Important for KiCad 6 users:
- You need KiBot 1.0.0 or newer
- The docker images tagged
ki6anddev_k6has KiCad 6. - The GitHub actions with KiCad 6 support are tagged as
v2_k6(stable) andv2_dk6(development). Consult: Github Actions tags - When using KiCad 6 you must migrate the whole project and pass the migrated files to KiBot.
New on v1.2.0
- Navigate results output. Here is an example using the following example repo.
- Introduction
- Installation
- Configuration
- Usage
- Usage for CI/CD
- Contributing
- Notes about Gerber format
- Notes about the position file
- Credits
KiBot is a program which helps you to generate the fabrication and documentation files for your KiCad projects easily, repeatable, and most of all, scriptably. This means you can use a Makefile to export your KiCad PCBs just as needed, or do it in a CI/CD environment.
For example, it's common that you might want for each board rev:
- Check ERC/DRC one last time (using KiCad Automation Scripts)
- Gerbers, drills and drill maps for a fab in their favourite format
- Fab docs for the assembler, including the BoM (Bill of Materials), costs spreadsheet and board view
- Pick and place files
- PCB 3D model in STEP format
- PCB 3D render in PNG format
You want to do this in a one-touch way, and make sure everything you need to do so is securely saved in version control, not on the back of an old datasheet.
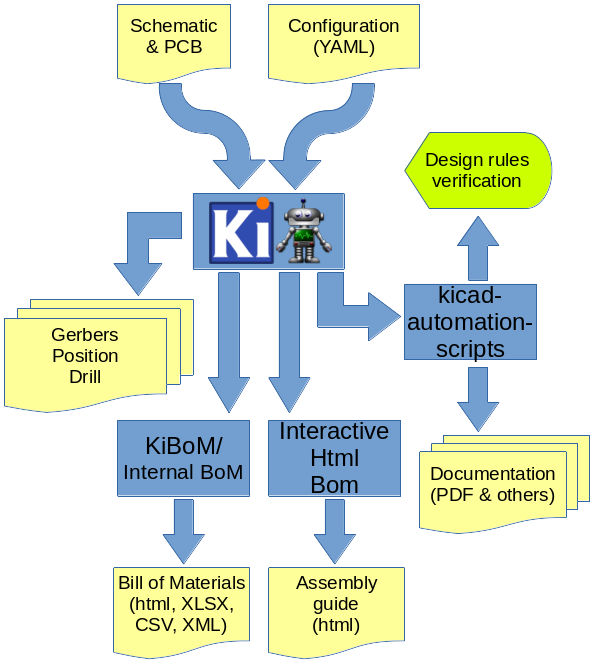
KiBot lets you do this. The following picture depicts the data flow:
If you want to see this concept applied to a real world project visit the Spora CI/CD example.
KiBot main target is Linux, but some user successfully use it on Windows. For Windows you'll need to install tools to mimic a Linux environment. Running KiBot on MacOSX should be possible now that KiCad migrated to Python 3.x.
You can also run KiBot using docker images in a CI/CD environment like GitHub or GitLab. In this case you don't need to install anything locally.
Notes:
- When installing from the Debian repo you don't need to worry about dependencies, just pay attention to recommended and suggested packages.
- When installing using
pipthe dependencies marked with will be automatically installed.
will be automatically installed. - The dependencies marked with
 can be downloaded on-demand by KiBot.
Note this is experimental and is mostly oriented to 64 bits Linux systems.
can be downloaded on-demand by KiBot.
Note this is experimental and is mostly oriented to 64 bits Linux systems. - The
kibot-checktool can help you to know which dependencies are missing. - Note that on some systems (i.e. Debian) ImageMagick disables PDF manipulation in its
policy.xmlfile. Comment or remove lines like this:<policy domain="coder" rights="none" pattern="PDF" />(On Debian:/etc/ImageMagick-6/policy.xml)  Link to Debian stable package.
Link to Debian stable package. This is a Python module, not a separated tool.
This is a Python module, not a separated tool. This is an independent tool, can be a binary or a Python script.
This is an independent tool, can be a binary or a Python script.
- Mandatory
- Mandatory
KiCad Automation tools v1.6.13 


- Mandatory for:
gencad,netlist,pdf_pcb_print,pdf_sch_print,render_3d,run_drc,run_erc,step,svg_pcb_print,svg_sch_print,update_xml - Optional to print the page frame in GUI mode for
pcb_print
KiCost v1.1.8 

- Mandatory for
kicost - Optional to find components costs and specs for
bom
PcbDraw v0.9.0 

- Mandatory for
pcbdraw - Optional to create realistic solder masks for
pcb_print
Interactive HTML BoM v2.4.1.4 

- Mandatory for
ibom
KiBoM v1.8.0 

- Mandatory for
kibom
- Mandatory for
pcb_print
- Mandatory for
qr_lib
- Optional to get color messages in a portable way for general use
RSVG tools v2.40 


- Optional to:
- Create outputs preview for
navigate_results - Create PNG icons for
navigate_results - Create PDF, PNG and PS formats for
pcb_print - Create EPS format for
pcb_print(v2.40) - Create PNG and JPG images for
pcbdraw
- Create outputs preview for
- Optional to:
- Find commit hash and/or date for
pcb_replace - Find commit hash and/or date for
sch_replace - Find commit hash and/or date for
set_text_variables
- Find commit hash and/or date for
- Optional to:
- Create outputs preview for
navigate_results - Create monochrome prints for
pcb_print - Create JPG images for
pcbdraw
- Create outputs preview for
- Optional to:
- Create outputs preview for
navigate_results - Create PS files for
pcb_print
- Create outputs preview for
- Optional to create PDF/ODF/DOCX files for
report
- Optional to compress in RAR format for
compress
- Optional to create XLSX files for
bom
The easiest way is to use the repo, but if you want to manually install the individual .deb files you can:
Get the Debian package from the releases section and run:
sudo apt install ./kibot*_all.debImportant note: Sometimes the release needs another packages that aren't part of the stable Debian distribution. In this case the packages are also included in the release page. As an example version 0.6.0 needs:
sudo apt install ./python3-mcpy_2.0.2-1_all.deb ./kibot_0.6.0-1_all.debImportant note: The KiCad Automation Scripts packages are a mandatory dependency. The KiBoM, InteractiveHtmlBom and PcbDraw are recommended.
pip install --no-compile kibotNote that pip has the dubious idea of compiling everything it downloads.
There is no advantage in doing it and it interferes with the mcpy macros.
Also note that in modern Linux systems pip was renamed to pip3, to avoid confusion with pip from Python 2.
If you are installing at system level I recommend generating the compilation caches after installing.
As root just run:
kibot --help-outputs > /dev/nullNote that pip will automatically install all the needed Python dependencies.
But it won't install other interesting dependencies.
In particular you should take a look at the KiCad Automation Scripts dependencies.
If you have a Debian based OS I strongly recommend trying to use the .deb packages for all the tools.
If you want to install the code only for the current user add the --user option.
If you want to install the last git code from GitHub using pip use:
pip3 install --user git+https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBot.gitYou can also clone the repo, change to its directory and install using:
pip3 install --user -e .In this way you can change the code and you won't need to install again.
If you try to use a Python virtual environment you'll need to find a way to make the KiCad module (pcbnew) available on it.
I don't know how to make it.
- Install KiCad 5.1.6 or newer
- Install Python 3.5 or newer
- Install the Python Yaml and requests modules
- Run the script src/kibot
KiBot uses a configuration file where you can specify what outputs to generate and which pre-flight (before launching the outputs generation) actions to perform. By default you'll generate all of them, but you can specify which ones from the command line.
The configuration file should be named using the .kibot.yaml suffix, i.e. my_project.kibot.yaml. The format used is YAML. This is basically a text file with some structure. This file can be compressed using gzip file format.
If you never used YAML read the following explanation. Note that the explanation could be useful even if you know YAML.
If you want to learn by examples, or you just want to take a look a what
KiBot can do, you can use the --quick-start command line option.
First change to the directory where your project (or projects) is located. Now run KiBot like this:
kibot --quick-startThis will look for KiCad projects starting from the current directory and going down the directory structure. For each project found KiBot will generate a configuration file showing some common outputs. After cerating the configuration files KiBot will start the outputs generation.
Here is an example of what's generated using the following example repo.
You can use the generated files as example of how to configure KiBot. If you want to just generate the configuration files and not the outputs use:
kibot --quick-start --dryIf you want to know about all the possible options for all the available outputs you can try:
kibot --exampleThis will generate a configuration file with all the available outputs and all their options.
All configuration files must start with:
kibot:
version: 1This tells to KiBot that this file is using version 1 of the format.
This section is used to specify tasks that will be executed before generating any output.
annotate_pcb: [dict] Annotates the PCB according to physical coordinates. This preflight modifies the PCB and schematic, use it only in revision control environments. Used to assign references according to footprint coordinates. The project must be fully annotated first.annotate_power: [boolean=false] Annotates all power components. This preflight modifies the schematic, use it only in revision control environments. Used to solve ERC problems when using filters that remove power reference numbers.check_zone_fills: [boolean=false] Zones are filled before doing any operation involving PCB layers. The original PCB remains unchanged.erc_warnings: [boolean=false] Option forrun_erc. ERC warnings are considered errors.fill_zones: [boolean=false] Fill all zones again and save the PCB.filters: [list(dict)] A list of entries to filter out ERC/DRC messages.- Valid keys:
error: [string=''] Error id we want to exclude. A name for KiCad 6 or a number for KiCad 5, but always a string.- error_number: Alias for number.
filter: [string=''] Name for the filter, for documentation purposes.- filter_msg: Alias for filter.
number: [number=0] Error number we want to exclude. KiCad 5 only.regex: [string=''] Regular expression to match the text for the error we want to exclude.- regexp: Alias for regex.
- Valid keys:
ignore_unconnected: [boolean=false] Option forrun_drc. Ignores the unconnected nets. Useful if you didn't finish the routing.pcb_replace: [dict] Replaces tags in the PCB. I.e. to insert the git hash or last revision date. This is useful for KiCad 5, useset_text_variableswhen using KiCad 6. This preflight modifies the PCB. Even when a back-up is done use it carefully.- Valid keys:
date_command: [string=''] Command to get the date to use in the PCB.
git log -1 --format='%as' -- $KIBOT_PCB_NAME
Will return the date in YYYY-MM-DD format.
date -d @`git log -1 --format='%at' -- $KIBOT_PCB_NAME` +%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S
Will return the date in YYYY-MM-DD_HH-MM-SS format.
Important: on KiCad 6 the title block data is optional. This command will work only if you have a date in the PCB/Schematic.replace_tags: [dict|list(dict)] Tag or tags to replace.- Valid keys:
after: [string=''] Text to add after the output ofcommand.before: [string=''] Text to add before the output ofcommand.command: [string=''] Command to execute to get the text, will be used only iftextis empty. KIBOT_PCB_NAME variable is the name of the current PCB.tag: [string=''] Name of the tag to replace. Useversionfor a tag named@version@.tag_delimiter: [string='@'] Character used to indicate the beginning and the end of a tag. Don't change it unless you really know about KiCad's file formats.text: [string=''] Text to insert instead of the tag.
- Valid keys:
- Valid keys:
run_drc: [boolean=false] Runs the DRC (Distance Rules Check). To ensure we have a valid PCB. The report file name is controlled by the global output pattern (%i=drc %x=txt).run_erc: [boolean=false] Runs the ERC (Electrical Rules Check). To ensure the schematic is electrically correct. The report file name is controlled by the global output pattern (%i=erc %x=txt).sch_replace: [dict] Replaces tags in the schematic. I.e. to insert the git hash or last revision date. This is useful for KiCad 5, useset_text_variableswhen using KiCad 6. This preflight modifies the schematics. Even when a back-up is done use it carefully.- Valid keys:
date_command: [string=''] Command to get the date to use in the SCH.
git log -1 --format='%as' -- $KIBOT_SCH_NAME
Will return the date in YYYY-MM-DD format.
date -d @`git log -1 --format='%at' -- $KIBOT_SCH_NAME` +%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S
Will return the date in YYYY-MM-DD_HH-MM-SS format.
Important: on KiCad 6 the title block data is optional. This command will work only if you have a date in the SCH/Schematic.replace_tags: [dict|list(dict)] Tag or tags to replace.- Valid keys:
after: [string=''] Text to add after the output ofcommand.before: [string=''] Text to add before the output ofcommand.command: [string=''] Command to execute to get the text, will be used only iftextis empty. KIBOT_SCH_NAME variable is the name of the current sheet. KIBOT_TOP_SCH_NAME variable is the name of the top sheet.tag: [string=''] Name of the tag to replace. Useversionfor a tag named@version@.tag_delimiter: [string='@'] Character used to indicate the beginning and the end of a tag. Don't change it unless you really know about KiCad's file formats.text: [string=''] Text to insert instead of the tag.
- Valid keys:
- Valid keys:
set_text_variables: [dict|list(dict)] Defines KiCad 6 variables. They are expanded using ${VARIABLE}, and stored in the project file. This preflight replacespcb_replaceandsch_replacewhen using KiCad 6. The KiCad project file is modified.- Valid keys:
after: [string=''] Text to add after the output ofcommand.before: [string=''] Text to add before the output ofcommand.command: [string=''] Command to execute to get the text, will be used only iftextis empty.expand_kibot_patterns: [boolean=true] Expand %X patterns. The context isschematic.name: [string=''] Name of the variable. Theversionvariable will be expanded using${version}.text: [string=''] Text to insert instead of the variable.- variable: Alias for name.
- Valid keys:
update_qr: [boolean=false] Update the QR codes. Complements theqr_liboutput. The KiCad 6 files and the KiCad 5 PCB needs manual update, generating a new library isn't enough.update_xml: [boolean=false] Update the XML version of the BoM (Bill of Materials). To ensure our generated BoM is up to date. Note that this isn't needed when using the internal BoM generator (bom).
Here is an example of a preflight section:
preflight:
run_erc: true
update_xml: true
run_drc: true
check_zone_fills: true
ignore_unconnected: falseThese options are supposed to be used in a version control environment. This is because, unlike other options, they modify the PCB and/or schematic and might damage them. In a version control environment you can just roll-back the changes.
Don't be afraid, they make a back-up of the files and also tries to disable dangerous changes. But should be used carefully. They are ideal for CI/CD environment where you don't actually commit any changes.
Sometimes KiCad reports DRC or ERC errors that you can't get rid off. This could be just because you are part of a team including lazy people that doesn't want to take the extra effort to solve some errors that aren't in fact errors, just small violations made on purpose. In this case you could exclude some known errors.
For this you must declare filters entry in the preflight section. Then you can add as many filter entries as you want.
Each filter entry has an optional description and defines to which error type is applied (number) and a regular expression
that the error must match to be ignored (regex). Like this:
filters:
- filter: 'Optional filter description'
error: 'Error_type'
regex: 'Expression to match'Here is a KiCad 5 example, suppose you are getting the following errors:
** Found 1 DRC errors **
ErrType(4): Track too close to pad
@(177.185 mm, 78.315 mm): Track 1.000 mm [Net-(C3-Pad1)] on F.Cu, length: 1.591 mm
@(177.185 mm, 80.715 mm): Pad 2 of C3 on F.Cu and others
** Found 1 unconnected pads **
ErrType(2): Unconnected items
@(177.185 mm, 73.965 mm): Pad 2 of C4 on F.Cu and others
@(177.185 mm, 80.715 mm): Pad 2 of C3 on F.Cu and others
And you want to ignore them. You can add the following filters:
filters:
- filter: 'Ignore C3 pad 2 too close to anything'
error: '4'
regex: 'Pad 2 of C3'
- filter: 'Ignore unconnected pad 2 of C4'
error: '2'
regex: 'Pad 2 of C4'If you need to match text from two different lines in the error message try using (?s)TEXT(.*)TEXT_IN_OTHER_LINE.
If you have two or more different options for a text to match try using (OPTION1|OPTION2).
A complete Python regular expressions explanation is out of the scope of this manual. For a complete reference consult the Python manual.
KiCad 6 uses strings to differentiate errors, use them for the error field. To keep compatibility you can use the number or error_number options for KiCad 5.
Note that this will ignore the errors, but they will be reported as warnings. If you want to suppress these warnings take a look at Filtering KiBot warnings
Important note: this will create a file named kibot_errors.filter in the output directory.
The section global contains default global options that affects all the outputs.
Currently only a few option are supported.
This option controls the default file name pattern used by all the outputs. This makes all the file names coherent. You can always choose the file name for a particular output.
The pattern uses the following expansions:
- %c company from pcb/sch metadata.
- %C
ncomments linenfrom pcb/sch metadata. - %d pcb/sch date from metadata if available, file modification date otherwise.
- %D date the script was started.
- %f original pcb/sch file name without extension.
- %F original pcb/sch file name without extension. Including the directory part of the name.
- %g the
file_idof the global variant. - %G the
nameof the global variant. - %i a contextual ID, depends on the output type.
- %I an ID defined by the user for this output.
- %p pcb/sch title from pcb metadata.
- %r revision from pcb/sch metadata.
- %T time the script was started.
- %x a suitable extension for the output type.
- %v the
file_idof the current variant, or the global variant if outside a variant scope. - %V the
nameof the current variant, or the global variant if outside a variant scope.
They are compatible with the ones used by IBoM.
The default value for global.output is %f-%i.%x.
If you want to include the revision you could add the following definition:
global:
output: '%f_rev_%r-%i.%x'Note that the following patterns: %c, %Cn, %d, %f, %F, %p and %r depends on the context.
If you use them for an output related to the PCB these values will be obtained from the PCB.
If you need to force the origin of the data you can use %bX for the PCB and %sX for the schematic, where
X is the pattern to expand.
The default dir value for any output is .. You can change it here.
Expansion patterns are allowed.
Note that you can use this value as a base for output's dir options. In this case the value defined in the output must start with +.
In this case the + is replaced by the default dir value defined here.
This option controls the default variant applied to all the outputs. Example:
global:
variant: 'production'This option controls the default value for the position and bom outputs.
If you don't define it then the internal defaults of each output are applied. But when you define it the default is the defined value.
On KiCad 6 the dimensions has units. When you create a new dimension it uses automatic units. This means that KiCad uses the units currently selected.
This selection isn't stored in the PCB file. The global units value is used by KiBot instead.
The out_dir option can define the base output directory. This is the same as the -d/--out-dir command line option.
Note that the command line option has precedence over it.
Expansion patterns are applied to this value, but you should avoid using patterns that expand according to the context, i.e. %c, %d, %f, %F, %p and %r. The behavior of these patterns isn't fully defined in this case and the results may change in the future.
- The %d, %sd and %bd patterns use the date and time from the PCB and schematic.
When abscent they use the file timestamp, and the
date_time_formatglobal option controls the format used. When available, and in ISO format, thedate_formatcontrols the format used. You can disable this reformatting assigningfalseto thedate_reformatoption. - The %D format is controlled by the
date_formatglobal option. - The %T format is controlled by the
time_formatglobal option.
In all cases the format is the one used by the strftime POSIX function, for more information visit this site.
The following variables control the default colors and they are used for documentation purposes:
pcb_material[FR4] PCB core material. Currently known are FR1 to FR5solder_mask_color[green] Color for the solder mask. Currently known are green, black, white, yellow, purple, blue and red.silk_screen_color[white] Color for the markings. Currently known are black and white.pcb_finish[HAL] Finishing used to protect pads. Currently known are None, HAL, HASL, ENIG and ImAg.
KiBot warnings are marked with (Wn) where n is the warning id.
Some warnings are just recommendations and you could want to avoid them to focus on details that are more relevant to your project. In this case you can define filters in a similar way used to filter DRC/ERC errors.
As an example, if you have the following warning:
WARNING:(W43) Missing component `l1:FooBar`
You can create the following filter to remove it:
global:
filters:
- number: 43
regex: 'FooBar'global:
- Valid keys:
castellated_pads: [boolean=false] Has the PCB castelletad pads? KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Board Finish -> Has castellated pads.- copper_finish: Alias for pcb_finish.
copper_thickness: [number|string] Copper thickness in micrometers (1 Oz is 35 micrometers). KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Physical Stackup.cross_no_body: [boolean=false] Cross components even when they don't have a body. Only for KiCad 6.date_format: [string='%Y-%m-%d'] Format used for the day we started the script. Is also used for the PCB/SCH date formatting whentime_reformatis enabled (default behavior). Uses thestrftimeformat.date_time_format: [string='%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S'] Format used for the PCB and schematic date when using the file timestamp. Uses thestrftimeformat.dir: [string=''] Default pattern for the output directories.drill_size_increment: [number=0.05] This is the difference between drill tools in millimeters. A manufacturer with 0.05 of increment has drills for 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.25, etc..edge_connector: [string='no'] [yes,no,bevelled] Has the PCB edge connectors? KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Board Finish -> Edge card connectors.edge_plating: [boolean=false] Has the PCB a plated board edge? KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Board Finish -> Plated board edge.environment: [dict] Used to define environment variables used by KiCad. The values defined here are exported as environment variables and has more precedence than KiCad paths defined in the GUI. You can make reference to any OS environment variable using ${VARIABLE}. The KIPRJMOD is also available for expansion.- Valid keys:
define_old: [boolean=false] Also define legacy versions of the variables. Useful when using KiCad 6 and some libs uses old KiCad 5 names.footprints: [string=''] System level footprints (aka modules) dir. KiCad 5: KICAD_FOOTPRINT_DIR and KISYSMOD. KiCad 6: KICAD6_FOOTPRINT_DIR.models_3d: [string=''] System level 3D models dir. KiCad 5: KISYS3DMOD. KiCad 6: KICAD6_3DMODEL_DIR.symbols: [string=''] System level symbols dir. KiCad 5: KICAD_SYMBOL_DIR. KiCad 6: KICAD6_SYMBOL_DIR.templates: [string=''] System level templates dir. KiCad 5: KICAD_TEMPLATE_DIR. KiCad 6: KICAD6_TEMPLATE_DIR.third_party: [string=''] 3rd party dir. KiCad 6: KICAD6_3RD_PARTY.user_templates: [string=''] User level templates dir. KiCad 5/6: KICAD_USER_TEMPLATE_DIR.
- Valid keys:
extra_pth_drill: [number=0.1] How many millimeters the manufacturer will add to plated holes. This is because the plating reduces the hole, so you need to use a bigger drill. For more information consult: https://www.eurocircuits.com/pcb-design-guidelines/drilled-holes/.field_3D_model: [string='_3D_model'] Name for the field controlling the 3D models used for a component.filters: [list(dict)] KiBot warnings to be ignored.- Valid keys:
error: [string=''] Error id we want to exclude. A name for KiCad 6 or a number for KiCad 5, but always a string.- error_number: Alias for number.
filter: [string=''] Name for the filter, for documentation purposes.- filter_msg: Alias for filter.
number: [number=0] Error number we want to exclude. KiCad 5 only.regex: [string=''] Regular expression to match the text for the error we want to exclude.- regexp: Alias for regex.
- Valid keys:
impedance_controlled: [boolean=false] The PCB needs specific dielectric characteristics. KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Physical Stackup.kiauto_time_out_scale: [number=0.0] Time-out multiplier for KiAuto operations.kiauto_wait_start: [number=0] Time to wait for KiCad in KiAuto operations.out_dir: [string=''] Base output dir, same as command line--out-dir.output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Default pattern for output file names. Affected by global options.pcb_finish: [string='HAL'] Finishing used to protect pads. Currently used for documentation and to choose default colors. KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Board Finish -> Copper Finish option. Currently known are None, HAL, HASL, HAL SnPb, HAL lead-free, ENIG, ENEPIG, Hard gold, ImAg, Immersion Silver, Immersion Ag, ImAu, Immersion Gold, Immersion Au, Immersion Tin, Immersion Nickel, OSP and HT_OSP.pcb_material: [string='FR4'] PCB core material. Currently used for documentation and to choose default colors. Currently known are FR1 to FR5.silk_screen_color: [string='white'] Color for the markings. Currently used for documentation and to choose default colors. KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Physical Stackup. Currently known are black and white.silk_screen_color_bottom: [string=''] Color for the bottom silk screen. When not definedsilk_screen_coloris used. Readsilk_screen_colorhelp.silk_screen_color_top: [string=''] Color for the top silk screen. When not definedsilk_screen_coloris used. Readsilk_screen_colorhelp.solder_mask_color: [string='green'] Color for the solder mask. Currently used for documentation and to choose default colors. KiCad 6: you should set this in the Board Setup -> Physical Stackup. Currently known are green, black, white, yellow, purple, blue and red.solder_mask_color_bottom: [string=''] Color for the bottom solder mask. When not definedsolder_mask_coloris used. Readsolder_mask_colorhelp.solder_mask_color_top: [string=''] Color for the top solder mask. When not definedsolder_mask_coloris used. Readsolder_mask_colorhelp.time_format: [string='%H-%M-%S'] Format used for the time we started the script. Uses thestrftimeformat.time_reformat: [boolean=true] Tries to reformat the PCB/SCH date using thedate_format. This assumes you let KiCad fill this value and hence the time is in ISO format (YY-MM-DD).units: [string=''] [millimeters,inches,mils] Default units. Affectspositionandbomoutputs. Also KiCad 6 dimensions.variant: [string=''] Default variant to apply to all outputs.
The filters and variants are mechanisms used to modify the circuit components. Both concepts are closely related. In fact variants can use filters.
The current implementation of the filters allow to exclude components from some of the processing stages. The most common use is to exclude them from some output. You can also change components fields/properties and also the 3D model.
Variants are currently used to create assembly variants. This concept is used to manufacture one PCB used for various products. You can learn more about KiBot variants on the following example repo. The example is currently using KiCad 6, if you want to see the example files for KiCad 5 go here.
As mentioned above the current use of filters is to mark some components. Mainly to exclude them, but also to mark them as special. This is the case of do not change components in the BoM.
Filters and variants are defined in separated sections. A filter section looks like this:
filters:
- name: 'a_short_name'
type: 'generic'
comment: 'A description'
# Filter options- field_rename: Field_Rename
This filter implements a field renamer.
The internal
_kicost_renamefilter emulates the KiCost behavior.- Valid keys:
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.rename: [list(dict)] Fields to rename.- Valid keys:
field: [string=''] Name of the field to rename.name: [string=''] New name.
- Valid keys:
- Valid keys:
- generic: Generic filter
This filter is based on regular expressions.
It also provides some shortcuts for common situations.
Note that matches aren't case sensitive and spaces at the beginning and the end are removed.
The internal
_mechanicalfilter emulates the KiBoM behavior for default exclusions. The internal_kicost_dnpfilter emulates KiCost'sdnpfield.- Valid keys:
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.config_field: [string='Config'] Name of the field used to classify components.config_separators: [string=' ,'] Characters used to separate options inside the config field.exclude_all_hash_ref: [boolean=false] Exclude all components with a reference starting with #.exclude_any: [list(dict)] A series of regular expressions used to exclude parts. If a component matches ANY of these, it will be excluded. Column names are case-insensitive.- Valid keys:
column: [string=''] Name of the column to apply the regular expression.- field: Alias for column.
invert: [boolean=false] Invert the regex match result.match_if_field: [boolean=false] Match if the field exists, no regex applied. Not affected byinvert.match_if_no_field: [boolean=false] Match if the field doesn't exists, no regex applied. Not affected byinvert.regex: [string=''] Regular expression to match.- regexp: Alias for regex.
skip_if_no_field: [boolean=false] Skip this test if the field doesn't exist.
- Valid keys:
exclude_config: [boolean=false] Exclude components containing a key value in the config field. Separators are applied.exclude_empty_val: [boolean=false] Exclude components with empty 'Value'.exclude_field: [boolean=false] Exclude components if a field is named as any of the keys.exclude_refs: [list(string)] List of references to be excluded. Use R* for all references with R prefix.exclude_smd: [boolean=false] KiCad 5: exclude components marked as smd in the PCB.exclude_tht: [boolean=false] KiCad 5: exclude components marked as through-hole in the PCB.exclude_value: [boolean=false] Exclude components if their 'Value' is any of the keys.exclude_virtual: [boolean=false] KiCad 5: exclude components marked as virtual in the PCB.include_only: [list(dict)] A series of regular expressions used to include parts. If there are any regex defined here, only components that match against ANY of them will be included. Column/field names are case-insensitive. If empty this rule is ignored.- Valid keys:
column: [string=''] Name of the column to apply the regular expression.- field: Alias for column.
invert: [boolean=false] Invert the regex match result.match_if_field: [boolean=false] Match if the field exists, no regex applied. Not affected byinvert.match_if_no_field: [boolean=false] Match if the field doesn't exists, no regex applied. Not affected byinvert.regex: [string=''] Regular expression to match.- regexp: Alias for regex.
skip_if_no_field: [boolean=false] Skip this test if the field doesn't exist.
- Valid keys:
invert: [boolean=false] Invert the result of the filter.keys: [string|list(string)=dnf_list] [dnc_list,dnf_list] List of keys to match. Thednf_listanddnc_listinternal lists can be specified as strings. Usednf_listfor ['dnf', 'dnl', 'dnp', 'do not fit', 'do not load', 'do not place', 'no stuff', 'nofit', 'noload', 'noplace', 'nostuff', 'not fitted', 'not loaded', 'not placed']. Usednc_listfor ['dnc', 'do not change', 'fixed', 'no change'].name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.
- Valid keys:
- rot_footprint: Rot_Footprint
This filter can rotate footprints, used for the positions file generation.
Some manufacturers use a different rotation than KiCad.
The internal
_rot_footprintfilter implements the simplest case.- Valid keys:
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.extend: [boolean=true] Extends the internal list of rotations with the one provided. Otherwise just use the provided list.invert_bottom: [boolean=false] Rotation for bottom components is negated, resulting in either:(- component rot - angle)or when combined withnegative_bottom,(angle - component rot).name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.negative_bottom: [boolean=true] Rotation for bottom components is computed via subtraction as(component rot - angle).rotations: [list(list(string))] A list of pairs regular expression/rotation. Components matching the regular expression will be rotated the indicated angle.skip_bottom: [boolean=false] Do not rotate components on the bottom.skip_top: [boolean=false] Do not rotate components on the top.
- Valid keys:
- subparts: Subparts
This filter implements the KiCost subparts mechanism.
- Valid keys:
check_multiplier: [list(string)] List of fields to include for multiplier computation. If empty all fields insplit_fieldsandmanf_pn_fieldare used.comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.manf_field: [string='manf'] Field for the manufacturer name.manf_pn_field: [string='manf#'] Field for the manufacturer part number.modify_first_value: [boolean=true] Modify even the value for the first component in the list (KiCost behavior).modify_value: [boolean=true] Add '- p N/M' to the value.mult_separators: [string=':'] Separators used for the multiplier. Each character in this string is a valid separator.multiplier: [boolean=true] Enables the subpart multiplier mechanism.name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.ref_sep: [string='#'] Separator used in the reference (i.e. R10#1).separators: [string=';,'] Separators used between subparts. Each character in this string is a valid separator.split_fields: [list(string)] List of fields to split, usually the distributors part numbers.split_fields_expand: [boolean=false] Whentruethe fields insplit_fieldsare added to the internal names.use_ref_sep_for_first: [boolean=true] Force the reference separator use even for the first component in the list (KiCost behavior).value_alt_field: [string='value_subparts'] Field containing replacements for theValuefield. So we get real values for split parts.
- Valid keys:
- var_rename: Var_Rename
This filter implements the VARIANT:FIELD=VALUE renamer to get FIELD=VALUE when VARIANT is in use.
- Valid keys:
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.force_variant: [string=''] Use this variant instead of the current variant. Useful for IBoM variants.name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.separator: [string=':'] Separator used between the variant and the field name.variant_to_value: [boolean=false] Rename fields matching the variant to the value of the component.
- Valid keys:
- var_rename_kicost: Var_Rename_KiCost
This filter implements the kicost.VARIANT:FIELD=VALUE renamer to get FIELD=VALUE when VARIANT is in use.
It applies the KiCost concept of variants (a regex to match the VARIANT).
The internal
_var_rename_kicostfilter emulates the KiCost behavior.- Valid keys:
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes.name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular filter definition.prefix: [string='kicost.'] A mandatory prefix. Is not case sensitive.separator: [string=':'] Separator used between the variant and the field name.variant: [string=''] Variant regex to match the VARIANT part. When empty the currently selected variant is used.variant_to_value: [boolean=false] Rename fields matching the variant to the value of the component.
- Valid keys:
The tests/yaml_samples directory contains all the regression tests. Many of them test the filters functionality.
- int_bom_exclude_any.kibot.yaml: Shows how to use regular expressions to match fields and exclude components. Is the more powerful filter mechanism.
- int_bom_fil_1.kibot.yaml: Shows various mechanisms. In particular how to change the list of keywords, usually used to match 'DNF', meaning you can exclude components with arbitrary text.
- int_bom_fil_2.kibot.yaml: Shows how to use KiCad 5 module attributes (from the PCB) to filter SMD, THT and Virtual components. Note KiCad 6 is redefining the attributes.
- int_bom_include_only.kibot.yaml: Shows how to use regular expressions to match only some components, instead of including a few.
- int_bom_var_t2is_csv.kibot.yaml: Shows how to use filters and variants simultaneously, not a good idea, but possible.
- print_pdf_no_inductors_1.kibot.yaml: Shows how to change the
dnf_filterfor a KiBoM variant. - print_pdf_no_inductors_2.kibot.yaml: Shows how to do what
print_pdf_no_inductors_1.kibot.yamldoes but without the need of a variant.
- _mechanical is used to exclude:
- References that start with #
- Virtual components
- References that match: '^TP[0-9]*' or '^FID'
- Part names that match: 'regex': 'mount.*hole' or 'solder.*bridge' or 'solder.*jump' or 'test.*point'
- Footprints that match: 'test.*point' or 'mount.*hole' or 'fiducial'
- _var_rename is a default
var_renamefilter - _var_rename_kicost is a default
var_rename_kicostfilter - _kicost_rename is a
field_renamefilter that applies KiCost renamings.- Includes all
manf#andmanfvariations supported by KiCost - Includes all distributor part number variations supported by KiCost
- 'version' -> 'variant'
- 'nopop' -> 'dnp'
- 'description' -> 'desc'
- 'pdf' -> 'datasheet'
- Includes all
- _kicost_dnp used emulate the way KiCost handles the
dnpfield.- If the field is 0 the component is included, otherwise excluded.
- _rot_footprint is a default
rot_footprintfilter - _kibom_dnf_Config it uses the internal
dnf_listto exclude components with- Value matching any of the keys
- Any of the keys in the
Configfield (comma or space separated)
- _kibom_dnc_Config it uses the internal
dnc_listto exclude components with- Value matching any of the keys
- Any of the keys in the
Configfield (comma or space separated)
Note that the last two uses a field named Config, but you can customise them invoking _kibom_dnf_FIELD. This will create an equivalent filter, but using the indicated FIELD.
This mechanism allows small changes to the 3D model. Is simple to use, but the information is located in the schematic.
If a component defines the field _3D_model then its value will replace the 3D model.
You can use var_rename or var_rename_kicost filter to define this field only for certain variants.
In this way you can change the 3D model according to the component variant.
When the component has more than one 3D model you must provide a comma separated list of models to replace the current models.
When the a component has a long list of 3D models and you want to keep all the information in the PCB you can use this mechanism.
The information is stored in the Text items of the footprint. If you want to change the 3D models for certain variant you must add an item containing:
%VARIANT_NAME:SLOT1,SLOT2,SLOTN%
Where VARIANT_NAME is the name of the variant that will change the list of 3D models.
The SLOT1,SLOT2,SLOTN is a comma separated list of 3D model positions in the list of 3D models.
All the slots listed will be enabled, the rest will be disabled.
Here is an example. In this example we have a display whose aspect and connectio can radically change according to the variant. We have two variants:
left, uses a ERM1602DNS-2.1 with a connector on the left and two other pins on the righttop, uses a WH1602B-TMI-JT# with a single connector on the top
We have the following list of 3D models:
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_2x07_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_1x16_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_1x01_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_1x01_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
${KIPRJMOD}/steps/WH1602B-TMI-JT#.step
${KIPRJMOD}/steps/ERM1602DNS-2.1.step
The ERM1602DNS-2.1 uses slots 1, 3, 4 and 6. So the effective list will be:
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_2x07_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_1x01_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_1x01_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
${KIPRJMOD}/steps/ERM1602DNS-2.1.step
The WH1602B-TMI-JT# uses slots 2 and 5. So the effective list will be:
${KISYS3DMOD}/Connector_PinHeader_2.54mm.3dshapes/PinHeader_1x16_P2.54mm_Vertical.wrl
${KIPRJMOD}/steps/WH1602B-TMI-JT#.step
To achieve it we define the following texts in the footprint: %left:1,3,4,6% and %top:2,5%.
Here are both variants:
If you preffer to use the variant specific matching mechanism you can use the following syntax:
$TEXT_TO_MATCH:SLOT1,SLOT2,SLOTN$
In this case the variant will be applied to the TEXT_TO_MATCH, if it matches (equivalent to a component fitted) the SLOT will be used.
Some important notes:
- If you want to control what models are used when no variant is used you'll need to create a
defaultvariant. This is what the above example does. In this case thedefaultvariant shows all the connectors, but no display. Note that changing the 3D model needs the variants infrastructure. - If you are using variants and a lot of them select the same slots you can add a special text:
%_default_:SLOTS%. This will be used if none %VARIANT_NAME:SLOT%` matched. - If you want to disable a model and avoid any kind of warning add
_Disabled_by_KiBotto the 3D model path. This could be needed if you want to remove some model and you don't want to adjust the slot numbers. - This mechanism can be used with any of the available variants. For this reason we use the
VARIANT_NAMEand we avoid relying on any variant specific mechanism. But you can use the alternative syntax if you preffer the variant specific matching system.
The current list of DNF keys is:
- dnf
- dnl
- dnp
- do not fit
- do not place
- do not load
- nofit
- nostuff
- noplace
- noload
- not fitted
- not loaded
- not placed
- no stuff
The current list of DNC keys is:
- dnc
- do not change
- no change
- fixed
You can define your own lists as the int_bom_fil_1.kibot.yaml shows.
In this section you put all the things that you want to generate. This section contains one or more outputs. Each output contain the following data:
namea name so you can easily identify it.commenta short description of this output.typeselects which type of output will be generated. Examples are gerbers, drill files and pick & place filesdiris the directory where this output will be stored.extendsused to use another output'soptionsas base.run_by_defaultindicates this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.disable_run_by_defaultcan be used to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output.output_idtext to use for the %I expansion content.optionscontains one or more options to configure this output.layersa list of layers used for this output. Not all outputs needs this subsection.
Important note about the layers: In the original kiplot (from John Beard) the name of the inner layers was Inner.N where N is the number of the layer, i.e. Inner.1 is the first inner layer. This format is supported for compatibility. Note that this generated a lot of confusion because the default KiCad name for the first inner layer is In1.Cu. People filled issues and submitted pull-requests to fix it, thinking that inner layers weren't supported. Currently KiCad allows renaming these layers, so this version of kiplot supports the name used in KiCad. Just use the same name you see in the user interface.
The available values for type are:
- Plot formats:
gerberthe gerbers for fabrication.pspostscript plothpglformat for laser printerssvgscalable vector graphicspdfportable document formatdxfmechanical CAD format
- Drill formats:
excellondata for the drilling machinegerb_drilldrilling positions in a gerber file
- Pick & place
positionof the components for the pick & place machine
- Documentation
pdf_sch_printschematic in PDF formatsvg_sch_printschematic in SVG formatpdf_pcb_printPDF file containing one or more layer and the page framesvg_pcb_printSVG file containing one or more layer and the page framepcb_printPDF/SVG/PNG/EPS/PS, similar topdf_pcb_printandsvg_pcb_print, with more flexibilityreportgenerates a report about the PDF. Can include images from the above outputs.
- Bill of Materials
bomThe internal BoM generator.kibomBoM in HTML or CSV format generated by KiBoMibomInteractive HTML BoM generated by InteractiveHtmlBomkicostBoM in XLSX format with costs generated by KiCost
- 3D model:
stepStandard for the Exchange of Product Data for the PCBrender_3dPCB render, from the KiCad's 3D Viewer (broken in KiCad 6.0.0)
- Others:
boardviewcreates a file useful to repair the board, but without disclosing the full layout.gencadexports the PCB in GENCAD format.compresscreates an archive containing generated data.download_datasheetsdownloads the datasheets for all the components.pcbdrawnice images of the PCB in customized colors.pdfunitejoins various PDF files into one.qr_libgenerates symbol and footprints for QR codes.sch_variantthe schematic after applying all filters and variants, including crossed components.
Here is an example of a configuration file to generate the gerbers for the top and bottom layers:
kibot:
version: 1
preflight:
run_drc: true
outputs:
- name: 'gerbers'
comment: "Gerbers for the board house"
type: gerber
dir: gerberdir
options:
# generic layer options
exclude_edge_layer: false
exclude_pads_from_silkscreen: false
plot_sheet_reference: false
plot_footprint_refs: true
plot_footprint_values: true
force_plot_invisible_refs_vals: false
tent_vias: true
line_width: 0.15
# gerber options
use_aux_axis_as_origin: false
subtract_mask_from_silk: true
use_protel_extensions: false
gerber_precision: 4.5
create_gerber_job_file: true
use_gerber_x2_attributes: true
use_gerber_net_attributes: false
layers:
- 'F.Cu'
- 'B.Cu'Most options are the same you'll find in the KiCad dialogs.
Outputs are generated in the order they are declared in the YAML file.
To create them in an arbitrary order use the --cli-order command line option and they will be created in the order specified in the command line.
You have various ways to specify the layers. If you need to specify just one layer you can just use its name:
layers: 'F.Cu'If you want to specify all the available layers:
layers: 'all'You can also select the layers you want in KiCad (using File, Plot dialog) and save your PCB. Then you just need to use:
layers: 'selected'You can also use any of the following grup of layers:
- copper all the copper layers
- technical all the technical layers (silk sreen, solder mask, paste, adhesive, etc.)
- user all the user layers (draw, comments, eco, margin, edge cuts, etc.)
You can also mix the above definitions using a list:
layers:
- 'copper'
- 'Dwgs.User'This will select all the copper layers and the user drawings. Note that the above mentioned options will use file name suffixes and descriptions selected automatically. If you want to use a particular suffix and provide better descriptions you can use the following format:
layers:
- layer: 'F.Cu'
suffix: 'F_Cu'
description: 'Front copper'
- layer: 'B.Cu'
suffix: 'B_Cu'
description: 'Bottom copper'You can also mix the styles:
layers:
- 'copper'
- layer: 'Cmts.User'
suffix: 'Cmts_User'
description: 'User comments'
- 'Dwgs.User'If you need to use the same list of layers for various outputs you can use YAML anchors. The first time you define the list of layers just assign an anchor, here is an example:
layers: &copper_and_cmts
- copper
- 'Cmts.User'Next time you need this list just use an alias, like this:
layers: *copper_and_cmtsNotes:
- Most relevant options are listed first and in bold. Which ones are more relevant is quite arbitrary, comments are welcome.
- Aliases are listed in italics.
-
BoardView
- Type:
boardview - Description: Exports the PCB in board view format. This format allows simple pads and connections navigation, mainly for circuit debug. The output can be loaded using Open Board View (https://openboardview.org/)
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for theboardviewoutput.- Valid keys:
-
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=boardview, %x=brd). Affected by global options.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
- Type:
-
BoM (Bill of Materials)
- Type:
bom - Description: Used to generate the BoM in CSV, HTML, TSV, TXT, XML or XLSX format using the internal BoM.
This output can generate XYRS files (pick and place files).
Is compatible with KiBoM, but doesn't need to update the XML netlist because the components
are loaded from the schematic.
Important differences with KiBoM output:
- All options are in the main
optionssection, not inconfsubsection. - TheComponentcolumn is namedRowand works just like any other column. This output is what you get from the 'Tools/Generate Bill of Materials' menu in eeschema. - Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thebomoutput.- Valid keys:
-
columns: [list(dict)|list(string)] List of columns to display. Can be just the name of the field.- Valid keys:
-
field: [string=''] Name of the field to use for this column. -
name: [string=''] Name to display in the header. The field is used when empty. -
comment: [string=''] Used as explanation for this column. The XLSX output uses it. -
join: [list(dict)|list(string)|string=''] List of fields to join to this column.- Valid keys:
-
field: [string=''] Name of the field. -
text: [string=''] Text to use instead of a field. This option is incompatible with thefieldoption. Any space to separate it should be added in the text. Use \n for newline and \t for tab. -
text_after: [string=''] Text to add after the field content. Will be added only if the field isn't empty. Any space to separate it should be added in the text. Use \n for newline and \t for tab. -
text_before: [string=''] Text to add before the field content. Will be added only if the field isn't empty. Any space to separate it should be added in the text. Use \n for newline and \t for tab.
-
- Valid keys:
-
level: [number=0] Used to group columns. The XLSX output uses it to collapse columns.
-
- Valid keys:
-
csv: [dict] Options for the CSV, TXT and TSV formats.- Valid keys:
-
quote_all: [boolean=false] Enclose all values using double quotes. -
separator: [string=','] CSV Separator. TXT and TSV always use tab as delimiter. -
hide_header: [boolean=false] Hide the header line (names of the columns). -
hide_pcb_info: [boolean=false] Hide project information. -
hide_stats_info: [boolean=false] Hide statistics information.
-
- Valid keys:
-
format: [string=''] [HTML,CSV,TXT,TSV,XML,XLSX] format for the BoM. Defaults to CSV or a guess according to the options.. -
group_fields: [list(string)] List of fields used for sorting individual components into groups. Components which match (comparing all fields) will be grouped together. Field names are case-insensitive. If empty: ['Part', 'Part Lib', 'Value', 'Footprint', 'Footprint Lib', 'Voltage', 'Tolerance', 'Current', 'Power'] is used. -
html: [dict] Options for the HTML format.- Valid keys:
-
datasheet_as_link: [string=''] Column with links to the datasheet. -
generate_dnf: [boolean=true] Generate a separated section for DNF (Do Not Fit) components. -
logo: [string|boolean=''] PNG file to use as logo, use false to remove. -
title: [string='KiBot Bill of Materials'] BoM title. -
col_colors: [boolean=true] Use colors to show the field type. -
digikey_link: [string|list(string)=''] Column/s containing Digi-Key part numbers, will be linked to web page. -
extra_info: [string|list(string)=''] Information to put after the title and before the pcb and stats info. -
hide_pcb_info: [boolean=false] Hide project information. -
hide_stats_info: [boolean=false] Hide statistics information. -
highlight_empty: [boolean=true] Use a color for empty cells. Applies only whencol_colorsistrue. -
style: [string='modern-blue'] Page style. Internal styles: modern-blue, modern-green, modern-red and classic. Or you can provide a CSS file name. Please use .css as file extension..
-
- Valid keys:
-
ignore_dnf: [boolean=true] Exclude DNF (Do Not Fit) components. -
normalize_values: [boolean=false] Try to normalize the R, L and C values, producing uniform units and prefixes. -
number: [number=1] Number of boards to build (components multiplier). -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] filename for the output (%i=bom). Affected by global options. -
sort_style: [string='type_value'] [type_value,type_value_ref,ref] Sorting criteria. -
units: [string='millimeters'] [millimeters,inches,mils] Units used for the positions ('Footprint X' and 'Footprint Y' columns). Affected by global options. -
xlsx: [dict] Options for the XLSX format.- Valid keys:
-
datasheet_as_link: [string=''] Column with links to the datasheet. -
generate_dnf: [boolean=true] Generate a separated section for DNF (Do Not Fit) components. -
kicost: [boolean=false] Enable KiCost worksheet creation. -
logo: [string|boolean=''] PNG file to use as logo, use false to remove. -
specs: [boolean=false] Enable Specs worksheet creation. Contains specifications for the components. Works with only some KiCost APIs. -
title: [string='KiBot Bill of Materials'] BoM title. -
col_colors: [boolean=true] Use colors to show the field type. -
digikey_link: [string|list(string)=''] Column/s containing Digi-Key part numbers, will be linked to web page. -
extra_info: [string|list(string)=''] Information to put after the title and before the pcb and stats info. -
hide_pcb_info: [boolean=false] Hide project information. -
hide_stats_info: [boolean=false] Hide statistics information. -
highlight_empty: [boolean=true] Use a color for empty cells. Applies only whencol_colorsistrue. -
kicost_api_disable: [string|list(string)=''] List of KiCost APIs to disable. -
kicost_api_enable: [string|list(string)=''] List of KiCost APIs to enable. -
kicost_config: [string=''] KiCost configuration file. It contains the keys for the different distributors APIs. The regular KiCost config is used when empty. -
kicost_dist_desc: [boolean=false] Used to add a column with the distributor's description. So you can check this is the right component. -
logo_scale: [number=2] Scaling factor for the logo. Note that this value isn't honored by all spreadsheet software. -
max_col_width: [number=60] [20,999] Maximum column width (characters). -
specs_columns: [list(dict)|list(string)] Which columns are included in the Specs worksheet. UseReferencesfor the references, 'Row' for the order and 'Sep' to separate groups at the same level. By default all are included. Column names are distributor specific, the following aren't: '_desc', '_value', '_tolerance', '_footprint', '_power', '_current', '_voltage', '_frequency', '_temp_coeff', '_manf', '_size'.- Valid keys:
-
field: [string=''] Name of the field to use for this column. -
name: [string=''] Name to display in the header. The field is used when empty. -
comment: [string=''] Used as explanation for this column. The XLSX output uses it. -
join: [list(dict)|list(string)|string=''] List of fields to join to this column.- Valid keys:
-
field: [string=''] Name of the field. -
text: [string=''] Text to use instead of a field. This option is incompatible with thefieldoption. Any space to separate it should be added in the text. Use \n for newline and \t for tab. -
text_after: [string=''] Text to add after the field content. Will be added only if the field isn't empty. Any space to separate it should be added in the text. Use \n for newline and \t for tab. -
text_before: [string=''] Text to add before the field content. Will be added only if the field isn't empty. Any space to separate it should be added in the text. Use \n for newline and \t for tab.
-
-
level: [number=0] Used to group columns. The XLSX output uses it to collapse columns.
- Valid keys:
-
-
style: [string='modern-blue'] Head style: modern-blue, modern-green, modern-red and classic.
- Valid keys:
-
-
aggregate: [list(dict)] Add components from other projects.- Valid keys:
-
file: [string=''] Name of the schematic to aggregate. -
name: [string=''] Name to identify this source. If empty we use the name of the schematic. -
number: [number=1] Number of boards to build (components multiplier). Use negative to subtract. -
ref_id: [string=''] A prefix to add to all the references from this project.
-
- Valid keys:
-
angle_positive: [boolean=true] Always use positive values for the footprint rotation. -
bottom_negative_x: [boolean=false] Use negative X coordinates for footprints on bottom layer (for XYRS). -
component_aliases: [list(list(string))] A series of values which are considered to be equivalent for the part name. Each entry is a list of equivalen names. Example: ['c', 'c_small', 'cap' ] will ensure the equivalent capacitor symbols can be grouped together. If empty the following aliases are used: - ['r', 'r_small', 'res', 'resistor'] - ['l', 'l_small', 'inductor'] - ['c', 'c_small', 'cap', 'capacitor'] - ['sw', 'switch'] - ['zener', 'zenersmall'] - ['d', 'diode', 'd_small']. -
cost_extra_columns: [list(dict)|list(string)] List of columns to add to the global section of the cost. Can be just the name of the field.- Valid keys:
-
field: [string=''] Name of the field to use for this column. -
name: [string=''] Name to display in the header. The field is used when empty. -
comment: [string=''] Used as explanation for this column. The XLSX output uses it. -
join: [list(dict)|list(string)|string=''] List of fields to join to this column.- Valid keys:
-
field: [string=''] Name of the field. -
text: [string=''] Text to use instead of a field. This option is incompatible with thefieldoption. Any space to separate it should be added in the text. Use \n for newline and \t for tab. -
text_after: [string=''] Text to add after the field content. Will be added only if the field isn't empty. Any space to separate it should be added in the text. Use \n for newline and \t for tab. -
text_before: [string=''] Text to add before the field content. Will be added only if the field isn't empty. Any space to separate it should be added in the text. Use \n for newline and \t for tab.
-
- Valid keys:
-
level: [number=0] Used to group columns. The XLSX output uses it to collapse columns.
-
- Valid keys:
-
count_smd_tht: [boolean=false] Show the stats about how many of the components are SMD/THT. You must provide the PCB. -
distributors: [string|list(string)] Include this distributors list. Default is all the available. -
dnc_filter: [string|list(string)='_kibom_dnc'] Name of the filter to mark components as 'Do Not Change'. The default filter marks components with a DNC value or DNC in the Config field. -
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_kibom_dnf'] Name of the filter to mark components as 'Do Not Fit'. The default filter marks components with a DNF value or DNF in the Config field. -
exclude_filter: [string|list(string)='_mechanical'] Name of the filter to exclude components from BoM processing. The default filter excludes test points, fiducial marks, mounting holes, etc. -
fit_field: [string='Config'] Field name used for internal filters. -
footprint_populate_values: [string|list(string)='no,yes'] Values for theFootprint Populatecolumn. -
footprint_type_values: [string|list(string)='SMD,THT,VIRTUAL'] Values for theFootprint Typecolumn. -
group_connectors: [boolean=true] Connectors with the same footprints will be grouped together, independent of the name of the connector. -
group_fields_fallbacks: [list(string)] List of fields to be used when the fields ingroup_fieldsare empty. The first field in this list is the fallback for the first ingroup_fields, and so on. -
int_qtys: [boolean=true] Component quantities are always expressed as integers. Using the ceil() function. -
merge_blank_fields: [boolean=true] Component groups with blank fields will be merged into the most compatible group, where possible. -
merge_both_blank: [boolean=true] When creating groups two components with empty/missing field will be interpreted as with the same value. -
no_conflict: [list(string)] List of fields where we tolerate conflicts. Use it to avoid undesired warnings. By default the field indicated infit_field, the field used for variants and the fieldpartare excluded. -
no_distributors: [string|list(string)] Exclude this distributors list. They are removed after computingdistributors. -
normalize_locale: [boolean=false] When normalizing values use the locale decimal point. -
ref_id: [string=''] A prefix to add to all the references from this project. Used for multiple projects. -
ref_separator: [string=' '] Separator used for the list of references. -
source_by_id: [boolean=false] Generate theSource BoMcolumn using the reference ID instead of the project name. -
use_alt: [boolean=false] Print grouped references in the alternate compressed style eg: R1-R7,R18. -
use_aux_axis_as_origin: [boolean=true] Use the auxiliary axis as origin for coordinates (KiCad default) (for XYRS). -
variant: [string=''] Board variant, used to determine which components are output to the BoM..
- Valid keys:
-
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
- Type:
Archiver (files compressor)
- Type:
compress - Description: Generates a compressed file containing output files. This is used to generate groups of files in compressed file format.
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thecompressoutput.- Valid keys:
-
files: [list(dict)] Which files will be included.- Valid keys:
-
from_output: [string=''] Collect files from the selected output. When used thesourceoption is ignored. -
source: [string='*'] File names to add, wildcards allowed. Use ** for recursive match. By default this pattern is applied to the output dir specified with-dcommand line option. See thefrom_cwdoption. -
dest: [string=''] Destination directory inside the archive, empty means the same of the file. -
filter: [string='.*'] A regular expression that source files must match. -
from_cwd: [boolean=false] Use the current working directory instead of the dir specified by-d.
-
- Valid keys:
-
format: [string='ZIP'] [ZIP,TAR,RAR] Output file format. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the generated archive (%i=name of the output %x=according to format). Affected by global options. -
compression: [string='auto'] [auto,stored,deflated,bzip2,lzma] Compression algorithm. Use auto to let KiBot select a suitable one. -
move_files: [boolean=false] Move the files to the archive. In other words: remove the files after adding them to the archive. - remove_files: Alias for move_files.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=10] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
Datasheets downloader
- Type:
download_datasheets - Description: Downloads the datasheets for the project
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thedownload_datasheetsoutput.- Valid keys:
-
field: [string='Datasheet'] Name of the field containing the URL. -
dnf: [boolean=false] Include the DNF components. -
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
link_repeated: [boolean=true] Instead of download things we already downloaded use symlinks. -
output: [string='${VALUE}.pdf'] Name used for the downloaded datasheet. ${FIELD} will be replaced by the FIELD content. -
repeated: [boolean=false] Download URLs that we already downloaded. It only makes sense if theoutputfield makes their output different. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
DXF (Drawing Exchange Format)
- Type:
dxf - Description: Exports the PCB to 2D mechanical EDA tools (like AutoCAD). This output is what you get from the File/Plot menu in pcbnew.
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
layers: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user] List of PCB layers to plot.- Valid keys:
-
description: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes. -
layer: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad. -
suffix: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
-
- Valid keys:
-
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thedxfoutput.- Valid keys:
-
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty. Affected by global options. -
plot_sheet_reference: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result Thepcb_printoutput can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs. -
custom_reports: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.- Valid keys:
-
content: [string=''] Content for the report. Use${basename} for the project name without extension. Use $ {filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER. -
output: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
-
- Valid keys:
-
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
drill_marks: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale). -
edge_cut_extension: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot. -
exclude_edge_layer: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer. -
exclude_pads_from_silkscreen: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only). -
force_plot_invisible_refs_vals: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible. -
inner_extension_pattern: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers. The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number. Example '.g%n'. -
metric_units: [boolean=false] Use mm instead of inches. -
plot_footprint_refs: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references. -
plot_footprint_values: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values. -
polygon_mode: [boolean=true] Plot using the contour, instead of the center line. -
sketch_plot: [boolean=false] Don't fill objects, just draw the outline. -
tent_vias: [boolean=true] Cover the vias. -
uppercase_extensions: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions. -
use_aux_axis_as_origin: [boolean=false] Use the auxiliary axis as origin for coordinates. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
Excellon drill format
- Type:
excellon - Description: This is the main format for the drilling machine. You can create a map file for documentation purposes. This output is what you get from the 'File/Fabrication output/Drill Files' menu in pcbnew.
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for theexcellonoutput.- Valid keys:
-
metric_units: [boolean=true] Use metric units instead of inches. -
mirror_y_axis: [boolean=false] Invert the Y axis. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] name for the drill file, KiCad defaults if empty (%i='PTH_drill'). Affected by global options. -
pth_and_npth_single_file: [boolean=true] Generate one file for both, plated holes and non-plated holes, instead of two separated files. -
left_digits: [number=0] number of digits for integer part of coordinates (0 is auto). -
map: [dict|string] [hpgl,ps,gerber,dxf,svg,pdf] Format for a graphical drill map. Not generated unless a format is specified.- Valid keys:
-
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the map file, KiCad defaults if empty (%i='PTH_drill_map'). Affected by global options. -
type: [string='pdf'] [hpgl,ps,gerber,dxf,svg,pdf] Format for a graphical drill map.
-
- Valid keys:
-
minimal_header: [boolean=false] Use a minimal header in the file. -
npth_id: [string] Force this replacement for %i when generating NPTH files. -
pth_id: [string] Force this replacement for %i when generating PTH and unified files. -
report: [dict|string] Name of the drill report. Not generated unless a name is specified.- Valid keys:
-
filename: [string=''] Name of the drill report. Not generated unless a name is specified. (%i='drill_report' %x='txt').
-
- Valid keys:
-
right_digits: [number=0] number of digits for mantissa part of coordinates (0 is auto). -
route_mode_for_oval_holes: [boolean=true] Use route command for oval holes (G00), otherwise use G85. -
use_aux_axis_as_origin: [boolean=false] Use the auxiliary axis as origin for coordinates. -
zeros_format: [string='DECIMAL_FORMAT'] [DECIMAL_FORMAT,SUPPRESS_LEADING,SUPPRESS_TRAILING,KEEP_ZEROS] How to handle the zeros.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
GenCAD
- Type:
gencad - Description: Exports the PCB in GENCAD format. This format is interpreted by some CADCAM software and helps certain manufacturers
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thegencadoutput.- Valid keys:
-
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=gencad, %x=cad). Affected by global options. -
aux_origin: [boolean=false] Use auxiliary axis as origin. -
flip_bottom_padstacks: [boolean=false] Flip bottom footprint padstacks. -
no_reuse_shapes: [boolean=false] Generate a new shape for each footprint instance (Do not reuse shapes). -
save_origin: [boolean=false] Save the origin coordinates in the file. -
unique_pin_names: [boolean=false] Generate unique pin names.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
Gerber drill format
- Type:
gerb_drill - Description: This is the information for the drilling machine in gerber format. You can create a map file for documentation purposes. This output is what you get from the 'File/Fabrication output/Drill Files' menu in pcbnew.
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thegerb_drilloutput.- Valid keys:
-
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] name for the drill file, KiCad defaults if empty (%i='PTH_drill'). Affected by global options. -
map: [dict|string] [hpgl,ps,gerber,dxf,svg,pdf] Format for a graphical drill map. Not generated unless a format is specified.- Valid keys:
-
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the map file, KiCad defaults if empty (%i='PTH_drill_map'). Affected by global options. -
type: [string='pdf'] [hpgl,ps,gerber,dxf,svg,pdf] Format for a graphical drill map.
-
- Valid keys:
-
npth_id: [string] Force this replacement for %i when generating NPTH files. -
pth_id: [string] Force this replacement for %i when generating PTH and unified files. -
report: [dict|string] Name of the drill report. Not generated unless a name is specified.- Valid keys:
-
filename: [string=''] Name of the drill report. Not generated unless a name is specified. (%i='drill_report' %x='txt').
-
- Valid keys:
-
use_aux_axis_as_origin: [boolean=false] Use the auxiliary axis as origin for coordinates.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
Gerber format
- Type:
gerber - Description: This is the main fabrication format for the PCB. This output is what you get from the File/Plot menu in pcbnew.
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
layers: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user] List of PCB layers to plot.- Valid keys:
-
description: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes. -
layer: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad. -
suffix: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
-
- Valid keys:
-
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thegerberoutput.- Valid keys:
-
create_gerber_job_file: [boolean=true] Creates a file with information about all the generated gerbers. You can use it in gerbview to load all gerbers at once. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty. Affected by global options. -
plot_sheet_reference: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result Thepcb_printoutput can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs. -
subtract_mask_from_silk: [boolean=false] Subtract the solder mask from the silk screen. -
use_gerber_net_attributes: [boolean=true] Include netlist metadata. -
use_gerber_x2_attributes: [boolean=true] Use the extended X2 format (otherwise use X1 formerly RS-274X). -
use_protel_extensions: [boolean=false] Use legacy Protel file extensions. -
custom_reports: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.- Valid keys:
-
content: [string=''] Content for the report. Use${basename} for the project name without extension. Use $ {filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER. -
output: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
-
- Valid keys:
-
disable_aperture_macros: [boolean=false] Disable aperture macros (workaround for buggy CAM software) (KiCad 6). -
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
edge_cut_extension: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot. -
exclude_edge_layer: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer. -
exclude_pads_from_silkscreen: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only). -
force_plot_invisible_refs_vals: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible. -
gerber_job_file: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the gerber job file (%i='job', %x='gbrjob'). Affected by global options. -
gerber_precision: [number=4.6] This the gerber coordinate format, can be 4.5 or 4.6. -
inner_extension_pattern: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers. The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number. Example '.g%n'. -
line_width: [number=0.1] [0.02,2] Line_width for objects without width [mm] (KiCad 5). -
plot_footprint_refs: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references. -
plot_footprint_values: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values. -
tent_vias: [boolean=true] Cover the vias. -
uppercase_extensions: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions. -
use_aux_axis_as_origin: [boolean=false] Use the auxiliary axis as origin for coordinates. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
HPGL (Hewlett & Packard Graphics Language)
- Type:
hpgl - Description: Exports the PCB for plotters and laser printers. This output is what you get from the File/Plot menu in pcbnew.
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
layers: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user] List of PCB layers to plot.- Valid keys:
-
description: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes. -
layer: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad. -
suffix: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
-
- Valid keys:
-
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thehpgloutput.- Valid keys:
-
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty. Affected by global options. -
plot_sheet_reference: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result Thepcb_printoutput can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs. -
custom_reports: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.- Valid keys:
-
content: [string=''] Content for the report. Use${basename} for the project name without extension. Use $ {filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER. -
output: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
-
- Valid keys:
-
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
drill_marks: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale). -
edge_cut_extension: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot. -
exclude_edge_layer: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer. -
exclude_pads_from_silkscreen: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only). -
force_plot_invisible_refs_vals: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible. -
inner_extension_pattern: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers. The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number. Example '.g%n'. -
mirror_plot: [boolean=false] Plot mirrored. -
pen_number: [number=1] [1,16] Pen number. -
pen_speed: [number=20] [1,99] Pen speed. -
pen_width: [number=15] [0,100] Pen diameter in MILS, useful to fill areas. However, it is in mm in HPGL files. -
plot_footprint_refs: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references. -
plot_footprint_values: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values. -
scaling: [number=0] Scale factor (0 means autoscaling). -
sketch_plot: [boolean=false] Don't fill objects, just draw the outline. -
tent_vias: [boolean=true] Cover the vias. -
uppercase_extensions: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
IBoM (Interactive HTML BoM)
- Type:
ibom - Description: Generates an interactive web page useful to identify the position of the components in the PCB. For more information: https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/InteractiveHtmlBom This output is what you get from the InteractiveHtmlBom plug-in (pcbnew).
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for theibomoutput.- Valid keys:
-
board_rotation: [number=0] Board rotation in degrees (-180 to 180). Will be rounded to multiple of 5. -
bom_view: [string='left-right'] [bom-only,left-right,top-bottom] Default BOM view. -
extra_fields: [string=''] Comma separated list of extra fields to pull from netlist or xml file. Using 'X,Y' is a shortcut forshow_fieldsandgroup_fieldswith values 'Value,Footprint,X,Y'. -
include_tracks: [boolean=false] Include track/zone information in output. F.Cu and B.Cu layers only. -
layer_view: [string='FB'] [F,FB,B] Default layer view. -
normalize_field_case: [boolean=false] Normalize extra field name case. E.g. 'MPN' and 'mpn' will be considered the same field. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output, use '' to use the IBoM filename (%i=ibom, %x=html). Affected by global options. -
show_fields: [string=''] Comma separated list of fields to show in the BOM. Value and Footprint are displayed when nothing is specified. -
blacklist: [string=''] List of comma separated blacklisted components or prefixes with . E.g. 'X1,MH'. IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters. -
blacklist_empty_val: [boolean=false] Blacklist components with empty value. IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters. -
checkboxes: [string='Sourced,Placed'] Comma separated list of checkbox columns. -
dark_mode: [boolean=false] Default to dark mode. -
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. Avoid using it in conjunction with IBoM native filtering options. -
dnp_field: [string=''] Name of the extra field that indicates do not populate status. Components with this field not empty will be blacklisted. IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters. -
extra_data_file: [string=''] Path to netlist or xml file. You can use '%F.xml' to avoid specifying the project name. Leave it blank for most uses, data will be extracted from the PCB. -
group_fields: [string=''] Comma separated list of fields that components will be grouped by. Value and Footprint are used when nothing is specified. -
hide_pads: [boolean=false] Hide footprint pads by default. -
hide_silkscreen: [boolean=false] Hide silkscreen by default. -
highlight_pin1: [boolean=false] Highlight pin1 by default. -
include_nets: [boolean=false] Include netlist information in output.. -
name_format: [string='ibom'] Output file name format supports substitutions: %f : original pcb file name without extension. %p : pcb/project title from pcb metadata. %c : company from pcb metadata. %r : revision from pcb metadata. %d : pcb date from metadata if available, file modification date otherwise. %D : bom generation date. %T : bom generation time. Extension .html will be added automatically. Note that this name is used only when output is ''. - netlist_file: Alias for extra_data_file.
-
no_blacklist_virtual: [boolean=false] Do not blacklist virtual components. IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters. -
no_compression: [boolean=false] Disable compression of pcb data. -
no_redraw_on_drag: [boolean=false] Do not redraw pcb on drag by default. -
show_fabrication: [boolean=false] Show fabrication layer by default. -
sort_order: [string='C,R,L,D,U,Y,X,F,SW,A,,HS,CNN,J,P,NT,MH'] Default sort order for components. Must contain '' once. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply. Avoid using it in conjunction with IBoM native filtering options. -
variant_field: [string=''] Name of the extra field that stores board variant for component. IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters. -
variants_blacklist: [string=''] List of board variants to exclude from the BOM. IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters. -
variants_whitelist: [string=''] List of board variants to include in the BOM. IBoM option, avoid using in conjunction with KiBot variants/filters.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
KiBoM (KiCad Bill of Materials)
- Type:
kibom - Description: Used to generate the BoM in HTML or CSV format using the KiBoM plug-in.
For more information: https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiBoM
Note that this output is provided as a compatibility tool.
We recommend using the
bomoutput instead. This output is what you get from the 'Tools/Generate Bill of Materials' menu in eeschema. - Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thekibomoutput.- Valid keys:
-
format: [string='HTML'] [HTML,CSV,XML,XLSX] Format for the BoM. -
number: [number=1] Number of boards to build (components multiplier). -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=bom). Affected by global options. -
conf: [string|dict] BoM configuration file, relative to PCB. Environment variables and ~ allowed. You can also define the configuration here, will be stored inconfig.kibom.ini.- Valid keys:
-
columns: [list(dict)|list(string)] List of columns to display. Can be just the name of the field.- Valid keys:
-
field: [string=''] Name of the field to use for this column. -
name: [string=''] Name to display in the header. The field is used when empty. -
join: [list(string)|string=''] List of fields to join to this column.
-
- Valid keys:
-
fit_field: [string='Config'] Field name used to determine if a particular part is to be fitted (also DNC and variants). -
group_fields: [list(string)] List of fields used for sorting individual components into groups. Components which match (comparing all fields) will be grouped together. Field names are case-insensitive. If empty: ['Part', 'Part Lib', 'Value', 'Footprint', 'Footprint Lib'] is used. -
ignore_dnf: [boolean=true] Exclude DNF (Do Not Fit) components. -
number_rows: [boolean=true] First column is the row number. -
component_aliases: [list(list(string))] A series of values which are considered to be equivalent for the part name. Each entry is a list of equivalen names. Example: ['c', 'c_small', 'cap' ] will ensure the equivalent capacitor symbols can be grouped together. If empty the following aliases are used: - ['r', 'r_small', 'res', 'resistor'] - ['l', 'l_small', 'inductor'] - ['c', 'c_small', 'cap', 'capacitor'] - ['sw', 'switch'] - ['zener', 'zenersmall'] - ['d', 'diode', 'd_small']. -
datasheet_as_link: [string=''] Column with links to the datasheet (HTML only). -
digikey_link: [string|list(string)=''] Column/s containing Digi-Key part numbers, will be linked to web page (HTML only). -
exclude_any: [list(dict)] A series of regular expressions used to exclude parts. If a component matches ANY of these, it will be excluded. Column names are case-insensitive. If empty the following list is used: - column: References regex: '^TP[0-9]*' - column: References regex: '^FID' - column: Part regex: 'mount.*hole' - column: Part regex: 'solder.*bridge' - column: Part regex: 'test.*point' - column: Footprint regex 'test.*point' - column: Footprint regex: 'mount.*hole' - column: Footprint regex: 'fiducial'.- Valid keys:
-
column: [string=''] Name of the column to apply the regular expression. - field: Alias for column.
-
regex: [string=''] Regular expression to match. - regexp: Alias for regex.
-
- Valid keys:
-
group_connectors: [boolean=true] Connectors with the same footprints will be grouped together, independent of the name of the connector. -
hide_headers: [boolean=false] Hide column headers. -
hide_pcb_info: [boolean=false] Hide project information. -
html_generate_dnf: [boolean=true] Generate a separated section for DNF (Do Not Fit) components (HTML only). -
include_only: [list(dict)] A series of regular expressions used to select included parts. If there are any regex defined here, only components that match against ANY of them will be included. Column names are case-insensitive. If empty all the components are included.- Valid keys:
-
column: [string=''] Name of the column to apply the regular expression. - field: Alias for column.
-
regex: [string=''] Regular expression to match. - regexp: Alias for regex.
-
- Valid keys:
-
merge_blank_fields: [boolean=true] Component groups with blank fields will be merged into the most compatible group, where possible. -
ref_separator: [string=' '] Separator used for the list of references. -
test_regex: [boolean=true] Each component group will be tested against a number of regular-expressions (see ``).. -
use_alt: [boolean=false] Print grouped references in the alternate compressed style eg: R1-R7,R18.
-
- Valid keys:
-
separator: [string=','] CSV Separator. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant(s), used to determine which components are output to the BoM. To specify multiple variants, with a BOM file exported for each variant, separate variants with the ';' (semicolon) character. This isn't related to the KiBot concept of variants.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
KiCost (KiCad Cost calculator)
- Type:
kicost - Description: Generates a spreadsheet containing components costs. For more information: https://github.com/INTI-CMNB/KiCost This output is what you get from the KiCost plug-in (eeschema).
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thekicostoutput.- Valid keys:
- board_qty: Alias for number.
-
currency: [string|list(string)=USD] Currency priority. Use ISO4217 codes (i.e. USD, EUR). -
distributors: [string|list(string)] Include this distributors list. Default is all the available. -
no_distributors: [string|list(string)] Exclude this distributors list. They are removed after computingdistributors. -
no_price: [boolean=false] Do not look for components price. For testing purposes. -
number: [number=100] Number of boards to build (components multiplier). -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=kicost, %x=xlsx). Affected by global options. -
aggregate: [list(dict)] Add components from other projects.- Valid keys:
- board_qty: Alias for number.
-
file: [string=''] Name of the XML to aggregate. -
number: [number=100] Number of boards to build (components multiplier). -
variant: [string=' '] Variant for this project.
- Valid keys:
-
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. Don't use thekicost_variantwhen using internal variants/filters. -
fields: [string|list(string)] List of fields to be added to the global data section. -
group_fields: [string|list(string)] List of fields that can be different for a group. Parts with differences in these fields are grouped together, but displayed individually. -
ignore_fields: [string|list(string)] List of fields to be ignored. -
kicost_variant: [string=''] Regular expression to match the variant field (KiCost option, not internal variants). -
no_collapse: [boolean=false] Do not collapse the part references (collapse=R1-R4). -
show_cat_url: [boolean=false] Include the catalogue links in the catalogue code. -
split_extra_fields: [string|list(string)] Declare part fields to include in multipart split process. -
translate_fields: [list(dict)] Fields to rename (KiCost option, not internal filters).- Valid keys:
-
field: [string=''] Name of the field to rename. -
name: [string=''] New name.
-
- Valid keys:
-
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply. Don't use thekicost_variantwhen using internal variants/filters.
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
Navigate Results
- Type:
navigate_results - Description: Generates a web page to navigate the generated outputs
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thenavigate_resultsoutput.- Valid keys:
-
link_from_root: [string=''] The name of a file to create at the main output directory linking to the home page. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=html, %x=navigate). Affected by global options.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=10] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
Netlist
- Type:
netlist - Description: Generates the list of connections for the project. The netlist can be generated in the classic format and in IPC-D-356 format, useful for board testing
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thenetlistoutput.- Valid keys:
-
format: [string='classic'] [classic,ipc] Theclassicformat is the KiCad internal format, and is generated from the schematic. Theipcformat is the IPC-D-356 format, useful for PCB testing, is generated from the PCB. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=netlist/IPC-D-356, %x=net/d356). Affected by global options.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
PCB Print
- Type:
pcb_print - Description: Prints the PCB using a mechanism that is more flexible than
pdf_pcb_printandsvg_pcb_print. Supports PDF, SVG, PNG, EPS and PS formats. KiCad 5: including the frame is slow. KiCad 6: for custom frames use theenable_ki6_frame_fix, is slow. - Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thepcb_printoutput.- Valid keys:
-
color_theme: [string='_builtin_classic'] Selects the color theme. Only applies to KiCad 6. To use the KiCad 6 default colors select_builtin_default. Usually user colors are stored asuser, but you can give it another name. -
force_edge_cuts: [boolean=false] Add theEdge.Cutsto all the pages. -
format: [string='PDF'] [PDF,SVG,PNG,EPS,PS] Format for the output file/s. Note that for PS you needghostscriptwhich isn't part of the default docker images. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=assembly, %x=pdf)/(%i=assembly_page_NN, %x=svg). Affected by global options. - output_name: Alias for output.
-
pages: [list(dict)] List of pages to include in the output document. Each page contains one or more layers of the PCB.- Valid keys:
-
layers: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] List of layers printed in this page. Order is important, the last goes on top.- Valid keys:
-
color: [string=''] Color used for this layer. -
description: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes. -
force_plot_invisible_refs_vals: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible. -
layer: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad. -
plot_footprint_refs: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references. -
plot_footprint_values: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values. -
suffix: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
-
- Valid keys:
-
scaling: [number=1.0] Scale factor (0 means autoscaling). -
sort_layers: [boolean=false] Try to sort the layers in the same order that uses KiCad for printing. -
colored_holes: [boolean=true] Change the drill holes to be colored instead of white. -
exclude_pads_from_silkscreen: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only). -
holes_color: [string='#000000'] Color used for the holes whencolored_holesis enabled. -
line_width: [number=0.1] [0.02,2] For objects without width [mm] (KiCad 5). -
mirror: [boolean=false] Print mirrored (X axis inverted). -
monochrome: [boolean=false] Print in gray scale. -
negative_plot: [boolean=false] Invert black and white. Only useful for a single layer. -
sheet: [string='Assembly'] Text to use for thesheetin the title block. -
sheet_reference_color: [string=''] Color to use for the frame and title block. -
tent_vias: [boolean=true] Cover the vias. -
title: [string=''] Text used to replace the sheet title. %VALUE expansions are allowed. If it starts with+the text is concatenated.
-
- Valid keys:
-
plot_sheet_reference: [boolean=true] Include the title-block (worksheet, frame, etc.). -
scaling: [number=1.0] Default scale factor (0 means autoscaling). -
add_background: [boolean=false] Add a background to the pages, seebackground_color. -
background_color: [string='#FFFFFF'] Color for the background whenadd_backgroundis enabled. -
background_image: [string=''] Background image, must be an SVG, only whenadd_backgroundis enabled. -
blind_via_color: [string=''] Color used for blind/buriedcolored_vias. -
colored_pads: [boolean=true] Plot through-hole in a different color. Like KiCad GUI does. -
colored_vias: [boolean=true] Plot vias in a different color. Like KiCad GUI does. -
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
drill_marks: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale). -
frame_plot_mechanism: [string='internal'] [gui,internal,plot] Plotting the frame from Python is problematic. This option selects a workaround strategy. gui: uses KiCad GUI to do it. Is slow but you get the correct frame. But it can't keep track of page numbers. internal: KiBot loads the.kicad_wksand does the drawing work. Best option, but some details are different from what the GUI generates. plot: uses KiCad Python API. Only available for KiCad 6. You get the default frame and some substitutions doesn't work. -
hide_excluded: [boolean=false] Hide components in the Fab layer that are marked as excluded by a variant. -
keep_temporal_files: [boolean=false] Store the temporal page and layer files in the output dir and don't delete them. -
micro_via_color: [string=''] Color used for microcolored_vias. -
pad_color: [string=''] Color used forcolored_pads. -
png_width: [number=1280] Width of the PNG in pixels. -
realistic_solder_mask: [boolean=true] Try to draw the solder mask as a real solder mask, not the negative used for fabrication. In order to get a good looking select a color with transparency, i.e. '#14332440'. PcbDraw must be installed in order to use this option. -
sheet_reference_layout: [string=''] Worksheet file (.kicad_wks) to use. Leave empty to use the one specified in the project. -
title: [string=''] Text used to replace the sheet title. %VALUE expansions are allowed. If it starts with+the text is concatenated. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply. -
via_color: [string=''] Color used for through-holecolored_vias.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
PcbDraw - Beautiful 2D PCB render
- Type:
pcbdraw - Description: Exports the PCB as a 2D model (SVG, PNG or JPG). Uses configurable colors. Can also render the components if the 2D models are available
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thepcbdrawoutput.- Valid keys:
-
bottom: [boolean=false] Render the bottom side of the board (default is top side). -
format: [string='svg'] [svg,png,jpg] Output format. Only used if nooutputis specified. -
mirror: [boolean=false] Mirror the board. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the generated file. Affected by global options. -
show_components: [list(string)|string=none] [none,all] List of components to draw, can be also a string for none or all. The default is none. -
style: [string|dict] PCB style (colors). An internal name, the name of a JSON file or the style options.- Valid keys:
-
board: [string='#208b47'] Color for the board without copper (covered by solder mask). -
clad: [string='#cabb3e'] Color for the PCB core (not covered by solder mask). -
copper: [string='#285e3a'] Color for the copper zones (covered by solder mask). -
outline: [string='#000000'] Color for the outline. -
pads: [string='#8b898c'] Color for the exposed pads (metal finish). -
silk: [string='#d5dce4'] Color for the silk screen. -
highlight_on_top: [boolean=false] Highlight over the component (not under). -
highlight_padding: [number=1.5] [0,1000] how much the highlight extends around the component [mm]. -
highlight_style: [string='stroke:none;fill:#ff0000;opacity:0.5;'] SVG code for the highlight style. -
vcut: [string='#bf2600'] Color for the V-CUTS.
-
- Valid keys:
-
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
dpi: [number=300] [10,1200] Dots per inch (resolution) of the generated image. -
highlight: [list(string)=[]] List of components to highlight. -
libs: [list(string)=[]] List of libraries. -
no_drillholes: [boolean=false] Do not make holes transparent. -
placeholder: [boolean=false] Show placeholder for missing components. -
remap: [dict|None] Replacements for PCB references using components (lib:component). -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply. -
vcuts: [boolean=false] Render V-CUTS on the Cmts.User layer. -
warnings: [string='visible'] [visible,all,none] Using visible only the warnings about components in the visible side are generated.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
PDF (Portable Document Format)
- Type:
pdf - Description: Exports the PCB to the most common exchange format. Suitable for printing.
Note that this output isn't the best for documating your project.
This output is what you get from the File/Plot menu in pcbnew.
The
pcb_printis usually a better alternative. - Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
layers: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user] List of PCB layers to plot.- Valid keys:
-
description: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes. -
layer: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad. -
suffix: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
-
- Valid keys:
-
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thepdfoutput.- Valid keys:
-
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty. Affected by global options. -
plot_sheet_reference: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result Thepcb_printoutput can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs. -
custom_reports: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.- Valid keys:
-
content: [string=''] Content for the report. Use${basename} for the project name without extension. Use $ {filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER. -
output: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
-
- Valid keys:
-
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
drill_marks: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale). -
edge_cut_extension: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot. -
exclude_edge_layer: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer. -
exclude_pads_from_silkscreen: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only). -
force_plot_invisible_refs_vals: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible. -
inner_extension_pattern: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers. The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number. Example '.g%n'. -
line_width: [number=0.1] [0.02,2] For objects without width [mm] (KiCad 5). -
mirror_plot: [boolean=false] Plot mirrored. -
negative_plot: [boolean=false] Invert black and white. -
plot_footprint_refs: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references. -
plot_footprint_values: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values. -
tent_vias: [boolean=true] Cover the vias. -
uppercase_extensions: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
-
- Valid keys:
-
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty. Affected by global options. -
plot_sheet_reference: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result Thepcb_printoutput can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs. -
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
custom_reports: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.- Valid keys:
-
content: [string=''] Content for the report. Use${basename} for the project name without extension. Use $ {filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER. -
output: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
-
- Valid keys:
-
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
drill_marks: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale). -
edge_cut_extension: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot. -
exclude_edge_layer: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer. -
exclude_pads_from_silkscreen: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only). -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
force_plot_invisible_refs_vals: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible. -
inner_extension_pattern: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers. The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number. Example '.g%n'. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
plot_footprint_refs: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references. -
plot_footprint_values: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested. -
tent_vias: [boolean=true] Cover the vias. -
uppercase_extensions: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
-
PDF PCB Print (Portable Document Format)
- Type:
pdf_pcb_print - Description: Exports the PCB to the most common exchange format. Suitable for printing.
This is the main format to document your PCB.
This output is what you get from the 'File/Print' menu in pcbnew.
The
pcb_printis usually a better alternative. - Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
layers: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user] List of PCB layers to include in the PDF.- Valid keys:
-
description: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes. -
layer: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad. -
suffix: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
-
- Valid keys:
-
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thepdf_pcb_printoutput.- Valid keys:
-
plot_sheet_reference: [boolean=true] Include the title-block. -
scaling: [number=1.0] Scale factor (0 means autoscaling). You should disableplot_sheet_referencewhen using it. -
separated: [boolean=false] Print layers in separated pages. -
color_theme: [string='_builtin_classic'] Selects the color theme. Onlyu applies to KiCad 6. To use the KiCad 6 default colors select_builtin_default. Usually user colors are stored asuser, but you can give it another name. -
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
drill_marks: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale). -
force_edge_cuts: [boolean=true] Only useful for KiCad 6 when printing in one page, you can disable the edge here. KiCad 5 forces it by default, and you can't control it from config files. Same for KiCad 6 when printing to separated pages. -
hide_excluded: [boolean=false] Hide components in the Fab layer that are marked as excluded by a variant. -
mirror: [boolean=false] Print mirrored (X axis inverted). ONLY for KiCad 6. -
monochrome: [boolean=false] Print in black and white. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output PDF (%i=layers, %x=pdf). Affected by global options. - output_name: Alias for output.
-
title: [string=''] Text used to replace the sheet title. %VALUE expansions are allowed. If it starts with+the text is concatenated. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
PDF Schematic Print (Portable Document Format)
- Type:
pdf_sch_print - Description: Exports the PCB to the most common exchange format. Suitable for printing. This is the main format to document your schematic. This output is what you get from the 'File/Print' menu in eeschema.
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thepdf_sch_printoutput.- Valid keys:
-
frame: [boolean=true] Include the frame and title block. -
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
monochrome: [boolean=false] Generate a monochromatic PDF. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output PDF (%i=schematic, %x=pdf). Affected by global options. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply. Not fitted components are crossed.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
PDF joiner
- Type:
pdfunite - Description: Generates a new PDF from other outputs.
This is just a PDF joiner, using
pdfunitefrom Poppler Utils. - Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thepdfuniteoutput.- Valid keys:
-
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the generated PDF (%i=name of the output %x=pdf). Affected by global options. -
outputs: [list(dict)] Which files will be included.- Valid keys:
-
from_output: [string=''] Collect files from the selected output. When used thesourceoption is ignored. -
source: [string='*.pdf'] File names to add, wildcards allowed. Use ** for recursive match. By default this pattern is applied to the output dir specified with-dcommand line option. See thefrom_cwdoption. -
filter: [string='.*.pdf'] A regular expression that source files must match. -
from_cwd: [boolean=false] Use the current working directory instead of the dir specified by-d.
-
- Valid keys:
-
use_external_command: [boolean=false] Use thepdfunitetool instead of PyPDF2 Python module.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
Pick & place
- Type:
position - Description: Generates the file with position information for the PCB components, used by the pick and place machine. This output is what you get from the 'File/Fabrication output/Footprint position (.pos) file' menu in pcbnew.
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thepositionoutput.- Valid keys:
-
format: [string='ASCII'] [ASCII,CSV] Format for the position file. -
only_smd: [boolean=true] Only include the surface mount components. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name (%i='top_pos'|'bottom_pos'|'both_pos', %x='pos'|'csv'). Affected by global options. -
separate_files_for_front_and_back: [boolean=true] Generate two separated files, one for the top and another for the bottom. -
units: [string='millimeters'] [millimeters,inches,mils] Units used for the positions. Affected by global options. -
bottom_negative_x: [boolean=false] Use negative X coordinates for footprints on bottom layer. -
columns: [list(dict)|list(string)] Which columns are included in the output.- Valid keys:
-
id: [string=''] [Ref,Val,Package,PosX,PosY,Rot,Side] Internal name. -
name: [string=''] Name to use in the output file. The id is used when empty.
-
- Valid keys:
-
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
include_virtual: [boolean=false] Include virtual components. For special purposes, not pick & place. -
use_aux_axis_as_origin: [boolean=true] Use the auxiliary axis as origin for coordinates (KiCad default). -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
PS (Postscript)
- Type:
ps - Description: Exports the PCB to a format suitable for printing.
This output is what you get from the File/Plot menu in pcbnew.
The
pcb_printis usually a better alternative. - Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
layers: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user] List of PCB layers to plot.- Valid keys:
-
description: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes. -
layer: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad. -
suffix: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
-
- Valid keys:
-
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thepsoutput.- Valid keys:
-
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty. Affected by global options. -
plot_sheet_reference: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result Thepcb_printoutput can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs. -
scaling: [number=1] Scale factor (0 means autoscaling). -
a4_output: [boolean=true] Force A4 paper size. -
custom_reports: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.- Valid keys:
-
content: [string=''] Content for the report. Use${basename} for the project name without extension. Use $ {filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER. -
output: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
-
- Valid keys:
-
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
drill_marks: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale). -
edge_cut_extension: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot. -
exclude_edge_layer: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer. -
exclude_pads_from_silkscreen: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only). -
force_plot_invisible_refs_vals: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible. -
inner_extension_pattern: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers. The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number. Example '.g%n'. -
line_width: [number=0.15] [0.02,2] For objects without width [mm] (KiCad 5). -
mirror_plot: [boolean=false] Plot mirrored. -
negative_plot: [boolean=false] Invert black and white. -
plot_footprint_refs: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references. -
plot_footprint_values: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values. -
scale_adjust_x: [number=1.0] Fine grain adjust for the X scale (floating point multiplier). -
scale_adjust_y: [number=1.0] Fine grain adjust for the Y scale (floating point multiplier). -
sketch_plot: [boolean=false] Don't fill objects, just draw the outline. -
tent_vias: [boolean=true] Cover the vias. -
uppercase_extensions: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply. -
width_adjust: [number=0] This width factor is intended to compensate PS printers/plotters that do not strictly obey line width settings. Only used to plot pads and tracks.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
QR_Lib
- Type:
qr_lib - Description: Generates a QR code symbol and footprint.
This output creates a library containing a symbol and footprint for a QR code.
To refresh the generated symbols and footprints use the
update_qrpreflight. The workflow is as follows: - Create the symbol and footprints using this output. - Use them in your schematic and PCB. - To keep them updated add theupdate_qrpreflight - Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for theboardviewoutput.- Valid keys:
-
lib: [string='QR'] Short name for the library. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output (%i=qr, %x=lib). Affected by global options. -
qrs: [list(dict)] QR codes to include in the library.- Valid keys:
-
layer: [string='silk'] [silk,copper] Layer for the footprint. -
name: [string='QR'] Name for the symbol/footprint. -
size_pcb: [number=15] Size of the QR footprint. -
size_sch: [number=15] Size of the QR symbol. -
text: [string='%p %r'] Text to encode as QR. -
correction_level: [string='low'] [low,medium,quartile,high] Error correction level. -
pcb_negative: [boolean=false] Generate a negative image for the PCB. -
size_units: [string='millimeters'] [millimeters,inches] Units used for the size.
-
- Valid keys:
-
reference: [string='QR'] The reference prefix. -
use_sch_dir: [boolean=true] Generate the libs relative to the schematic/PCB dir.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=90] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
3D render of the PCB
- Type:
render_3d - Description: Exports the image generated by KiCad's 3D viewer.
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for therender_3doutput.- Valid keys:
-
download: [boolean=true] Downloads missing 3D models from KiCad git. Only applies to models in KISYS3DMOD. -
move_x: [number=0] Steps to move in the X axis, positive is to the right. Just like pressing the right arrow in the 3D viewer. -
move_y: [number=0] Steps to move in the Y axis, positive is up. Just like pressing the up arrow in the 3D viewer. -
no_virtual: [boolean=false] Used to exclude 3D models for components with 'virtual' attribute. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the generated image file (%i='3D_$VIEW' %x='png'). Affected by global options. -
ray_tracing: [boolean=false] Enable the ray tracing. Much better result, but slow, and you'll need to adjustwait_rt. -
rotate_x: [number=0] Steps to rotate around the X axis, positive is clockwise. Each step is currently 10 degrees. Only for KiCad 6. -
rotate_y: [number=0] Steps to rotate around the Y axis, positive is clockwise. Each step is currently 10 degrees. Only for KiCad 6. -
rotate_z: [number=0] Steps to rotate around the Z axis, positive is clockwise. Each step is currently 10 degrees. Only for KiCad 6. -
view: [string='top'] [top,bottom,front,rear,right,left,z,Z,y,Y,x,X] Point of view. -
zoom: [number=0] Zoom steps. Use positive to enlarge, get closer, and negative to reduce. Same result as using the mouse wheel in the 3D viewer. -
background1: [string='#66667F'] First color for the background gradient. -
background2: [string='#CCCCE5'] Second color for the background gradient. -
board: [string='#332B16'] Color for the board without copper or solder mask. -
copper: [string='#8b898c'] Color for the copper. -
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
height: [number=720] Image height (aprox.). -
kicad_3d_url: [string='https://gitlab.com/kicad/libraries/kicad-packages3D/-/raw/master/'] Base URL for the KiCad 3D models. -
no_smd: [boolean=false] Used to exclude 3D models for surface mount components. -
no_tht: [boolean=false] Used to exclude 3D models for through hole components. -
orthographic: [boolean=false] Enable the orthographic projection mode (top view looks flat). -
silk: [string='#d5dce4'] Color for the silk screen. -
solder_mask: [string='#208b47'] Color for the solder mask. -
solder_paste: [string='#808080'] Color for the solder paste. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply. - wait_ray_tracing: Alias for wait_render.
-
wait_render: [number=-600] How many seconds we must wait before capturing the render (ray tracing or normal). Lamentably KiCad can save an unfinished image. Enlarge it if your image looks partially rendered. Use negative values to enable the auto-detect using CPU load. In this case the value is interpreted as a time-out.. -
width: [number=1280] Image width (aprox.).
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
Design report
- Type:
report - Description: Generates a report about the design. Mainly oriented to be sent to the manufacturer or check PCB details.
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thereportoutput.- Valid keys:
-
convert_to: [string='pdf'] Target format for the report conversion. Seedo_convert. -
do_convert: [boolean=false] RunPandocto convert the report. Note that Pandoc must be installed. The conversion is done assuming the report is inconvert_fromformat. The output file will be inconvert_toformat. The available formats depends on thePandocinstallation. In CI/CD environments: thekicad_auto_testdocker image contains it. In Debian/Ubuntu environments: installpandoc,texlive-latex-baseandtexlive-latex-recommended. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name (%i='report', %x='txt'). Affected by global options. -
template: [string='full'] Name for one of the internal templates (full, full_svg, simple) or a custom template file. Environment variables and ~ are allowed. Note: when converting to PDF PanDoc can fail on some Unicode values (usesimple_ASCII). -
convert_from: [string='markdown'] Original format for the report conversion. Current templates aremarkdown. Seedo_convert. -
converted_output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Converted output file name (%i='report', %x=convert_to). Note that the extension should match theconvert_tovalue. Affected by global options. -
eurocircuits_class_target: [string='10F'] Which Eurocircuits class are we aiming at.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
Schematic with variant generator
- Type:
sch_variant - Description: Creates a copy of the schematic with all the filters and variants applied. This copy isn't intended for development. Is just a tweaked version of the original where you can look at the results.
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thesch_variantoutput.- Valid keys:
-
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
STEP (ISO 10303-21 Clear Text Encoding of the Exchange Structure)
- Type:
step - Description: Exports the PCB as a 3D model. This is the most common 3D format for exchange purposes. This output is what you get from the 'File/Export/STEP' menu in pcbnew.
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thestepoutput.- Valid keys:
-
download: [boolean=true] Downloads missing 3D models from KiCad git. Only applies to models in KISYS3DMOD. -
no_virtual: [boolean=false] Used to exclude 3D models for components with 'virtual' attribute. -
origin: [string='grid'] Determines the coordinates origin. Using grid the coordinates are the same as you have in the design sheet. The drill option uses the auxiliary reference defined by the user. You can define any other origin using the format 'X,Y', i.e. '3.2,-10'. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Name for the generated STEP file (%i='3D' %x='step'). Affected by global options. -
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
kicad_3d_url: [string='https://gitlab.com/kicad/libraries/kicad-packages3D/-/raw/master/'] Base URL for the KiCad 3D models. -
metric_units: [boolean=true] Use metric units instead of inches. -
min_distance: [number=-1] The minimum distance between points to treat them as separate ones (-1 is KiCad default: 0.01 mm). -
subst_models: [boolean=true] Substitute STEP or IGS models with the same name in place of VRML models. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics)
- Type:
svg - Description: Exports the PCB to a format suitable for 2D graphics software.
Unlike bitmaps SVG drawings can be scaled without losing resolution.
This output is what you get from the File/Plot menu in pcbnew.
The
pcb_printis usually a better alternative. - Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
layers: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user] List of PCB layers to plot.- Valid keys:
-
description: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes. -
layer: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad. -
suffix: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
-
- Valid keys:
-
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thesvgoutput.- Valid keys:
-
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Output file name, the default KiCad name if empty. Affected by global options. -
plot_sheet_reference: [boolean=false] Include the frame and title block. Only available for KiCad 6 and you get a poor result Thepcb_printoutput can do a better job for PDF, SVG, PS, EPS and PNG outputs. -
custom_reports: [list(dict)] A list of customized reports for the manufacturer.- Valid keys:
-
content: [string=''] Content for the report. Use${basename} for the project name without extension. Use $ {filename(LAYER)} for the file corresponding to LAYER. -
output: [string='Custom_report.txt'] File name for the custom report.
-
- Valid keys:
-
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
drill_marks: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale). -
edge_cut_extension: [string=''] Used to configure the edge cuts layer extension for Protel mode. Include the dot. -
exclude_edge_layer: [boolean=true] Do not include the PCB edge layer. -
exclude_pads_from_silkscreen: [boolean=false] Do not plot the component pads in the silk screen (KiCad 5.x only). -
force_plot_invisible_refs_vals: [boolean=false] Include references and values even when they are marked as invisible. -
inner_extension_pattern: [string=''] Used to change the Protel style extensions for inner layers. The replacement pattern can contain %n for the inner layer number and %N for the layer number. Example '.g%n'. -
line_width: [number=0.25] [0.02,2] For objects without width [mm] (KiCad 5). -
mirror_plot: [boolean=false] Plot mirrored. -
negative_plot: [boolean=false] Invert black and white. -
plot_footprint_refs: [boolean=true] Include the footprint references. -
plot_footprint_values: [boolean=true] Include the footprint values. -
tent_vias: [boolean=true] Cover the vias. -
uppercase_extensions: [boolean=false] Use uppercase names for the extensions. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
SVG PCB Print (Scalable Vector Graphics)
- Type:
svg_pcb_print - Description: Exports the PCB to the scalable vector graphics format.
This output is what you get from the 'File/Print' menu in pcbnew.
The
pcb_printis usually a better alternative. - Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
layers: [list(dict)|list(string)|string] [all,selected,copper,technical,user] List of PCB layers to include in the PDF.- Valid keys:
-
description: [string=''] A description for the layer, for documentation purposes. -
layer: [string=''] Name of the layer. As you see it in KiCad. -
suffix: [string=''] Suffix used in file names related to this layer. Derived from the name if not specified.
-
- Valid keys:
-
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thepdf_pcb_printoutput.- Valid keys:
-
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output SVG (%i=layers, %x=svg). Affected by global options. - output_name: Alias for output.
-
plot_sheet_reference: [boolean=true] Include the title-block. -
scaling: [number=1.0] Scale factor (0 means autoscaling). You should disableplot_sheet_referencewhen using it. -
separated: [boolean=false] Print layers in separated pages. -
color_theme: [string='_builtin_classic'] Selects the color theme. Onlyu applies to KiCad 6. To use the KiCad 6 default colors select_builtin_default. Usually user colors are stored asuser, but you can give it another name. -
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
drill_marks: [string='full'] [none,small,full] What to use to indicate the drill places, can be none, small or full (for real scale). -
enable_ki5_page_fix: [boolean=true] Enable workaround for KiCad 5 bug. -
enable_ki6_page_fix: [boolean=true] Enable workaround for KiCad 6 bug #11033. -
force_edge_cuts: [boolean=true] Only useful for KiCad 6 when printing in one page, you can disable the edge here. KiCad 5 forces it by default, and you can't control it from config files. Same for KiCad 6 when printing to separated pages. -
hide_excluded: [boolean=false] Hide components in the Fab layer that are marked as excluded by a variant. -
mirror: [boolean=false] Print mirrored (X axis inverted). ONLY for KiCad 6. -
monochrome: [boolean=false] Print in black and white. -
title: [string=''] Text used to replace the sheet title. %VALUE expansions are allowed. If it starts with+the text is concatenated. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
SVG Schematic Print
- Type:
svg_sch_print - Description: Exports the PCB. Suitable for printing. This is a format to document your schematic.
- Valid keys:
-
comment: [string=''] A comment for documentation purposes. -
dir: [string='./'] Output directory for the generated files. If it starts with+the rest is concatenated to the default dir. -
name: [string=''] Used to identify this particular output definition. -
options: [dict] Options for thesvg_sch_printoutput.- Valid keys:
-
frame: [boolean=true] Include the frame and title block. -
dnf_filter: [string|list(string)='_none'] Name of the filter to mark components as not fitted. A short-cut to use for simple cases where a variant is an overkill. -
monochrome: [boolean=false] Generate a monochromatic PDF. -
output: [string='%f-%i%I%v.%x'] Filename for the output SVG (%i=schematic, %x=svg). Affected by global options. -
variant: [string=''] Board variant to apply. Not fitted components are crossed.
-
- Valid keys:
-
category: [string|list(string)=''] The category for this output. If not specified an internally defined category is used. Categories looks like file system paths, i.e. PCB/fabrication/gerber. -
disable_run_by_default: [string|boolean] Use it to disable therun_by_defaultstatus of other output. Useful when this output extends another and you don't want to generate the original. Use the boolean true value to disable the output you are extending. -
extends: [string=''] Copy theoptionssection from the indicated output. -
output_id: [string=''] Text to use for the %I expansion content. To differentiate variations of this output. -
priority: [number=50] [0,100] Priority for this output. High priority outputs are created first. Internally we use 10 for low priority, 90 for high priority and 50 for most outputs. -
run_by_default: [boolean=true] When enabled this output will be created when no specific outputs are requested.
-
Some times your project is composed by various boards, other times you are producing various products at the same time. In both cases you would want to consolidate the components acquisition in one operation. Of course you can create individual BoMs for each project in CSV format and then consolidate them using a spreadsheet editor. But KiBot offers another option: you create a BoM for your main project and then aggregate the components from the other projects.
Here is a simple example. Suppose you have three projects: merge_1, merge_2 and merge_3. For the merge_1 project you could use the following output:
kibot:
version: 1
outputs:
- name: 'bom_csv'
comment: "Bill of Materials in CSV format"
type: bom
dir: BoM
options:
use_alt: trueUsing the tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_1.sch from the git repo and storing the above example in m1.kibot.yaml you could run:
src/kibot -c m1.kibot.yaml -e tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_1.sch -d test_mergeAnd get test_merge/BoM/merge_1-bom.csv:
| Row | Description | Part | References | Value | Footprint | Quantity Per PCB | Status | Datasheet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | C1 | 1nF | 1 | ~ | ||
| 2 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | C2 | 10nF | 1 | ~ | ||
| 3 | Resistor | R | R1-R3 | 1k | 3 | ~ |
| Project info: | |
|---|---|
| Schematic: | merge_1 |
| Variant: | default |
| Revision: | |
| Date: | 2021-02-02_12-12-27 |
| KiCad Version: | 5.1.9-73d0e3b20d~88~ubuntu21.04.1 |
| Statistics: | |
| Component Groups: | 3 |
| Component Count: | 5 |
| Fitted Components: | 5 |
| Number of PCBs: | 1 |
| Total Components: | 5 |
This CSV says you have five components groped in three different types. They are one 1 nF capacitor, one 10 nF capacitor and three 1 k resistors. Now lets generate BoMs for the merge_2 example:
src/kibot -c m1.kibot.yaml -e tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_2.sch -d test_mergeWe'll get test_merge/BoM/merge_2-bom.csv:
| Row | Description | Part | References | Value | Footprint | Quantity Per PCB | Status | Datasheet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | C2 | 1nF | 1 | ~ | ||
| 2 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | C1 | 10nF | 1 | ~ | ||
| 3 | Resistor | R | R2-R4 | 1000 | 3 | ~ | ||
| 4 | Resistor | R | R1 | 10k | 1 | ~ |
| Project info: | |
|---|---|
| Schematic: | merge_2 |
| Variant: | default |
| Revision: | |
| Date: | 2021-01-27_10-19-46 |
| KiCad Version: | 5.1.9-73d0e3b20d~88~ubuntu21.04.1 |
| Statistics: | |
| Component Groups: | 4 |
| Component Count: | 6 |
| Fitted Components: | 6 |
| Number of PCBs: | 1 |
| Total Components: | 6 |
In this project we have six components from four different types. They are similar to merge_1 but now we also have a 10 k resistor. We don't need to generate this BoM to consolidate our projects, but is good to know what we have. And now lets generate BoMs for the merge_3 example:
src/kibot -c m1.kibot.yaml -e tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_3.sch -d test_mergeWe'll get test_merge/BoM/merge_3-bom.csv:
| Row | Description | Part | References | Value | Footprint | Quantity Per PCB | Status | Datasheet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Resistor | R | R5 | 1k | 1 | ~ | ||
| 2 | Resistor | R | R1-R4 | 10k | 4 | ~ |
| Project info: | |
|---|---|
| Schematic: | merge_3 |
| Variant: | default |
| Revision: | |
| Date: | 2021-01-27_10-21-29 |
| KiCad Version: | 5.1.9-73d0e3b20d~88~ubuntu21.04.1 |
| Statistics: | |
| Component Groups: | 2 |
| Component Count: | 5 |
| Fitted Components: | 5 |
| Number of PCBs: | 1 |
| Total Components: | 5 |
This time we also have five components, but from two different types. They are one 1 k resistor and four 10 k resistors. Now suppose we want to create 10 boards for merge_1, 20 for merge_2 and 30 for merge_3. We could use the following configuration:
kibot:
version: 1
outputs:
- name: 'bom_csv'
comment: "Bill of Materials in CSV format"
type: bom
dir: BoM
options:
use_alt: true
number: 10
aggregate:
- file: tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_2.sch
number: 20
- file: tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_3.sch
number: 30Save it as m2.kibot.yaml and run:
src/kibot -c m2.kibot.yaml -e tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_1.sch -d test_merge_consolidateThe test_merge_consolidate/BoM/merge_1-bom.csv file will be generated containing:
| Row | Description | Part | References | Value | Footprint | Quantity Per PCB | Build Quantity | Status | Datasheet | Source BoM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | C1 C2 | 1nF | 2 | 30 | ~ | merge_1(1) merge_2(1) | ||
| 2 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | C2 C1 | 10nF | 2 | 30 | ~ | merge_1(1) merge_2(1) | ||
| 3 | Resistor | R | R1-R3 R2-R4 R5 | 1k | 7 | 120 | ~ | merge_1(3) merge_2(3) merge_3(1) | ||
| 4 | Resistor | R | R1 R1-R4 | 10k | 5 | 140 | ~ | merge_2(1) merge_3(4) |
| Project info: | |
|---|---|
| Variant: | default |
| KiCad Version: | 5.1.9-73d0e3b20d~88~ubuntu21.04.1 |
| Global statistics: | |
| Component Groups: | 4 |
| Component Count: | 16 |
| Fitted Components: | 16 |
| Number of PCBs: | 60 |
| Total Components: | 320 |
| Project info: | merge_1 |
| Schematic: | merge_1 |
| Revision: | |
| Date: | 2021-02-02_12-12-27 |
| Company: | Test company |
| Statistics: | merge_1 |
| Component Groups: | 3 |
| Component Count: | 5 |
| Fitted Components: | 5 |
| Number of PCBs: | 10 |
| Total Components: | 50 |
| Project info: | merge_2 |
| Schematic: | merge_2 |
| Revision: | |
| Date: | 2021-01-27_10-19-46 |
| Statistics: | merge_2 |
| Component Groups: | 4 |
| Component Count: | 6 |
| Fitted Components: | 6 |
| Number of PCBs: | 20 |
| Total Components: | 120 |
| Project info: | merge_3 |
| Schematic: | merge_3 |
| Revision: | |
| Date: | 2021-01-27_10-21-29 |
| Statistics: | merge_3 |
| Component Groups: | 2 |
| Component Count: | 5 |
| Fitted Components: | 5 |
| Number of PCBs: | 30 |
| Total Components: | 150 |
You can see that now we have much more stats. They say we have four different types, thirteen for board sets, a total of 60 boards and 250 components. Then we have individual stats for each project. The capacitors are easy to interpret, we have 30 1 nF capacitors merge_1 project has one and merge_2 another. As we have 10 merge_1 and 20 merge_2 boards this is clear. But looking at the 1 k resistors is harder. We have 80, three from merge_1, one from merge_2 and another from merge_3. So we have 103+203+30=120, this is clear, but the BoM says they are R1-R3 R2-R4 R5, which is a little bit confusing. In this simple example is easy to correlate R1-R3 to merge_1, R2-R4 to merge_2 and R5 to merge_1. For bigger projects this gets harder. Lets assign an id to each project, we'll use 'A' for merge_1, 'B' for merge_2 and 'C' for merge_3:
kibot:
version: 1
outputs:
- name: 'bom_csv'
comment: "Bill of Materials in CSV format"
type: bom
dir: BoM
options:
use_alt: true
number: 10
ref_id: 'A:'
aggregate:
- file: tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_2.sch
number: 20
ref_id: 'B:'
- file: tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_3.sch
number: 30
ref_id: 'C:'Now test_merge_consolidate/BoM/merge_1-bom.csv will have the following information:
| Row | Description | Part | References | Value | Footprint | Quantity Per PCB | Build Quantity | Status | Datasheet | Source BoM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | A:C1 B:C2 | 1nF | 2 | 30 | ~ | merge_1(1) merge_2(1) | ||
| 2 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | A:C2 B:C1 | 10nF | 2 | 30 | ~ | merge_1(1) merge_2(1) | ||
| 3 | Resistor | R | A:R1-A:R3 B:R2-B:R4 C:R5 | 1k | 7 | 120 | ~ | merge_1(3) merge_2(3) merge_3(1) | ||
| 4 | Resistor | R | B:R1 C:R1-C:R4 | 10k | 5 | 140 | ~ | merge_2(1) merge_3(4) |
As you can see now we know A has R1-R3, B R2-R4 and for C R5 is the 1k resistor.
If we want to compact the Source BoM column we just need to enable the source_by_id option:
kibot:
version: 1
outputs:
- name: 'bom_csv'
comment: "Bill of Materials in CSV format"
type: bom
dir: BoM
options:
use_alt: true
number: 10
ref_id: 'A:'
source_by_id: true
aggregate:
- file: tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_2.sch
number: 20
ref_id: 'B:'
- file: tests/board_samples/kicad_5/merge_3.sch
number: 30
ref_id: 'C:'And we'll get:
| Row | Description | Part | References | Value | Footprint | Quantity Per PCB | Build Quantity | Status | Datasheet | Source BoM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | A:C1 B:C2 | 1nF | 2 | 30 | ~ | A:(1) B:(1) | ||
| 2 | Unpolarized capacitor | C | A:C2 B:C1 | 10nF | 2 | 30 | ~ | A:(1) B:(1) | ||
| 3 | Resistor | R | A:R1-A:R3 B:R2-B:R4 C:R5 | 1k | 7 | 120 | ~ | A:(3) B:(3) C:(1) | ||
| 4 | Resistor | R | B:R1 C:R1-C:R4 | 10k | 5 | 140 | ~ | B:(1) C:(4) |
In some cases you may want to reuse configuration files. An example of this are the example files that generate gerbers and drill files for various manufacturers (see).
In this case you can create a section named import containing a list of configuration files. Here is an example:
import:
- configs/Elecrow.kibot.yaml
- configs/FusionPCB.kibot.yaml
- configs/JLCPCB.kibot.yaml
- configs/P-Ban.kibot.yaml
- configs/PCBWay.kibot.yamlThis will import all the outputs from the listed files.
If you need to define an output that is similar to another, and you want to avoid copying the options from the former, you can extend an output.
To achieve it just specify the name of the base output in the extends value.
Note that this will use the options of the other output as base, not other data as the comment.
Also note that you can use YAML anchors, but this won't work if you are importing the base output from other file.
Additionally you must be aware that extending an output doesn't disable the base output.
If you need to disable the original output use disable_run_by_default option.
This is a more complex case of the previous Importing outputs from another file. In this case you must use the more general syntax:
import:
- file: FILE_CONTAINING_THE_YAML_DEFINITIONS
outputs: LIST_OF_OUTPUTS
preflights: LIST_OF_PREFLIGHTS
filters: LIST_OF_FILTERS
variants: LIST_OF_VARIANTS
global: LIST_OF_GLOBALSThis syntax is flexible. If you don't define which outputs, filters, variants and/or global all will be imported. So you can just omit them, like this:
import:
- file: FILE_CONTAINING_THE_YAML_DEFINITIONSThe LIST_OF_items can be a YAML list or just one string. Here is an example:
import:
- file: FILE_CONTAINING_THE_YAML_DEFINITIONS
outputs: one_name
filters: ['name1', 'name2']This will import the one_name output and the name1 and name2 filters. As variants is omitted, all variants will be imported.
You can also use the all and none special names, like this:
import:
- file: FILE_CONTAINING_THE_YAML_DEFINITIONS
outputs: all
filters: all
variants: none
global: noneThis will import all outputs and filters, but not variants or globals. Also note that imported globals has more precedence than the ones defined in the same file.
For a quick start just go to the project's dir and run:
kibot --quick-startThis will generate a configuration and generate outputs. If you want to just generate the configuration, and not the outputs, use:
kibot --quick-start --dryIf you need a more exhaustive configuration file try:
kibot --exampleThis will generate a file named example.kibot.yaml containing all the available options and comments about them.
You can use it to create your own configuration file.
If you want to use the layers of a particular PCB in the example use:
kibot -b PCB_FILE --exampleAnd if you want to use the same options selected in the plot dialog use:
kibot -b PCB_FILE -p --exampleIf the current directory contains only one PCB file and only one configuration file (named *.kibot.yaml) you can just call kibot.
No arguments needed.
The tool will figure out which files to use.
If more than one file is found in the current directory kibot will use the first found and issue a warning.
If you need to use other file just tell it explicitly:
kibot -b PCB_FILE.kicad_pcb -c CONFIG.kibot.yamlA simple target can be added to your makefile, so you can just run make pcb_files or integrate into your current build process.
pcb_files:
kibot -b $(PCB) -c $(KIBOT_CFG)If you need to suppress messages use --quiet or -q and if you need to get more information about what's going on use --verbose or -v.
If you want to generate only some of the outputs use:
kibot OUTPUT_1 OUTPUT_2If you want to generate all outputs with some exceptions use:
kibot --invert-sel OUTPUT_1 OUTPUT_2Note that you can use the run_by_default option of the output you want to exclude from the default runs.
If you want to skip the DRC and ERC use:
kibot --skip-pre run_erc,run_drcIf you want to skip all the preflight tasks use:
kibot --skip-pre allAll outputs are generated using the current directory as base. If you want to use another directory as base use:
kibot --out-dir OTHER_PLACEIf you want to list the available outputs defined in the configuration file use:
kibot --listKiBot: KiCad automation tool for documents generation
Usage:
kibot [-b BOARD] [-e SCHEMA] [-c CONFIG] [-d OUT_DIR] [-s PRE]
[-q | -v...] [-C | -i | -n] [-m MKFILE] [-A] [-g DEF] ... [TARGET...]
kibot [-v...] [-b BOARD] [-e SCHEMA] [-c PLOT_CONFIG] --list
kibot [-v...] [-b BOARD] [-d OUT_DIR] [-p | -P] --example
kibot [-v...] [--start PATH] [-d OUT_DIR] [--dry] [-t, --type TYPE]...
--quick-start
kibot [-v...] --help-filters
kibot [-v...] [--markdown|--json] --help-dependencies
kibot [-v...] --help-global-options
kibot [-v...] --help-list-outputs
kibot [-v...] --help-output=HELP_OUTPUT
kibot [-v...] --help-outputs
kibot [-v...] --help-preflights
kibot -h | --help
kibot --version
Arguments:
TARGET Outputs to generate, default is all
Options:
-A, --no-auto-download Disable dependencies auto-download
-b BOARD, --board-file BOARD The PCB .kicad-pcb board file
-c CONFIG, --plot-config CONFIG The plotting config file to use
-C, --cli-order Generate outputs using the indicated order
-d OUT_DIR, --out-dir OUT_DIR The output directory [default: .]
-e SCHEMA, --schematic SCHEMA The schematic file (.sch)
-g DEF, --global-redef DEF Overwrite a global value (VAR=VAL)
-i, --invert-sel Generate the outputs not listed as targets
-l, --list List available outputs (in the config file)
-m MKFILE, --makefile MKFILE Generate a Makefile (no targets created)
-n, --no-priority Don't sort targets by priority
-p, --copy-options Copy plot options from the PCB file
-P, --copy-and-expand As -p but expand the list of layers
-q, --quiet Remove information logs
-s PRE, --skip-pre PRE Skip preflights, comma separated or `all`
-v, --verbose Show debugging information
-V, --version Show program's version number and exit
-x, --example Create a template configuration file
Quick start options:
--quick-start Generates demo config files and their outputs
--dry Just generate the config files
--start PATH Starting point for the search [default: .]
-t, --type TYPE Generate examples only for the indicated type/s
Help options:
-h, --help Show this help message and exit
--help-dependencies List dependencies in human readable format
--help-filters List supported filters and details
--help-global-options List supported global variables
--help-list-outputs List supported outputs
--help-output HELP_OUTPUT Help for this particular output
--help-outputs List supported outputs and details
--help-preflights List supported preflights and details
When using a GitHub or GitLab repo you can use KiBot to generate all the needed stuff each time you commit a change to the schematic and/or PCB file.
If you want a quick demo of what KiBot can do on a GitHub project try the following workflow.
You just need to enable GitHub workflows and copy this workflow to your .github/workflows/ folder. In this mode KiBot will detect the project files, create a configuration and generate the targets.
This workflow collects the generated files in Automatic_outputs.zip.
Examples of how to use KiBot can be found here for GitHub and here for GitLab.
In order to run KiBot on these environments you need a lot of software installed. The usual mechanism to achieve this is using docker. Docker images containing KiBot, all the supporting scripts and a corresponding KiCad can be found at Docker Hub as setsoft/kicad_auto:latest. This image is based on setsoft/kicad_debian:latest, containing KiCad on Debian GNU/Linux.
If you need to run the current development version of KiBot you can use the following docker image: setsoft/kicad_auto:dev.
The most important images are:
| Name | KiBot | KiCad |
|---|---|---|
| latest | last release | 5.1.9 |
| ki6 | last release | 6.x |
| dev | git code | 5.1.9 |
| dev_k6 | git code | 6.x |
| 10.4-5.1.9 | 1.2.0 | 5.1.9 |
| ki6.0.5_Debian | 1.2.0 | 6.0.5 |
For more information about the docker images visit kicad_debian and kicad_auto.
Note: You can also use --quick-start functionality with GitHub actions, and example is this workflow
You need to put a config.kibot.yaml file into the KiCad project folder.
Here is an example of workflow file using the GitHub Action:
name: example
on:
push:
paths:
- '**.sch'
- '**.kicad_pcb'
pull_request:
paths:
- '**.sch'
- '**.kicad_pcb'
jobs:
example:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- uses: INTI-CMNB/KiBot@v2
with:
# Required - kibot config file
config: config.kibot.yaml
# optional - prefix to output defined in config
dir: output
# optional - schematic file
schema: 'schematic.sch'
# optional - PCB design file
board: 'pcb.kicad_pcb'
- name: upload results
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
with:
name: output
path: outputFor KiCad 6 use v2_k6 instead of v2.
These actions use the last KiBot stable release, to use the current development code use v2_dk6 (KiCad 6) and v2_d (KiCad 5).
A working example applied to a repo can be found here (spora_main.yml). Another example, but using variants can be found here (kibot_action.yml for KiCad 6, kibot_action.yml for KiCad 5)
The available options are:
- config: The KiBot config file to use. The first file that matches
*.kibot.yamlis used when omitted. - dir: Output directory for the generated files. The current directory is used when omitted.
- board: Name of the PCB file. The first file that matches
*.kicad_pcbis used when omitted. - quickstart: When
YESignores all the other options and runs in--quick-startmode. No configuration needed. - schema: Name of the schematic file. The first file that matches
*.*schis used when omitted. - skip: Skip preflights, comma separated or all. Nothing is skipped when omitted.
- targets: List of targets to generate separated by spaces. To only run preflights use NONE. All targets are generated when omitted.
- variant: Global variant to use. No variant is applied when omitted.
- verbose: Level of verbosity. Valid values are 0, 1, 2 or 3. Default is 0.
There are several tags you can choose:
| Tag | API | KiBot | KiCad |
|---|---|---|---|
| v1 | 1 | 1.2.0 | 5.1.9 |
| v1_k6 | 1 | 1.2.0 | 6.0.5 |
| v2_1_2_0 | 2 | 1.2.0 | 5.1.9 |
| v2_k6_1_2_0 | 2 | 1.2.0 | 6.0.5 |
| v2 | 2 | last release | 5.1.9 |
| v2_k6 | 2 | last release | 6.x |
| v2_d | 2 | git code | 5.1.9 |
| v2_dk6 | 2 | git code | 6.x |
The main differences between API 1 and 2 are:
- API 2 adds support for variants and quick-start
- In API 2 you can select which targets are created
- In API 1 you must specify the input files, in API 2 can be omitted
- API 1 supports wildcards in the filenames, API 2 doesn't
- API 2 supports spaces in the filenames, API 1 doesn't
If you find KiBot useful please consider contributing to the project. There various ways to contribute. Of course donations are welcome (donate), but there are other ways to contribute:
- In general:
- Your workflow: What's missing in KiBot for your workflow? Comment it in the discussions
- Configuration for a manufacturer: If you have a configuration known to work for a manufacturer please consider contributing it. Even if this is a small manufacurer, this helps to know what are the most common options.
- Mention KiBot: If your project or company uses KiBot you can mention it, so people know about KiBot. Also if you are reporting a KiCad issue, currently KiCad developers doesn't pay much attention to automation details.
- If you are a Windows/Mac OS X user:
- If you managed to run it locally consider contributing a tutorial of how to do it.
- If you run KiBot on CI/CD and want to run it locally: consider investing some time on tests. Just comment in the discussions and I'll help you to run tests to adapt the code. Now that KiCad 6 uses Python 3 most of KiBot functionality should work on Windows and Mac OS X. People is using WSL to run KiBot, but we don't have a tutorial about how to do it.
- If you use a Linux that isn't derived from Debian:
- Consider helping to add better support for it. Do you know the name of the packages for the dependencies? Do you know how to create a package for your distro?
- If you are good writing tutorials:
- Consider writing some tutorial about using KiBot. Some examples:
- How to start using it
- How to use filters/variants
- How to create good BoMs
- Consider writing some tutorial about using KiBot. Some examples:
- If you know Python:
- Create a new output: KiBot is modular, creating a new output can be done just using some of the
kibot/out_*files as template. The outputs works as plugins and they are automatically discovered by KiBot. Note that you can add them to~/.config/kibot/plugins - Add regression tests: If you know about Python testing you can add tests to
tests/test_plot/. We try to cover 100% of the code. Even simple tests that check the code executes are welcome.
- Create a new output: KiBot is modular, creating a new output can be done just using some of the
- If you know HTML/CSS:
- Internal BoM styles: You can just take a look at the generated HTMLs and contribute a CSS, or take a look at the code
(
kibot/bom/html_writer.py) and add more functionality. - Navigate results styles: Similar to the above but for the
navigate_resultsoutput (kibot/out_navigate_results.py).
- Internal BoM styles: You can just take a look at the generated HTMLs and contribute a CSS, or take a look at the code
(
- If you have drawing skills:
- Navigate results icons: Currently we have only one set of icons, they are from KiCad 6. Alternative icons are welcome.
I found this topic poorly documented and quite complex. So here is what I know, feel free to send me any corrections. Note that this is a very dynamic topic and this text was written in november 2020.
The gerber format is controlled by Ucamco, a leading manufacturer of equipment and software for PCB fabrication. Even when this isn't an open standard they release the spec for free and interact with Jean-Pierre Charras (father of KiCad). So KiCad support for gerber format is really updated.
The gerber format evolved with time, here are the versions I know:
- RS-274D obsolete version of the format.
- RS-274X (aka X1) this is the extended version of the format. Is the most widely supported, but has some limitations.
- X2 this is the format currently recommended by Ucamco and the default for modern KiCad versions. This extension adds important meta-data to the files. It helps CAM operators to know what's every drawing in the image. So you know which are pads, tracks, etc. And also more interesting information: impedance controlled tracks, the role of each file, etc. Using X2 you can know what is each file without the need of special names or file extensions. KiCad can generate drill files using X2.
- X3 this is the current draft. One interesting addition is the Components role. These files replaces the position files, adding important information about the footprint.
In addition to them is the spec for the Gerber Job file. This file was introduced between X2 and X3, and is used to group all the gerber files. The gbrjob file contains all the missing stack-up information.
KiCad 5 can generate X1, X2 and gerber job files, including drill information in gerber format. KiCad 5.99 (6.0 pre-release) can also generate X3 files (position files in gerber format).
As you can see the idea of Ucamco is to unify all fabrication information in one format.
The X2 format was designed in a way that software that fully implement X1 can just ignore the added meta-data. In an ideal world you shouldn't bother about it and generate X2 files. Just use the gbr file extension and a gbrjob file. The problem is with poorly implemented CAM tools. In particular CAM350, used by various important cheap China manufacturers. This software has known issues interpretating aperture macros and some X2 data. If your manufacturer has problems with your files check the following:
- Put gerber, drill and position files in the same directory.
- Disable X2 extensions (
use_gerber_x2_attributesset tofalse) - Use arcaic role mechanism (
use_protel_extensionsset totrue) - Disable aperture macros (KiCad 6 only:
disable_aperture_macrosset totrue)
The kicad-gerberzipper is an action plugin for KiCad oriented to help to generate gerber and drill files for some manufacturers.
I adapted the configurations from kicad-gerberzipper to KiBot configurations, you can find them in the docs/samples/ directory.
They include support for:
Position files are quite simple. You can generate them as plain text (ASCII) or as a spreadsheet (CSV).
But some conventions can make them tricky. Some manufacturers, like JLCPCB, uses conventions that are incompatible with KiCad.
The following blog explains how to adapt the position files generated by KiCad to what JLCPCB needs. To achieve it the author uses a script called JLCKicadTools.
You can achieve the same using KiBot. Here is a configuration example that generates the BoM and position files in the same way JLCKicadTools does:
kibot:
version: 1
filters:
- name: only_jlc_parts
comment: 'Only parts with JLC code'
type: generic
include_only:
- column: 'LCSC#'
regex: '^C\d+'
variants:
- name: rotated
comment: 'Just a place holder for the rotation filter'
type: kibom
variant: rotated
pre_transform: _rot_footprint
outputs:
- name: 'position'
comment: "Pick and place file, JLC style"
type: position
options:
variant: rotated
output: '%f_cpl_jlc.%x'
format: CSV
units: millimeters
separate_files_for_front_and_back: false
only_smd: true
columns:
- id: Ref
name: Designator
- Val
- Package
- id: PosX
name: "Mid X"
- id: PosY
name: "Mid Y"
- id: Rot
name: Rotation
- id: Side
name: Layer
- name: 'bom'
comment: "BoM for JLC"
type: bom
options:
output: '%f_%i_jlc.%x'
exclude_filter: 'only_jlc_parts'
ref_separator: ','
columns:
- field: Value
name: Comment
- field: References
name: Designator
- Footprint
- field: 'LCSC#'
name: 'LCSC Part #'
csv:
hide_pcb_info: true
hide_stats_info: true
quote_all: trueThe only_jlc_parts filter is used to generate the BoM and assumes you put the JLC component code in a field named LCSC# (JLC uses LCSC as supplier).
Note that the author of the blog simply used Field4 for this and his script searches for any field containing the ^C\d+ pattern.
I think this isn't a good idea and I suggest using a defined name, like in this example.
The rotated variant is used only to apply the _rot_footprint transformation filter. This filter is an internal filter of type rot_footprint.
Here is the same configuration file making explicit use of the rotation filter:
kibot:
version: 1
filters:
- name: fix_rotation
comment: 'Adjust rotation for JLC'
type: rot_footprint
- name: only_jlc_parts
comment: 'Only parts with JLC code'
type: generic
include_only:
- column: 'LCSC#'
regex: '^C\d+'
variants:
- name: rotated
comment: 'Just a place holder for the rotation filter'
type: kibom
variant: rotated
pre_transform: fix_rotation
outputs:
- name: 'position'
comment: "Pick and place file, JLC style"
type: position
options:
variant: rotated
output: '%f_cpl_jlc.%x'
format: CSV
units: millimeters
separate_files_for_front_and_back: false
only_smd: true
columns:
- id: Ref
name: Designator
- Val
- Package
- id: PosX
name: "Mid X"
- id: PosY
name: "Mid Y"
- id: Rot
name: Rotation
- id: Side
name: Layer
- name: 'bom'
comment: "BoM for JLC"
type: bom
options:
output: '%f_%i_jlc.%x'
exclude_filter: 'only_jlc_parts'
ref_separator: ','
columns:
- field: Value
name: Comment
- field: References
name: Designator
- Footprint
- field: 'LCSC#'
name: 'LCSC Part #'
csv:
hide_pcb_info: true
hide_stats_info: true
quote_all: trueAs you can see we now create a filter named fix_rotation of type rot_footprint:
- name: fix_rotation
comment: 'Adjust rotation for JLC'
type: rot_footprintUsing it, instead of the internal filter named _rot_footprint, is the same here. But you can then customize the filter.
The filter supports the following options:
extend: [boolean=true] Extends the internal list of rotations with the one provided. Otherwise just use the provided list.negative_bottom: [boolean=true] Rotation for bottom components is computed via subtraction as(component rot - angle). Note that this should be coherent with thebottom_negative_xof the position output.invert_bottom: [boolean=false] Rotation for bottom components is negated, resulting in either:(- component rot - angle)or when combined withnegative_bottom,(angle - component rot).rotations: [list(list(string))] A list of pairs regular expression/rotation. Components matching the regular expression will be rotated the indicated angle. Special names_topand_bottomwill match all components on that side of the board.
In order to add a new rotation or just change an existing one you just need to use the rotations option.
As an example: the internal list of rotations rotates QFN packages by 270 degrees, no suppose you want to rotate them just 90 degrees.
The filter will look like this:
- name: fix_rotation
comment: 'Adjust rotation for JLC'
type: rot_footprint
rotations:
- ["^QFN-", 90.0]This regular expression will match any footprint starting with QFN- and rotate it 90 degrees.
The internal list of rotations is:
| Footprint | Rotation |
|---|---|
^Bosch_LGA-8_2x2.5mm_P0.65mm_ClockwisePinNumbering |
90.0 |
^R_Array_Convex_ |
90.0 |
^R_Array_Concave_ |
90.0 |
^SOT-223 |
180.0 |
^SOT-23 |
180.0 |
^TSOT-23 |
180.0 |
^SOT-353 |
180.0 |
^QFN- |
270.0 |
^LQFP- |
270.0 |
^TQFP- |
270.0 |
^SOP-(?!18_) |
270.0 |
^TSSOP- |
270.0 |
^DFN- |
270.0 |
^SOIC- |
270.0 |
^VSSOP-10_ |
270.0 |
^CP_EIA-3216-18_ |
180.0 |
^CP_EIA-3528-15_AVX-H |
180.0 |
^CP_EIA-3528-21_Kemet-B |
180.0 |
^CP_Elec_8x10.5 |
180.0 |
^CP_Elec_6.3x7.7 |
180.0 |
^CP_Elec_8x6.7 |
180.0 |
^CP_Elec_8x10 |
180.0 |
^(.*?_|V)?QFN-(16|20|24|28|40)(-|_|$) |
270.0 |
^PowerPAK_SO-8_Single |
270.0 |
^HTSSOP-28-1EP_4.4x9.7mm* |
270.0 |
XYRS files are just BoM files in CSV format that includes pick and place data (X position, Y position, Rotation and Side).
You can generate them using the internal BoM generator (bom output).
The following fields contains the needed information:
Footprint XFootprint YFootprint RotFootprint Side
Additionally we support:
Footprint Type(SMD, THT, VIRTUAL)Footprint X-SizeFootprint Y-SizeFootprint Populate
- KiBot project: Salvador E. Tropea (@set-soft)
- Original KiPlot project: John Beard (@johnbeard)
- Original KiCad Automation Scripts: Scott Bezek, Productize SPRL
- KiBoM: Oliver Henry Walters (@SchrodingersGat)
- Interactive HTML BoM: @qu1ck
- PcbDraw: Jan Mrázek (@yaqwsx)
- KiCost: Dave Vandenbout (@devbisme) and Hildo Guillardi Júnior (@hildogjr)
- KiCAD to Boardview exporter: @whitequark
- S-expression parser: Takafumi Arakaki
- Python macros: Juha Jeronen (@Technologicat)
- Board2Pdf: Albin Dennevi
- PyPDF2: Mathieu Fenniak
- svgutils: Bartosz Telenczuk (@btel)
- Contributors:
- Error filters ideas: Leandro Heck (@leoheck)
- GitHub Actions Integration/SVG output: @nerdyscout
- Plug-in loader fix: Stavros Korokithakis (@skorokithakis)
- SCH loader fix: @Sabolik
- SCH library loader fix: Bernhard B. (@bbernhard)
- GitHub Actions fix: @TheSlowGrowth
- Easier README navigation: Robin Vobruba (@hoijui)
- Typos corrections: Seth Kaz (@sethkaz) and Sebastian Grau (@SebastianGrau)
- Various tools suggested: MDW (@mdeweerd)
- GENCAD export for KiAuto: Theo Hussey (@flaminggoat)
- Sources of inspiration and good ideas:
- JLC Kicad Tools: Matthew Lai (@matthewlai)
- KiCad Gerber Zipper: @g200kg
- pimpmykicadbom: Anton Savov (@antto)
- Others:
- Robot in the logo: Christian Plaza (from pixabay)
- Robot arm in assembly_simple.svg: Pixlok
- Chip in assembly_simple.svg: oNline Web Fonts
- Wrench: Freepik - Flaticon
- Most icons for the navigate_results output: The KiCad project