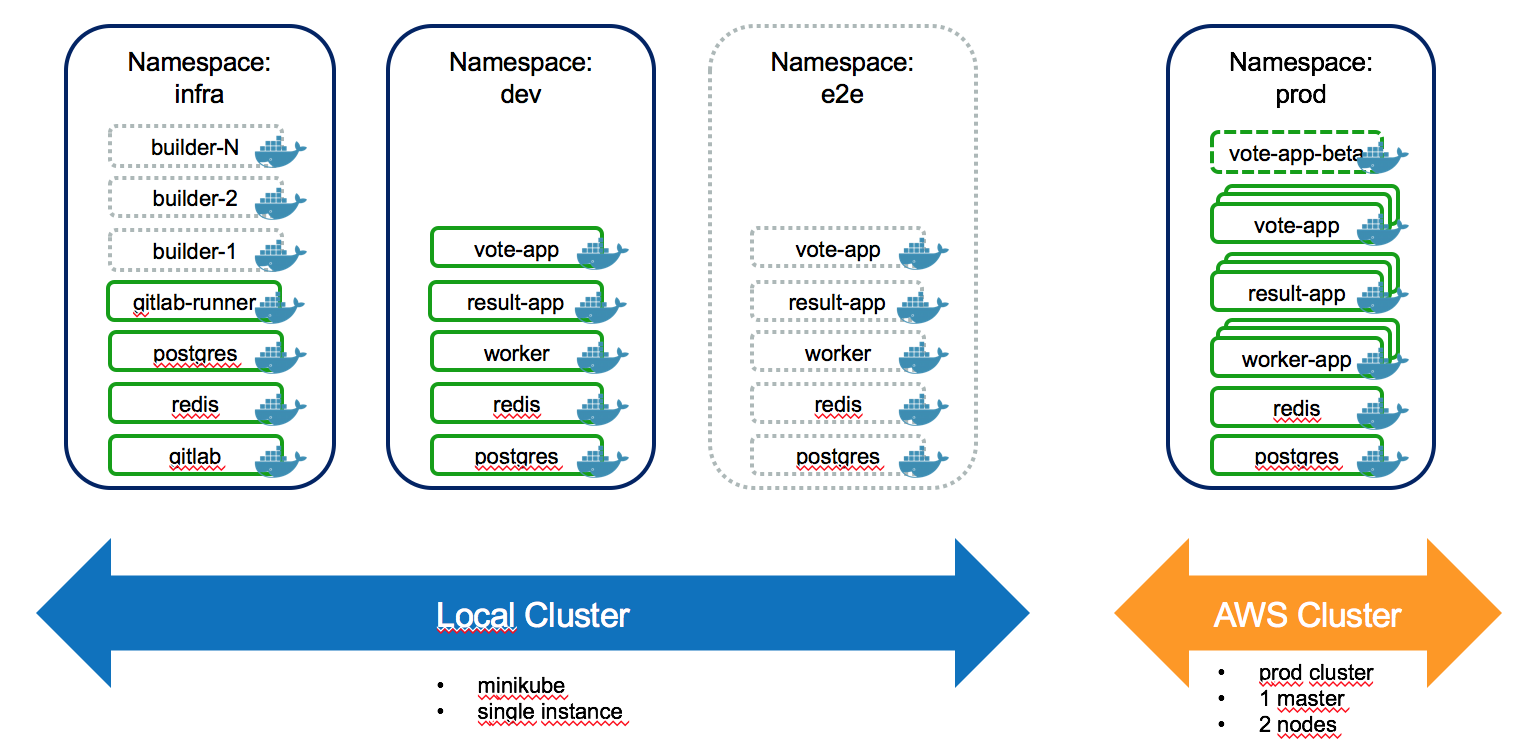
I took the docker example-voting-app and added some kubernetes, helm and gitlab love.
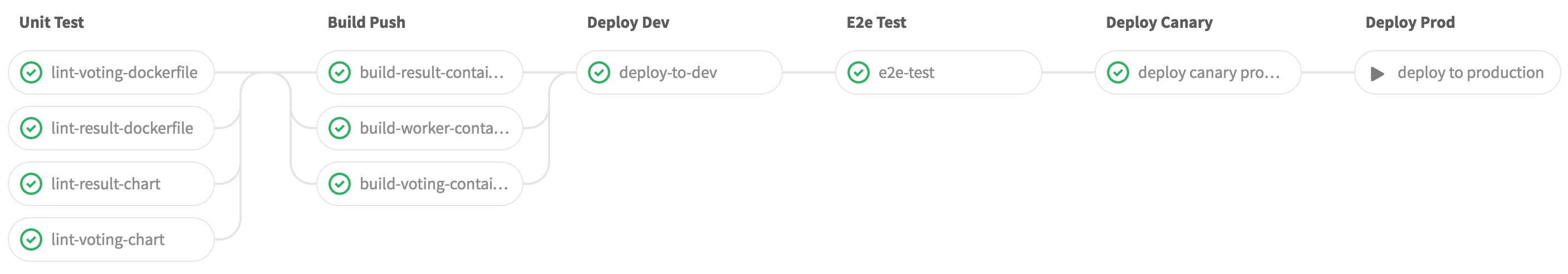
The example-voting-app will go through a CI/CD pipeline which is implemented with gitlab-ci autoscaled builders. It will run parallel linting tests, build and push the docker containers, deploy to development environment- then run end-2-end tests with phantomjs. If that succeeds the pipeline will automatically deploy a canary version to a production cluster on AWS. In the end the user is left with a manual step to fully deploy to production.
The pipeline looks like this:
Take a look at .gitlab-ci.yaml on how stages are defined.
Helm is used to install the example-voting-app into different Kubernetes namespaces (== environments).
Start minikube
minikube start --memory=4096
After a while you should be able to visit the dashboard. Check with minikube service list
Initialize helm, the swiss knife of kubernetes application deployment:
helm init
Helm installs its server-side component tiller in the cluster. Check with kubectl get pods --all-namespaces and helm version.
Now we can install the example-voting-app components:
helm install --namespace=dev --name postgres charts/example-voting-app/charts/postgres
helm install --namespace=dev --name redis charts/example-voting-app/charts/redis
helm install --namespace=dev --name worker charts/example-voting-app/charts/worker
helm install --namespace=dev --name voting-app charts/example-voting-app/charts/voting-app --set nodePort=30050
helm install --namespace=dev --name result-app charts/example-voting-app/charts/result-app --set nodePort=30051
Did everything went well? Check with helm ls and minikube service list.
You should be able to access the app at port 30050 and 30051!
Let's install gitlab but check the values in charts/gitlab/values.yaml first, here's where you want to customize things.
helm install --namespace=infra --name pg-gitlab charts/gitlab/postgres
helm install --namespace=infra --name redis-gitlab charts/gitlab/redis
helm install --namespace=infra --name gitlab charts/gitlab/gitlab
After a while you can access gitlab at http://$(minikube ip):30080. Default user/pass is root/passw0rd.
Got to http://$(minikube ip):30080/admin/runners and copy the registration token. Then register the gitlab-runner manually, because that's just the way it is:
kubectl run --namespace=infra gitlab-runner --image=gitlab/gitlab-runner:alpine-v1.7.1 --restart=Never -- register -n --executor kubernetes -u http://gitlab:30080/ -r Gq2_NEeKKcz7-7CwrZxW
Go back to admin console, grap the token for the runner and paste it in charts/gitlab-runner/values.yaml. Then install the (long-running) gitlab-runner:
helm install --namespace=infra -n gitlab-runner charts/gitlab-runner
The runner should now be active at http://$(minikube ip):30080/admin/runners
Now we can create a project in the webinterface and push this repo!
git remote add local http://$(minikube ip):30080/root/taw16.git
git push -u local master
If you want to push images to your dockerhub account, create charts/gitlab-runner/templates/secret-docker-cred.yaml with the following:
apiVersion: v1
data:
config.json: <insert output of $(base64 ~/.docker/config.json) here>
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: docker-cred
type: Opaque
If you want to push images to a different kubernetes cluster, create charts/gitlab-runner/templates/secret-kube-cred.yaml with the following:
apiVersion: v1
data:
config-aws: <insert output of $(base64 ~/.kube/config) here>
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: kube-cred
type: Opaque
make sure that only your aws credentials are in there, because kubernetes secrets have a size limit.
[1] Or do
kubectl run --namespace=infra -i -t gitlab-runner --image=gitlab/gitlab-runner:alpine-v1.7.1 --restart=Never --command bash
bash-4.3# gitlab-runner register -n --executor kubernetes -u http://gitlab/ -r C5HaFvoVkqJULxaskWu8
bash-4.3# grep token /etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml
token = "33231c882cf2545e3124a823dee982"
kubectl run voting-app-beta --image=willies/example-voting-app-vote -l app=voting-app,release=canary
helm install --namespace=uat --name postgres-uat charts/example-voting-app/charts/postgres
helm install --namespace=uat --name redis-uat charts/example-voting-app/charts/redis
helm install --namespace=uat --name worker-uat charts/example-voting-app/charts/worker
helm install --namespace=uat --name voting-app-uat charts/example-voting-app/charts/voting-app --set nodePort=30060
helm install --namespace=uat --name result-app-uat charts/example-voting-app/charts/result-app --set nodePort=30061
I hacked in support to use /var/run/docker.sock from the host and two secretes docker-cred and kube-cred to store the credentials to dockerhub and production k8s cluster. Source is available here: janwillies/gitlab-runner, corresponding issue for gitlab-ci: https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-ci-multi-runner/issues/1876
make build BUILD_PLATFORMS="-os=linux -arch=amd64"
or full
docker run --rm -it -v $(pwd)/:/go/src/gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-ci-multi-runner -w /go/src/gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-ci-multi-runner golang:1.7.1 make build_simple
cp out/binaries/gitlab-ci-multi-runner dockerfiles/alpine/gitlab-ci-multi-runner-linux-amd64
cd dockerfiles/alpine/
docker build -t willies/gitlab-runner:1.7.1_kube.3 .
docker push willies/gitlab-runner:1.7.1_kube.3
cd -
if you have trouble starting minikube, try to rerun instructions from docker-machine-driver-xhyve
sudo chown root:wheel $(brew --prefix)/opt/docker-machine-driver-xhyve/bin/docker-machine-driver-xhyve
sudo chmod u+s $(brew --prefix)/opt/docker-machine-driver-xhyve/bin/docker-machine-driver-xhyve