- Overview
- Installation
- Download the package
- Creating python environment
- Command-line interface
- What is included?
- File structure
- Documentation
- Read the Docs
- Examples
- Developer Guide
- GitHub refresher
- Areas of Active Development
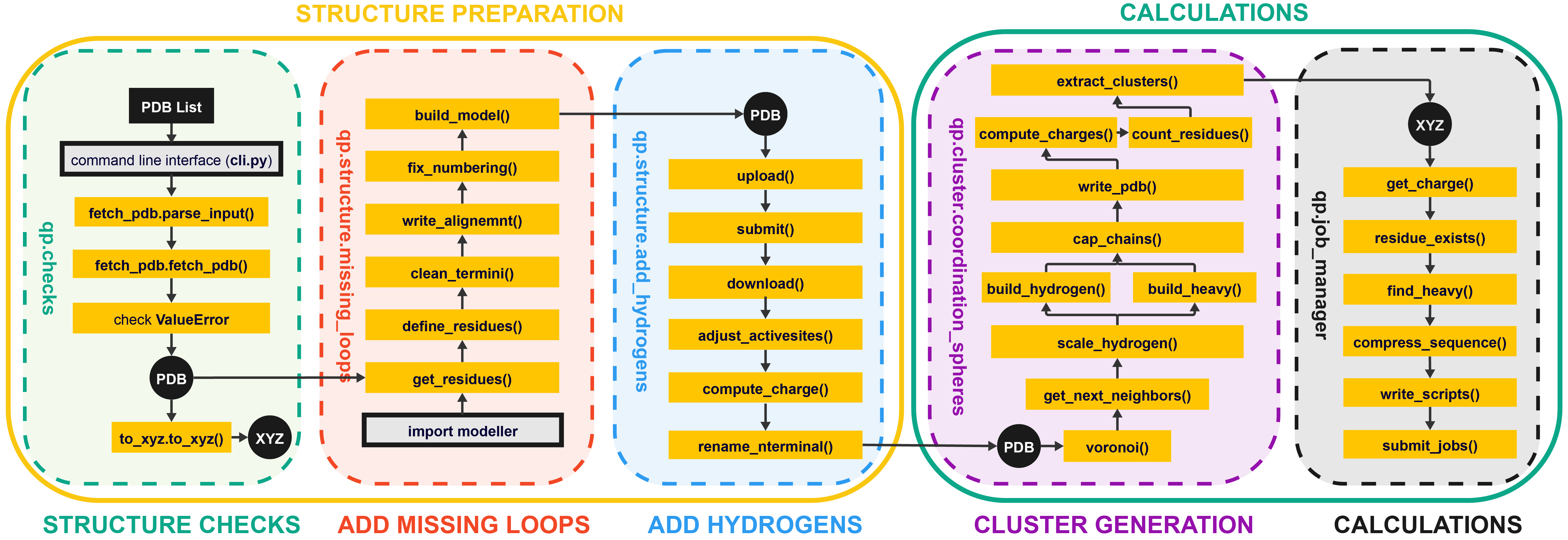
The purpose of quantumPDB (qp) is to serve as a toolkit for working with our database of proteins to setup and facilitate DFT-calculation and cluster model creation.
File Structure overview: Miro Board
Install the package by running the follow commands inside the repository. This will perform a developmental version install. It is good practice to do this inside of a virtual environment. A yaml environmental file has been created to facilitate the installation of dependencies.
To begin working with quantumPDB, first clone the repo and then move into the top-level directory of the package. Then perform a developer install. Remember to update your GitHub ssh keys.
git clone [email protected]:davidkastner/quantumPDB.gitAll the dependencies can be loaded together using the prebuilt environment.yml file. Compatibility is automatically tested for python versions 3.8 and higher. If you are only going to be using the package run:
cd quantumPDB
conda env create -f environment.yml
source activate qp
python -m pip install -e .All of the functionality of quantumPDB has been organized into a command-line interface (CLI).
After performing the developer install, the CLI can be called from anywhere using qpdb.
.
├── docs # Readthedocs documentation site
└── qp # quantumPDB subpackages and modules
|── cli.py # Command-line interface entry point
├── checks # Perform quality and structural checks
│ ├── fetch_pdb # Get a PDB
│ ├── check_edia # Check the quality of each chain
│ ├── choose_conformer # Choose the best conformer
│ ├── to_pdb # Save structure to a new PDB
│ └── to_xyz # Save structure to a new XYZ
├── structure # Correct the PDB structure
│ ├── missing_hetatoms # Add any missing heteroatoms
│ ├── missing_loops # Use modeller to add missing loops
│ ├── protoss_upload # Upload a PDB to Protoss to add hydrogens
│ └── protoss_download # Get the structure with hydrogens
└── clusters # Generalizable plotting and vizualization
├── find_metal # Identify the metal center
└── coordination_shells # Select the first, second, etc. spheres
make clean
make htmlUse this Git sequence to make a quick push.
git status
git pull
git add -A .
git commit -m "Change a specific functionality"
git push -u origin main
Use this Git sequence to make a branch and make a pull request. Recommend for significant changes.
git checkout main
git pull
# Before you begin making changes, create a new branch
git checkout -b new-feature-branch
git add -A
git commit -m "Detailed commit message describing the changes"
git push -u origin new-feature-branch
# Visit github.com to add description, submit, merge the pull request
# Once finished on github.com, return to local
git checkout main
git pull
# Delete the remote branch
git branch -d new-feature-branch
git stash push --include-untracked
git stash drop
git pull
Currently working on handling all edge cases, including non-canonical amino acids. Additionally, support for mmCIFs will eventually needed to be added to work with newer and larger PDBs. Documentation is present for all functions in the code, but should be added with external examples for use.
Copyright (c) 2023, David W. Kastner, Clorice R. Reinhardt and Wilson Ho
Project based on the Computational Molecular Science Python Cookiecutter version 1.1.