YugabyteDB is a high-performance, cloud-native distributed SQL database that aims to support all PostgreSQL features. It is best to fit for cloud-native OLTP (i.e. real-time, business-critical) applications that need absolute data correctness and require at least one of the following: scalability, high tolerance to failures, or globally-distributed deployments.
- Core Features
- Get Started
- Build Apps
- What's being worked on?
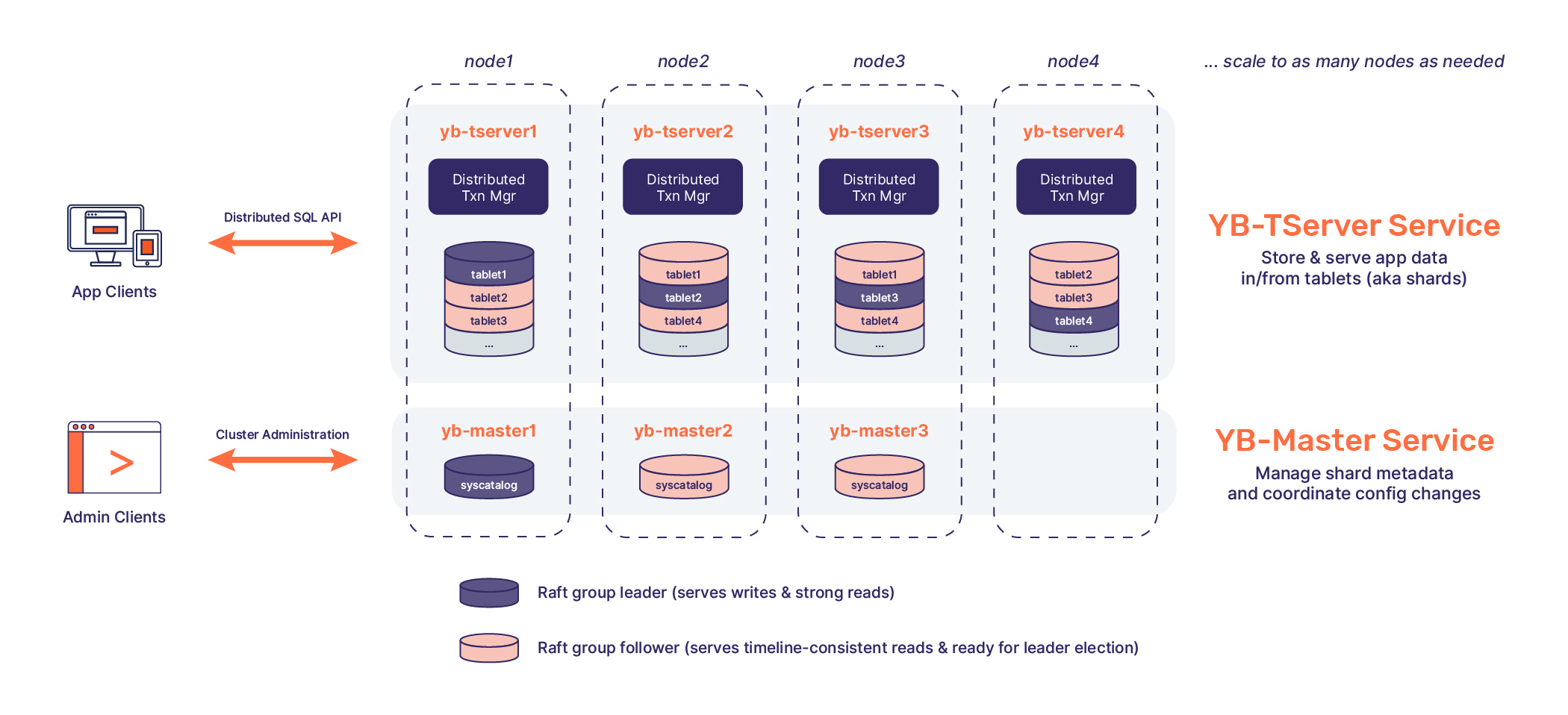
- Architecture
- Need Help?
- Contribute
- License
- Read More
-
Powerful RDBMS capabilities Yugabyte SQL (YSQL for short) reuses the query layer of PostgreSQL (similar to Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL), thereby supporting most of its features (datatypes, queries, expressions, operators and functions, stored procedures, triggers, extensions, etc). Here is a detailed list of features currently supported by YSQL.
-
Distributed transactions The transaction design is based on the Google Spanner architecture. Strong consistency of writes is achieved by using Raft consensus for replication and cluster-wide distributed ACID transactions using hybrid logical clocks. Snapshot, serializable and read committed isolation levels are supported. Reads (queries) have strong consistency by default, but can be tuned dynamically to read from followers and read-replicas.
-
Continuous availability YugabyteDB is extremely resilient to common outages with native failover and repair. YugabyteDB can be configured to tolerate disk, node, zone, region, and cloud failures automatically. For a typical deployment where a YugabyteDB cluster is deployed in one region across multiple zones on a public cloud, the RPO is 0 (meaning no data is lost on failure) and the RTO is 3 seconds (meaning the data being served by the failed node is available in 3 seconds).
-
Horizontal scalability Scaling a YugabyteDB cluster to achieve more IOPS or data storage is as simple as adding nodes to the cluster.
-
Geo-distributed, multi-cloud YugabyteDB can be deployed in public clouds and natively inside Kubernetes. It supports deployments that span three or more fault domains, such as multi-zone, multi-region, and multi-cloud deployments. It also supports xCluster asynchronous replication with unidirectional master-slave and bidirectional multi-master configurations that can be leveraged in two-region deployments. To serve (stale) data with low latencies, read replicas are also a supported feature.
-
Multi API design The query layer of YugabyteDB is built to be extensible. Currently, YugabyteDB supports two distributed SQL APIs: Yugabyte SQL (YSQL), a fully relational API that re-uses query layer of PostgreSQL, and Yugabyte Cloud QL (YCQL), a semi-relational SQL-like API with documents/indexing support with Apache Cassandra QL roots.
-
100% open source YugabyteDB is fully open-source under the Apache 2.0 license. The open-source version has powerful enterprise features such as distributed backups, encryption of data-at-rest, in-flight TLS encryption, change data capture, read replicas, and more.
Read more about YugabyteDB in our Docs.
- Install YugabyteDB
- Create a local cluster
- Start with Yugabyte Cloud
- Connect and try out SQL commands
- Build an app using a PostgreSQL-compatible driver or ORM.
- Try running a real-world demo application:
Cannot find what you are looking for? Have a question? Please post your questions or comments on our Community Slack or Forum.
YugabyteDB supports several languages and client drivers. Below is a brief list.
| Language | ORM | YSQL Drivers | YCQL Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Java | Spring/Hibernate | PostgreSQL JDBC | cassandra-driver-core-yb |
| Go | Gorm | pq | gocql |
| NodeJS | Sequelize | pg | cassandra-driver |
| Python | SQLAlchemy | psycopg2 | yb-cassandra-driver |
| Ruby | ActiveRecord | pg | yugabyte-ycql-driver |
| C# | EntityFramework | npgsql | CassandraCSharpDriver |
| C++ | Not tested | libpqxx | cassandra-cpp-driver |
| C | Not tested | libpq | Not tested |
This section was last updated in March, 2022.
Here is a list of some of the key features being worked on for the upcoming releases (the YugabyteDB v2.13 latest release has been released in March, 2022, and the v2.12 stable release was released in Feb 2022).
| Feature | Status | Release Target | Progress | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster Bulk-Data Loading in YugabyteDB | PROGRESS | v2.15 | Track | Master issue to track improvements to make it easier and faster to get large amounts of data into YugabyteDB. |
| Database-level multi-tenancy with tablegroups | PROGRESS | v2.15 | Track | Master issue to track Database-level multi-tenancy using tablegroups. |
| Upgrade to PostgreSQL v13 | PROGRESS | v2.15 | Track | For latest features, new PostgreSQL extensions, performance, and community fixes |
| Support for in-cluster PITR | PROGRESS | v2.15 | Track | Point in time recovery of YSQL databases, to a fixed point in time, across DDL and DML changes |
| Automatic tablet splitting enabled by default | PROGRESS | v2.15 | Track | Enables changing the number of tablets (which are splits of data) at runtime. |
| YSQL-table statistics and cost based optimizer(CBO) | PROGRESS | v2.15 | Track | Improve YSQL query performance |
| YSQL-Feature support - ALTER TABLE | PROGRESS | v2.15 | Track | Support for various ALTER TABLE variants |
| YSQL-Online schema migration | PROGRESS | v2.15 | Track | Schema migrations(includes DDL operations) to be safely run concurrently with foreground operations |
| Pessimistic locking Design | PROGRESS | v2.15 | Track | |
Make COLOCATED tables default for YSQL |
PLANNING | Track | ||
| Support for transactions in async xCluster replication | PLANNING | Track | Apply transactions atomically on consumer cluster. | |
| Support for GiST indexes | PLANNING | Track | Suppor for GiST (Generalized Search Tree) based index |
| Feature | Status | Release Target | Docs / Enhancements | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change Data Capture | ✅ DONE | v2.13 | Change data capture (CDC) allows multiple downstream apps and services to consume the continuous and never-ending stream(s) of changes to Yugabyte databases | |
| Support for materalized views | ✅ DONE | v2.13 | Docs | A materialized view is a pre-computed data set derived from a query specification and stored for later use |
| Geo-partitioning support for the transaction status table | ✅ DONE | v2.13 | Docs | Instead of central remote transaction execution metatda, it is now optimized for access from different regions. Since the transaction metadata is also geo partitioned, it eliminates the need for round-trip to remote regions to update transaction statuses. |
| Transparently restart transactions | ✅ DONE | v2.13 | Decrease the incidence of transaction restart errors seen in various scenarios | |
| Row-level geo-partitioning | ✅ DONE | v2.13 | Docs | Row-level geo-partitioning allows fine-grained control over pinning data in a user table (at a per-row level) to geographic locations, thereby allowing the data residency to be managed at the table-row level. |
YSQL-Support GIN indexes |
✅ DONE | v2.11 | Docs | Support for generalized inverted indexes for container data types like jsonb, tsvector, and array |
| YSQL-Collation Support | ✅ DONE | v2.11 | Docs | Allows specifying the sort order and character classification behavior of data per-column, or even per-operation according to language and country-specific rules |
| YSQL-Savepoint Support | ✅ DONE | v2.11 | Docs | Useful for implementing complex error recovery in multi-statement transaction |
| xCluster replication management through Platform | ✅ DONE | v2.11 | Docs | |
| Spring Data YugabyteDB module | ✅ DONE | v2.9 | Track | Bridges the gap for learning the distributed SQL concepts with familiarity and ease of Spring Data APIs |
| Support Liquibase, Flyway, ORM schema migrations | ✅ DONE | v2.9 | Docs | |
Support ALTER TABLE add primary key |
✅ DONE | v2.9 | Track | |
| YCQL-LDAP Support | ✅ DONE | v2.8 | Docs | support LDAP authentication in YCQL API |
| Platform Alerting and Notification | ✅ DONE | v2.8 | Docs | To get notified in real time about database alerts, user defined alert policies notify you when a performance metric rises above or falls below a threshold you set. |
| Platform API | ✅ DONE | v2.8 | Docs | Securely Deploy YugabyteDB Clusters Using Infrastructure-as-Code |
Review detailed architecture in our Docs.
-
You can ask questions, find answers, and help others on our Community Slack, Forum, Stack Overflow, as well as Twitter @Yugabyte
-
Please use GitHub issues to report issues or request new features.
-
To Troubleshoot YugabyteDB, cluser/node level isssues, Please refer to Troubleshooting documentation
As an an open-source project with a strong focus on the user community, we welcome contributions as GitHub pull requests. See our Contributor Guides to get going. Discussions and RFCs for features happen on the design discussions section of our Forum.
Source code in this repository is variously licensed under the Apache License 2.0 and the Polyform Free Trial License 1.0.0. A copy of each license can be found in the licenses directory.
The build produces two sets of binaries:
- The entire database with all its features (including the enterprise ones) are licensed under the Apache License 2.0
- The binaries that contain
-managedin the artifact and help run a managed service are licensed under the Polyform Free Trial License 1.0.0.
By default, the build options generate only the Apache License 2.0 binaries.
- To see our updates, go to The Distributed SQL Blog.
- For an in-depth design and the YugabyteDB architecture, see our design specs.
- Tech Talks and Videos.
- See how YugabyteDB compares with other databases.