Django model translation for perfectionists with deadlines.
There are two types of content, each of which has its own challenges for translation:
-
Static content: This is the content which is defined in the code. e.g. "Please enter a valid email address."
Django already provides a solution for translating static content.
-
Dynamic content: This is the content which is stored in the database. (We can't know it beforehand!)
Django Translations provides a solution for translating dynamic content.
Currently, this project is incompatible with PostgreSQL.
- Python (>=3.7, <4)
- Django (>=2.2, <6)
-
Install Django Translations using pip:
$ pip install django-translations
-
Add
translationsto theINSTALLED_APPSin the settings of your project:INSTALLED_APPS += [ 'translations', ]
-
Run
migrate:$ python manage.py migrate
-
Configure Django internationalization and localization settings:
USE_I18N = True # use internationalization USE_L10N = True # use localization MIDDLEWARE += [ # locale middleware 'django.middleware.locale.LocaleMiddleware', ] LANGUAGE_CODE = 'en-us' # default (fallback) language LANGUAGES = ( # supported languages ('en', 'English'), ('en-gb', 'English (Great Britain)'), ('de', 'German'), ('tr', 'Turkish'), )
Please note that these settings are for Django itself.
Inherit Translatable in any model you want translated:
from translations.models import Translatable
class Continent(Translatable):
code = models.Charfield(...)
name = models.Charfield(...)
denonym = models.Charfield(...)
class TranslatableMeta:
fields = ['name', 'denonym']No migrations needed afterwards.
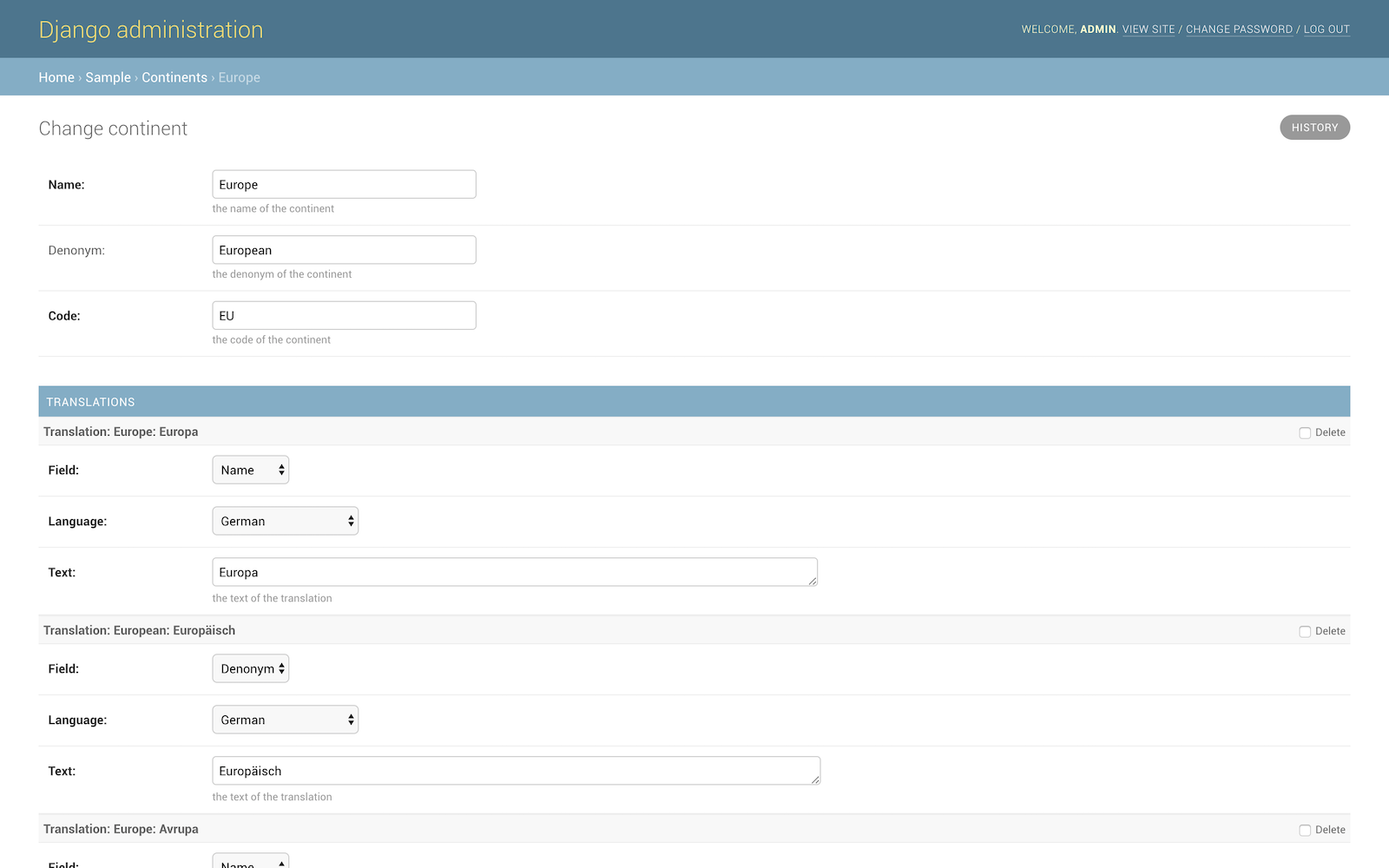
Use the admin extensions:
from translations.admin import TranslatableAdmin, TranslationInline
class ContinentAdmin(TranslatableAdmin):
inlines = [TranslationInline,]This provides specialized translation inlines for the model.
Use the queryset extensions:
>>> from sample.models import Continent
>>> continents = Continent.objects.all(
... ).distinct( # familiar distinct
... ).probe(['en', 'de'] # probe (filter, exclude, etc.) in English and German
... ).filter( # familiar filtering
... countries__cities__name__startswith='Köln'
... ).translate('de' # translate the results in German
... ).translate_related( # translate these relations as well
... 'countries', 'countries__cities',
... )
>>> print(continents)
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<Continent: Europa>,
]>
>>> print(continents[0].countries.all())
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<Country: Deutschland>,
]>
>>> print(continents[0].countries.all()[0].cities.all())
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<City: Köln>,
]>This provides a powerful yet familiar interface to work with the querysets.
Use the translation context:
>>> from translations.context import Context
>>> from sample.models import Continent
>>> continents = Continent.objects.all()
>>> relations = ('countries', 'countries__cities',)
>>> with Context(continents, *relations) as context:
... context.read('de') # read the translations onto the context
... print(':') # use the objects like before
... print(continents)
... print(continents[0].countries.all())
... print(continents[0].countries.all()[0].cities.all())
...
... continents[0].countries.all()[0].name = 'Change the name'
... context.update('de') # update the translations from the context
...
... context.delete('de') # delete the translations of the context
...
... context.reset() # reset the translations of the context
... print(':') # use the objects like before
... print(continents)
... print(continents[0].countries.all())
... print(continents[0].countries.all()[0].cities.all())
:
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<Continent: Asien>,
<Continent: Europa>,
]>
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<Country: Deutschland>,
]>
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<City: Köln>,
]>
:
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<Continent: Asia>,
<Continent: Europe>,
]>
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<Country: Germany>,
]>
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<City: Cologne>,
]>This can CRUD the translations of any objects (instance, queryset, list) and their relations.
For more interesting capabilities browse through the documentation.
Email [email protected] if you're really stuck.
To support the project you can:
- ⭐️: Star it on GitHub.
- 💻: Contribute to the code base.
- ☕️: Buy the maintainers coffee.