,可以看到给出的一个结果,如下图所示:
var {graphqlExpress,graphiqlExpress}=require('apollo-server-express')将会得到报错:graphqlExpress is not a function,详情可以参考apollo-server 2.0之后的更改,这里使用npm安装的是[email protected]的: https://www.apollographql.com/docs/apollo-server/api/apollo-server
使用Apollo作为Express的中间件
修改test2-apollo.js文件为:
const { ApolloServer, gql } = require('apollo-server-express');
var typeDefs = gql
` type Query {
hello: String
}
schema {
query: Query
}`
;
var resolvers = {
Query: {
hello(root) {
return 'world';
}
}
};
const app = require('express')();
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });
server.applyMiddleware({ app });
app.listen(4000, () => console.log('Now browse to localhost:4000/graphql'));运行
node index.js
打开浏览器,输入:http://localhost:4000/graphql
然后在界面上输入:{ hello },点击运行,可以看到给出的一个结果,如下图所示:
几乎任何一门语言,都是具有类型的。GraphQL常用的类型有:
- 标量类型
- 列表和非空
- 枚举类型
- 对象类型
- 接口
- 联合类型
- 输入类型 ...
标量类型 GraphQL 自带一组默认标量类型:
- Int:有符号 32 位整数。
- Float:有符号双精度浮点值。
- String:UTF‐8 的字符序列。
- Boolean:true或false。
- ID:ID 标量类型表示一个唯一标识符,通常用以重新获取对象或者作为缓存中的键。ID 类型使用和 String 一样的方式序列化;
列表和非空 默认情况下,每种类型都会返回null作为任何标量。与此相对的可以使用感叹号(!)表示非空类型。例如:String!表示非空字符串。 和大多数语言类似的,使用中括号来代表列表,例如:[Int]表示一个整型的列表。
枚举类型 枚举类型是一种特殊的标量,它限制在一个特殊的可选值集合内。例如:
enum Episode {
NEWHOPE
EMPIRE
JEDI
}
这表示了无论在schema中哪里使用了Episode ,其返回值肯定是NEWHOPE、EMPIRE、JEDI三个值其中一个。(注意,各种语言实现的 GraphQL 服务会有其独特的枚举处理方式。但对于JavaScript 在ES5中没有支持,些枚举值可能就被内部映射成整数值。但这都是内部的细节,并不会影响使用。)
对象类型 GraphQL schema 中的最基本的组件是对象类型。它就表示你可以从服务上获取到什么类型的对象,以及这个对象有什么字段。例如:
type Character {
name: String!
appearsIn: [Episode!]!
}
Character 是一个 GraphQL 对象类型,表示其是一个拥有一些字段的类型。
实例:修改test2-express.js中的hello world的demo为如下:
var express = require('express');
var graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
var { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
// Construct a schema, using GraphQL schema language
var schema = buildSchema(`
type objName {
name:String
}
type Query {
hello:objName
}
`);
// The root provides the top-level API endpoints
var root = {
hello: () => { return { name: 'hello world' } },
}
var app = express();
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({ schema: schema, rootValue: root, graphiql: true, }));
app.listen(4000); console.log('Running a GraphQL API server at localhost:4000/graphql');执行node test2-express.js。打开浏览器的调试工具,输入:
{
hello {
name
}
}
如图:

这里以官网的例子为例:
var express = require('express');
var graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
var { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
// Construct a schema, using GraphQL schema language
var schema = buildSchema(`
type Query {
rollDice(numDice: Int!, numSides: Int): [Int] }
`
);
// The root provides a resolver function for each API endpoint
var root = {
rollDice: function ({ numDice, numSides }) {
var output = [];
for (var i = 0; i < numDice; i++) {
output.push(1 + Math.floor(Math.random() * (numSides || 6)));
}
return output;
}
};
var app = express();
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({ schema: schema, rootValue: root, graphiql: true, }));
app.listen(4000);
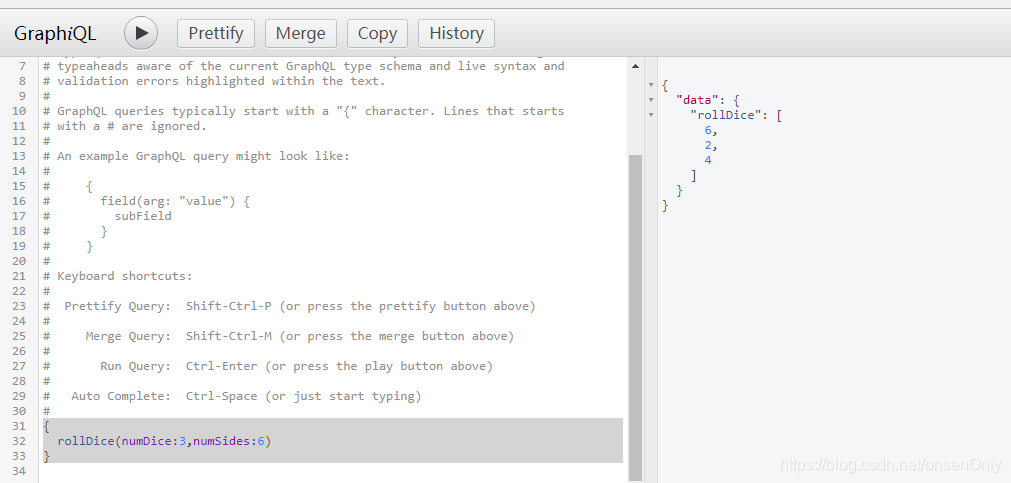
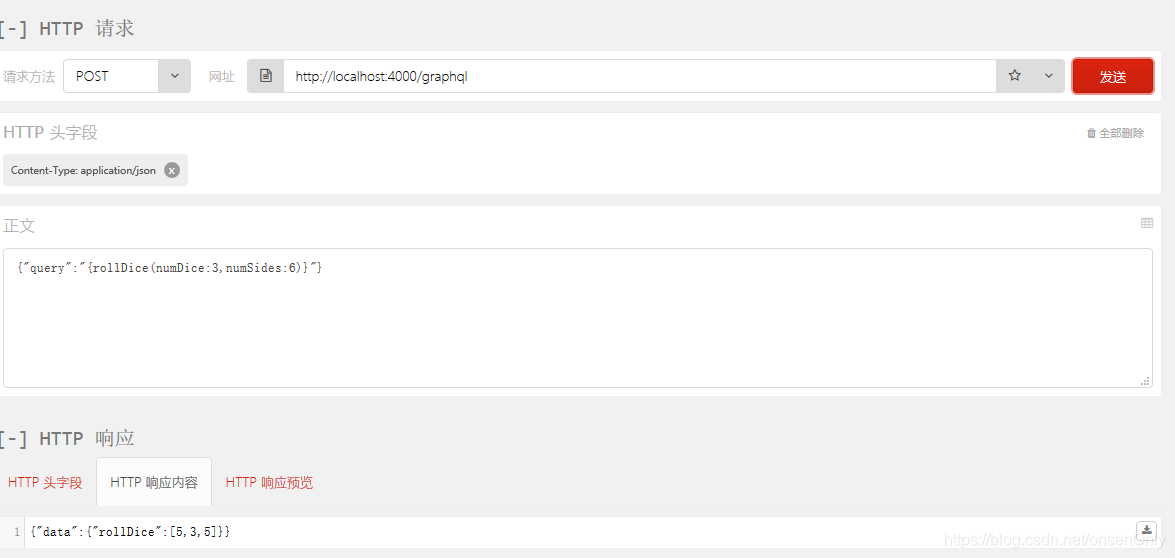
console.log('Running a GraphQL API server at localhost:4000/graphql');执行node test5-args.js。打开浏览器的调试工具,输入:
{
rollDice(numDice:3,numSides:6)
}
如图:
来自官网对于对象类型的例子,新建一个test6-object.js文件:
var express = require('express');
var graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
var { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
// Construct a schema, using GraphQL schema language
var schema = buildSchema(`
type RandomDie {
numSides: Int!
rollOnce: Int!
roll(numRolls: Int!): [Int]
}
type Query {
getDie(numSides: Int): RandomDie
} `
);
// This class implements the RandomDie GraphQL type
class RandomDie {
constructor(numSides) {
this.numSides = numSides;
}
rollOnce() {
return 1 + Math.floor(Math.random() * this.numSides);
}
roll({ numRolls }) {
var output = [];
for (var i = 0; i < numRolls; i++) {
output.push(this.rollOnce());
}
return output;
}
}
// The root provides the top-level API endpoints
var root = {
getDie: function ({ numSides }) {
return new RandomDie(numSides || 6);
}
}
var app = express();
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true,
}));
app.listen(4000);
console.log('Running a GraphQL API server at localhost:4000/graphql');执行node test6-object.js。打开浏览器的调试工具,输入:
{
getDie(numSides:3){
roll(numRolls:2)
rollOnce
}
}
如图:

对于许多应用程序,您可以在应用程序启动时定义固定模式,并使用GraphQL模式语言对其进行定义。在某些情况下,以构造类型是很有用的。 而且,使用GraphQLSchema构造类型来构建架构,可以把对应的schema作为单独的对象创建,这样就方便我们的项目目录管理了。 直接上官网的例子来对比说明, 过往的方式:
var express = require('express');
var graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
var { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
var schema = buildSchema(`
type User {
id: String
name: String
}
type Query {
user(id: String): User
} `
);
// Maps id to User object
var fakeDatabase = {
'a': {
id: 'a',
name: 'alice',
},
'b': {
id: 'b',
name: 'bob',
},
};
var root = {
user: function ({ id }) {
return fakeDatabase[id];
}
};
var app = express();
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true,
}));
app.listen(4000);
console.log('Running a GraphQL API server at localhost:4000/graphql');执行node test6-object.js。打开浏览器的调试工具,输入:
{
user(id:"a"){
name,
id
}
}
如图:

var express = require('express');
var graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
var graphql = require('graphql');
// Maps id to User object
var fakeDatabase = {
'a': {
id: 'a',
name: 'alice',
},
'b': {
id: 'b',
name: 'bob',
},
};
// Define the User type
var userType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'User',
fields: {
id: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
name: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
}
});
// Define the Query type
var queryType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Query',
fields: {
user: {
type: userType,
// `args` describes the arguments that the `user` query accepts
args: {
id: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
}
},
resolve: function (_, { id }) {
return fakeDatabase[id];
}
}
}
});
var schema = new graphql.GraphQLSchema({ query: queryType });
var app = express();
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
graphiql: true,
}));
app.listen(4000);
console.log('Running a GraphQL API server at localhost:4000/graphql');对比一下buildSchema和GraphQLSchema的创建方式,可以明显的发现使用GraphQLSchema的方式其定义的类型和原来的buildSchema方式的类型不一样了,并且GraphQLSchema更接近OOP的面向对象的思想。
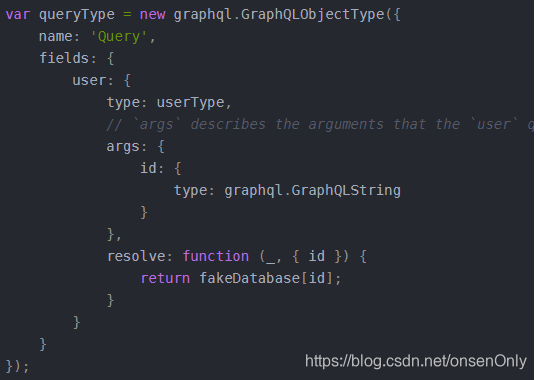
| 区别 | buildSchema | GraphQLSchema |
|---|---|---|
| 参数类型 | 字符串 | 对象 |
| 类名 | type 字符后面 | 参数对象的 name 属性 |
| 属性定义 | 定义在类型后,键值对形式 | 定义在参数对象 fields 属性中,值为对象,每个属性名为键名,值也是对象 |
同样GraphQLSchema 也有其对应的类型,例如: GraphQLEnumType、GraphQLFloat、GraphQLID。GraphQLInputObjectType。GraphQLInt、GraphQLInterfaceType、GraphQLList、GraphQLNonNull等等。 具体可以参考:https://graphql.org.cn/graphql-js/type.html
接口类型 接口是一个抽象类型,它包含某些字段,而对象类型需要实现该接口,必须包含这些字段,接口用interface表示。 这里直接引用官网的例子进行举例:
interface Character {
id: ID!
name: String!
friends: [Character]
appearsIn: [Episode]!
}
type Human implements Character {
id: ID!
name: String!
friends: [Character]
appearsIn: [Episode]!
starships: [Starship]
totalCredits: Int
}
type Droid implements Character {
id: ID!
name: String!
friends: [Character]
appearsIn: [Episode]!
primaryFunction: String
}
两个类型都具备 Character 接口的所有字段,但也引入了其他的字段 totalCredits、starships 和 primaryFunction,这都属于特定的类型的角色。(即:如果返回的类型是Character,需要primaryFunction属性的话就会报错。)
联合类型 联合类型和接口十分相似,但是它并不指定类型之间的任何共同字段,用union表示。例如:
union SearchResult = Human | Droid | Starship
表示任何返回一个 SearchResult 类型的地方,都可能得到一个 Human、Droid 或者 Starship。或许简单点的来理解就是一个或的运算。
输入类型 为了更容易的传递复杂对象,特别是在变更(mutation)中特别有用,比如需要传递一整个对象的时候。input就是用在这个时候的关键字。例如:
input ReviewInput {
stars: Int!
commentary: String
}
变更 我们知道query在GraphQL中一个读的操作,那么想修改数据的时候,那又应该怎样呢? 在GraphQL中有这样一个约定来规范任何导致写入的操作都应该显式通过变更(mutation)来发送。 就如同查询一样,如果任何变更字段返回一个对象类型,你也能请求其嵌套字段。获取一个对象变更后的新状态也是十分有用的。我们来看看一个变更例子:
mutation CreateReviewForEpisode($ep: Episode!, $review: ReviewInput!) {
createReview(episode: $ep, review: $review) {
stars
commentary
}
}
注意 createReview 字段如何返回了新建的 review 的 stars 和 commentary 字段。这在变更已有数据时特别有用,例如,当一个字段自增的时候,我们可以在一个请求中变更并查询这个字段的新值。 这个例子中,我们传递的 review 变量并非标量。它是一个输入对象类型,一种特殊的对象类型,可以作为参数传递。
在官网上就有这样的一个章节叫 Mutations And Input Types的。可以看得出一般mutations比较适合和Input类型一起使用,这里直接上官网的例子,新建一个test8-mutation.js文件,输入:
var express = require('express');
var graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
var { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
// Construct a schema, using GraphQL schema language
var schema = buildSchema(`
input MessageInput {
content: String
author: String
}
type Message {
id: ID!
content: String
author: String
}
type Query {
getMessage(id: ID!): Message
}
type Mutation {
createMessage(input: MessageInput): Message
updateMessage(id: ID!, input: MessageInput): Message
}
`
);
// If Message had any complex fields, we'd put them on this object.
class Message {
constructor(id, { content, author }) {
this.id = id;
this.content = content;
this.author = author;
}
}
// Maps username to content
var fakeDatabase = {};
var root = {
getMessage: function ({ id }) {
if (!fakeDatabase[id]) {
throw new Error('no message exists with id ' + id);
}
return new Message(id, fakeDatabase[id]);
},
createMessage: function ({ input }) {
// Create a random id for our "database".
var id = require('crypto').randomBytes(10).toString('hex');
fakeDatabase[id] = input;
return new Message(id, input);
},
updateMessage: function ({ id, input }) {
if (!fakeDatabase[id]) {
throw new Error('no message exists with id ' + id);
}
// This replaces all old data, but some apps might want partial update.
fakeDatabase[id] = input;
return new Message(id, input);
},
};
var app = express();
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({ schema: schema, rootValue: root, graphiql: true, }));
app.listen(4000, () => { console.log('Running a GraphQL API server at localhost:4000/graphql'); });在上面的例子中,我们可以看出这个文件中定义了三个操作方法,一个是getMessage(获取信息)、一个是createMessage(创建信息)、一个是updateMessage(更新信息)。
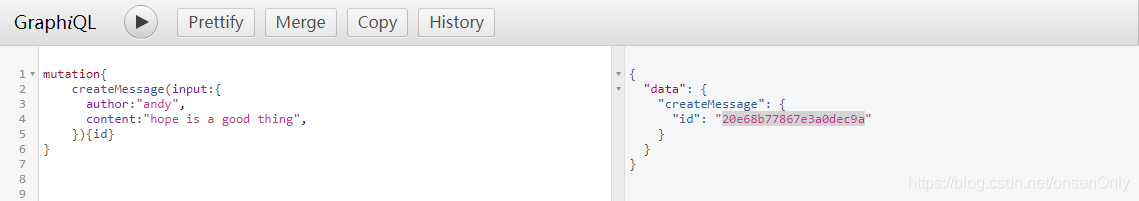
执行node test8-mutation.js。打开浏览器(localhost:4000/graphql)的调试工具,输入:
mutation{
createMessage(input:{
author:"andy",
content:"hope is a good thing",
}){id}
}
这里是创建一个信息。如图:
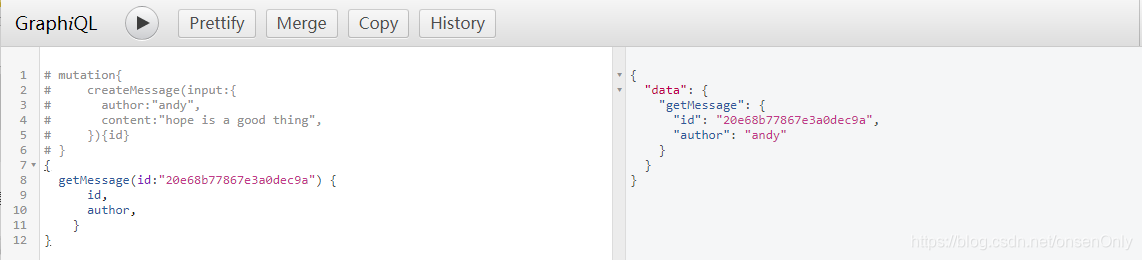
{
getMessage(id:"20e68b77867e3a0dec9a") {
id,
author,
}
}
如图:
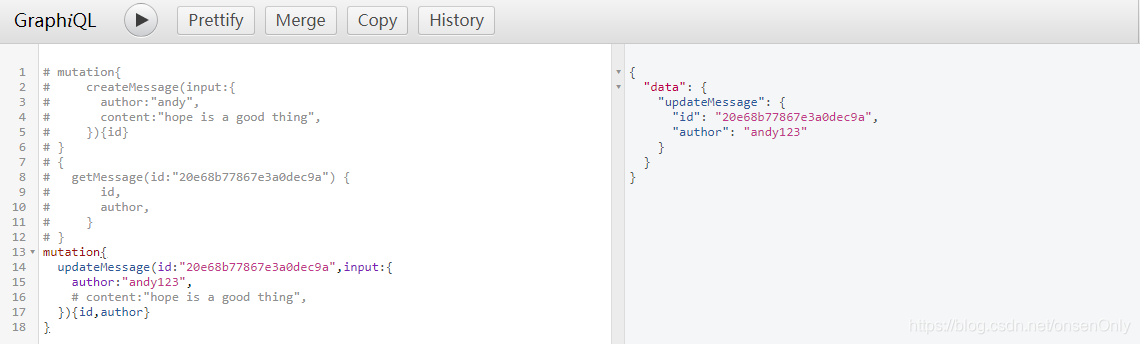
mutation{
updateMessage(id:"20e68b77867e3a0dec9a",input:{
author:"andy123",
# content:"hope is a good thing",
}){id,author}
}
得到的操作结果,如图:
然后,我们把上面用buildSchema的方式同样根据第二章节的做法进行用对象的形式改写一下,修改test8-mutation.js的文件:
var express = require('express');
var graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
var graphql = require('graphql');
// Maps id to User object
var fakeDatabase = {};
// Define the User type
class Message {
constructor(id, { content, author }) {
this.id = id;
this.content = content;
this.author = author;
}
}
var messageType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Message',
fields: {
id: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
author: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
content: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
}
});
var messageInputType = new graphql.GraphQLInputObjectType({
name: 'MessageInput',
fields: {
id: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
author: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
content: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
}
});
// Define the Query type
var queryType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Query',
fields: {
getMessage: {
type: messageType,
args: {
id: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
}
},
resolve: function (_, { id }) {
if (!fakeDatabase[id]) {
throw new Error('no message exists with id ' + id);
}
return new Message(id, fakeDatabase[id]);
}
}
}
});
var mutationType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Mutation',
fields: {
createMessage: {
type: messageType,
args: {
input: {
type: messageInputType
}
},
resolve: function (_, { input }) {
var id = require('crypto').randomBytes(10).toString('hex');
fakeDatabase[id] = input;
return new Message(id, input);
}
},
updateMessage: {
type: messageType,
args: {
id: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
input: {
type: messageInputType
}
},
resolve: function (_, { id, input }) {
if (!fakeDatabase[id]) {
throw new Error('no message exists with id ' + id);
}
// This replaces all old data, but some apps might want partial update.
fakeDatabase[id] = input;
return new Message(id, input);
}
}
}
});
var schema = new graphql.GraphQLSchema({ query: queryType, mutation: mutationType });
var app = express();
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
graphiql: true,
}));
app.listen(4000);
console.log('Running a GraphQL API server at localhost:4000/graphql');如上所示,我们把buildSchema中的type的Message和input的MessageInput分别用GraphQLObjectType和GraphQLInputObjectType表示,同时把Query读操作和变更操作的Mutations也用GraphQLObjectType表示。在Query中只有getMessage一个区域,在Mutations中有createMessage和updateMessage两个区域。 然后同样的执行node test8-mutation.js。打开浏览器(localhost:4000/graphql)的调试工具,输入上面测试用例进行调试即可。
新建一个文件夹,test9-query目录作为该项模拟的根目录。 新建schema目录,schema.js文件:
const graphql = require('graphql');
const queryType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Query',
fields: {
greeting: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString,
resolve: () => 'Hello GraphQL From TutorialsPoint !!',
},
sayHello: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString,
args: {
name: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
}
},
resolve: function (_, args) {
return `Hi ${args.name} GraphQL server says Hello to you!!`
}
}
}
});这里的schema.js文件中,就新建了一个Query的GraphQL的类型,里面包含了greeting,sayHello两个业务。
在根目录新建server.js文件:
const express = require('express');
const cors = require('cors')
const graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
const graphql = require('graphql');
const { queryType } = require("./schema/schema");
const schema = new graphql.GraphQLSchema({ query: queryType });
const app = express();
app.use(cors());
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
graphiql: true,
}));
app.listen(4000);
console.log('Running a GraphQL API server at localhost:4000/graphql');
module.exports = { queryType };根据之前的逻辑建立起一个服务。 注意:这里较之前的代码新加了一个cors模块,用来处理服务端本地的跨域问题。需要安装:
npm install --save cors
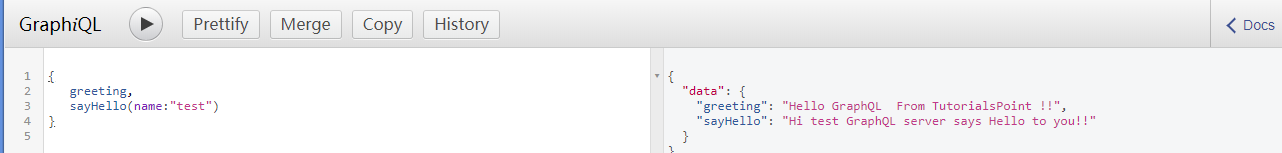
服务端ok之后,同样可以使用自带的工具进行验证:
{
greeting,
sayHello(name:"test")
}
如图:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.1.1.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function () {
$("#btnSayhello").click(function () {
const name = $("#txtName").val();
console.log(name);
$("#SayhelloDiv").html("loading....");
$.ajax({
url: "http://localhost:4000/graphql",
contentType: "application/json",
type: "POST",
data: JSON.stringify({
query: `{
sayHello(name:"${name}")}`
}),
success: function (result) {
console.log(JSON.stringify(result))
$("#SayhelloDiv").html("<h1>" + result.data.sayHello + "</h1>");
}
});
});
$("#btnGreet").click(function () {
$("#greetingDiv").html("loading....");
$.ajax({
url: "http://localhost:4000/graphql",
contentType: "application/json",
type: "POST",
dataType: 'json',
data: JSON.stringify({
query: `{greeting}`
}),
success: function (result) {
$("#greetingDiv").html("<h1>" + result.data.greeting + "</h1>");
}
});
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Jquery Client </h1>
<hr />
<section>
<button id="btnGreet">Greet</button>
<br /> <br />
<div id="greetingDiv"> </div>
</section>
<br /> <br /> <br />
<hr />
<section>
Enter a name:<input id="txtName" type="text" value="kannan" />
<button id="btnSayhello">SayHello</button>
<div id="SayhelloDiv"> </div>
</section>
</body>
</html>然后访问该文件,点击两个按钮,出现如图所示效果:

新建test10-react文件夹作为该模拟的项目子根目录。 新建react项目:
create-react-app hello-world-client
若是创建项目报not found的create-react-app的话,请自行安装脚手架工具(Create React App是FaceBook的React团队官方出的一个构建React单页面应用的脚手架工具)。
npm install -g create-react-app
然后在hello-world-client目录中,修改APP.js文件:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import logo from './logo.svg';
import './App.css';
async function loadGreeting() {
const response = await fetch('http://localhost:4000/graphql', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'content-type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({ query: '{greeting}' })
})
const rsponseBody = await response.json();
return rsponseBody.data.greeting;
console.log("end of function")
}
async function loadSayhello(name) {
const response = await fetch('http://localhost:4000/graphql', {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'content-type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({ query: `{sayHello(name:"${name}")}` })
})
const rsponseBody = await response.json();
return rsponseBody.data.sayHello;
}
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { greetingMessage: '', sayHelloMessage: '', userName: '' }
this.updateName = this.updateName.bind(this);
this.showSayHelloMessage = this.showSayHelloMessage.bind(this);
this.showGreeting = this.showGreeting.bind(this);
}
showGreeting() {
loadGreeting().then(g => this.setState({ greetingMessage: g + " :-)" }))
}
showSayHelloMessage() {
const name = this.state.userName;
console.log(name)
loadSayhello(name).then(m => this.setState({ sayHelloMessage: m }))
}
updateName(event) {
this.setState({ userName: event.target.value })
}
componentDidMount() {
this.showGreeting();
}
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<p>
Edit <code>src/App.js</code> and save to reload.
</p>
<a
className="App-link"
href="https://reactjs.org"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
Learn React
</a>
</header>
<br />
<section>
showGreeting:{this.state.greetingMessage}
</section>
<br />
<section>
Enter a name:<input id="txtName" type="text" onChange={this.updateName}
value={this.state.userName} />
<button id="btnSayhello" onClick={this.showSayHelloMessage}>SayHello</button>
<br />
user name is:{this.state.userName} <br />
<div id="SayhelloDiv">
<h1>{this.state.sayHelloMessage}</h1>
</div>
</section>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;在上面的代码中,分别封装了loadSayhello和loadGreeting两个方法进行范文graphql的服务,这个服务是上面test9-jquery中启动的服务。在hello-world-client项目中启动:
npm start
此时会自动打开默认的浏览器访问3000端口,如端口被占用,启动的时候会自动询问是否更换3001端口访问的。如图:

.App {
text-align: center;
min-height: 100vh;
}
.App-logo {
height: 40vmin;
}
.App-header {
background-color: #282c34;
min-height: 90%;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
font-size: calc(10px + 2vmin);
color: white;
}
.App-link {
color: #09d3ac;
}新建test11-apollo-react文件夹作为该模拟的项目子根目录。 新建server.js文件,这里和上面的server.js文件是一样的:
const express = require('express');
const cors = require('cors')
const graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
const graphql = require('graphql');
const { queryType } = require("./schema/schema");
const schema = new graphql.GraphQLSchema({ query: queryType });
const app = express();
app.use(cors());
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
graphiql: true,
}));
app.listen(4000);
console.log('Running a GraphQL API server at localhost:4000/graphql');同样的和上面的一样的新建schema文件夹,里面新建schema.js文件:
const graphql = require('graphql');
class Student {
constructor(id, firstName, lastName, college) {
this.id = id;
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.college = college;
}
}
students = [new Student('id1', 'firstName1', 'lastName1', { name: 'test1' }),
new Student('id2', 'firstName2', 'lastName2', { name: 'test2' }),
new Student('id3', 'firstName3', 'lastName3', { name: 'test3' })];
const collegeType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'College',
fields: {
id: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
name: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
location: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
rating: {
type: graphql.GraphQLFloat
}
}
});
const studentType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Student',
fields: {
id: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
firstName: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
lastName: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
college: {
type: collegeType
}
}
});
const queryType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Query',
fields: {
students: {
type: graphql.GraphQLList(studentType),
resolve: () => students,
}
}
});
module.exports = { queryType };这里就提供了students一个业务。
同样的在子根目录下创建react项目:
create-react-app hello-world-client
在hello-world-client目录中,安装客户端的graphql库以及Apollo Boost包:
npm install apollo-boost graphql
修改APP.js文件:
import React, {Component} from 'react';
// apollo client
import {ApolloClient, HttpLink, InMemoryCache} from 'apollo-boost'
import gql from 'graphql-tag'
const endPointUrl = 'http://localhost:4000/graphql'
const client = new ApolloClient({
link: new HttpLink({uri:endPointUrl}),
cache:new InMemoryCache()
});
async function loadStudentsAsync() {
const query = gql`
{
students{
id
firstName
lastName
college{
name
}
}
}
`
const {data} = await client.query({query}) ;
return data.students;
}
export default class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
students:[]
}
this.studentTemplate = [];
}
async loadStudents() {
const studentData = await loadStudentsAsync();
this.setState({
students: studentData
})
console.log("loadStudents")
}
render() {
return(
<div>
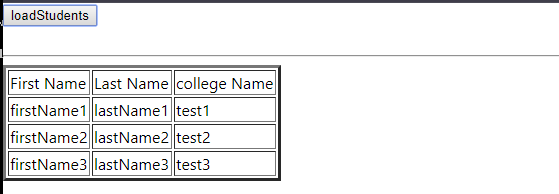
<input type = "button" value = "loadStudents" onClick = {this.loadStudents.bind(this)}/>
<div>
<br/>
<hr/>
<table border = "3">
<thead>
<tr>
<td>First Name</td>
<td>Last Name</td>
<td>college Name</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{
this.state.students.map(s => {
return (
<tr key = {s.id}>
<td>
{s.firstName}
</td>
<td>
{s.lastName}
</td>
<td>
{s.college.name}
</td>
</tr>
)
})
}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
)
}
}通过上面我们可以看到,通过apollo-boost,使用其ApolloClient, HttpLink, InMemoryCache三个模块。
ApolloClient: 使用Apollo Client,我们可以直接调用服务器而无需使用fetch API.此外,查询和突变不应嵌入使用反向刻度表示法的字符串中,这是因为, gql 函数直接解析查询.这意味着,在GraphiQL工具中编写查询时,程序员可以以相同的方式直接编写查询。 gql 是一个标记函数,它将后面的刻度表示法中的模板字符串解析为graphql查询对象. Apollo Client查询方法返回一个promise。
具体可以参考官网api解析: https://www.apollographql.com/docs/react/api/apollo-client/ https://www.apollographql.com/docs/react/caching/cache-configuration/
接口最终还是得持久化物理容器中做增删改查的操作。
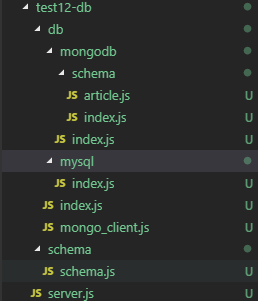
新建一下图片的目录,test12-db:
通常链接mongodb,我们使用mongoose模块来处理:
npm install --save mongoose
然后在db目录中封装了一个获取数据库链接对象的类MongoClient:
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
module.exports = class MongoClient {
constructor({ uri, options, schemas } = {}) {
this.schemas = schemas;
this.uri = uri;
this.options = options;
this.models = {};
this.connection = null;
}
async connect() {
let { uri, options } = this;
mongoose.set('useCreateIndex', true);
mongoose.set('bufferCommands', false);
mongoose.set('bufferMaxEntries', 0);
mongoose.set('autoIndex', false);
mongoose.connection.on('error', function () {
console.error('connection error: uri is %s,options is %s', uri, JSON.stringify(options));
});
mongoose.connection.once('open', function () {
console.info('connection success', uri);
});
let connection = await mongoose.createConnection(uri, options);
this.connection = connection;
console.info('Init mongoose success');
return connection;
}
getCollection(key) {
if (this.schemas[key]) {
if (this.models[key]) {
return this.models[key];
}
let model = this.connection.model(key, this.schemas[key]);
this.models[key] = model;
return model;
}
throw new Error("illegal key");
}
}在MongoClient中提供一个connect的方法返回链接对象,以面对多重链接的情况,同时提供getCollection提供给没有model首次链接的时候再获取链接对象,这种情况一般用于serverless的lambda函数,这里就直接拿着之前的封装直接来用了。 然后在mongodb目录下再提供了一个对象的index.js:
const MongoClient = require("../mongo_client");
const schemas = require("./schema");
const [uri, options] = [
"mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/onsen",
{
useNewUrlParser: true,
useCreateIndex: true,
},
]
const client = new MongoClient({ uri: uri, options: options, schemas: schemas });
module.exports = client;注:这里的数据库,就需要自己去创建模拟数据了。
在根目录的server.js文件中,创建graphql的服务:
const express = require('express');
const cors = require('cors')
const graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
const graphql = require('graphql');
const { queryType } = require("./schema/schema");
require("./db").mongodb.connect();
const schema = new graphql.GraphQLSchema({ query: queryType });
const app = express();
app.use(cors());
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
graphiql: true,
}));
app.listen(4000);
console.log('Running a GraphQL API server at localhost:4000/graphql');相比之前的代码,可以看到增加了:
require("./db").mongodb.connect();安装mysql的模块:
npm install --save mysql
同样的类似于mongodb的封装一样,这里也封装了一个mysql的客户对象:
var mysql = require('mysql');
class MysqlClient {
constructor(options = {}) {
this.pool = mysql.createPool(options);
}
doQuery(query) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
this.pool.getConnection((err, conn) => {
if (err) {
return reject(err);
}
console.info('getConnection ok')
conn.query(query, (err, results, fields) => {
conn.release();
if (err) {
return reject(err);
}
return resolve(results || null);
})
})
});
}
}
const options = {
connectionLimit: 1000,
host: '127.0.0.1',
password: 'password',
database: 'yiibaidb',
user: 'root',
}
module.exports = new MysqlClient(options);具体有关mysql模块的,见: https://www.npmjs.com/package/mysql
做好了数据库的引用,然后就可以像前面一样,直接使用schema中写业务逻辑了,见schema.js:
const graphql = require('graphql');
const mongodb = require("../db").mongodb;
const mysql = require("../db").mysql;
const ArticleType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Article',
fields: {
_id: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
title: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
source: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
}
});
const OrderType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Order',
fields: {
orderNumber: {
type: graphql.GraphQLInt
},
status: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
comments: {
type: graphql.GraphQLString
},
}
});
const queryType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Query',
fields: {
articles: {
type: graphql.GraphQLList(ArticleType),
resolve: async () => await mongodb.getCollection('Article').find({}),
},
orders: {
type: graphql.GraphQLList(OrderType),
args: {
page: {
type: graphql.GraphQLInt
},
pageSize: {
type: graphql.GraphQLInt
},
},
resolve: async (_, { page = 0, pageSize = 10 }) => await mysql.doQuery(`
SELECT * FROM orders limit ${((page - 1) < 0 ? 0 : (page - 1)) * pageSize},${pageSize};
`),
}
}
});
module.exports = { queryType };这里的业务提供了articles和orders的两个查询,分别用的是mongodb和mysql的数据库操作。
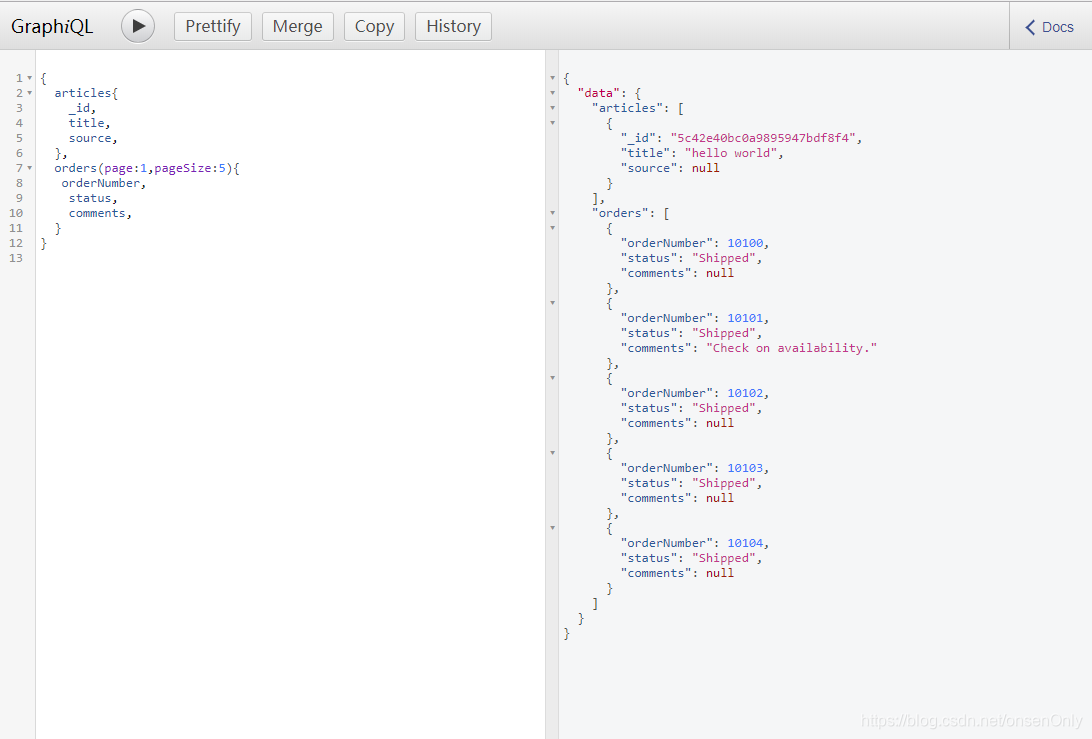
在工具上进行验证,输入:
{
articles{
_id,
title,
source,
},
orders(page:1,pageSize:5){
orderNumber,
status,
comments,
}
}