Use Pytorch to create an image captioning model with CNN and seq2seq LSTM and train on google collab GPU.
The COCO dataset is used. We used the year 2014 data.
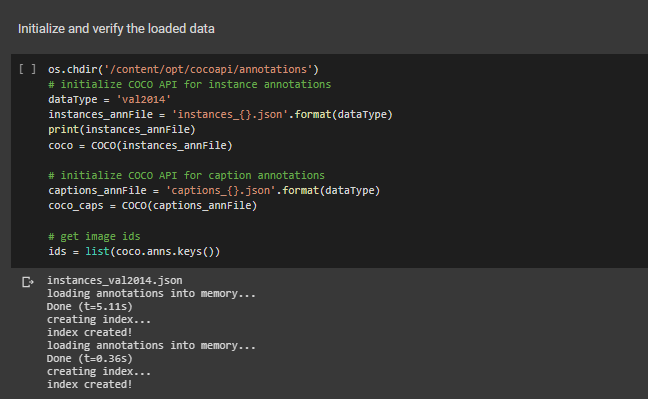
We can follow the official github repo to learn how to use the COCO API.
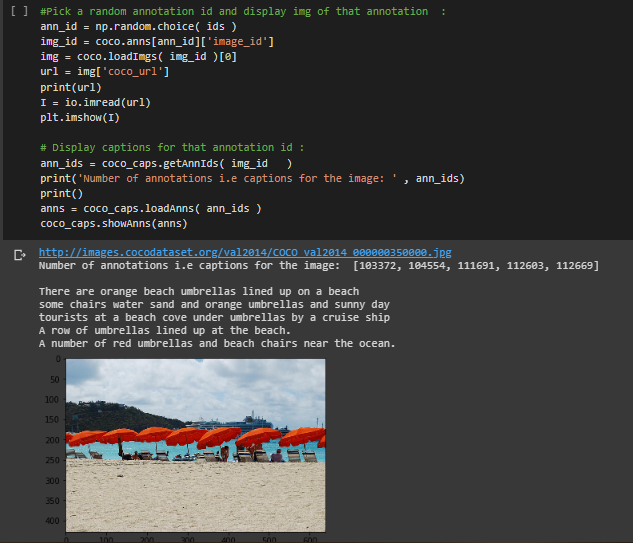
Input the path of the annotations file then we can visualize the image from dataset.
Applied usual preprocessing steps, such as resizing, random cropping, normalizing etc
We have used NLKT for tokenization of the captions and filtered rare words by occurence count that doesnt help in our training.
Observer below example we have added start and end to identify the start and end of the captions that correspond to indexes 0 and 1 in out idx2word dict
For example, a raw text sentence “ I am great” will be tokenized into [, ‘i’, ‘am’, 'great’,] and eventually become [0, 3, 98, 754, 1].
The length of caption on images are varying but our model require a fixed length input per batch.
Usually we will use the padding function in pytorch to pad or truncate to make them same length within mini batch.
Or we can use the SubsetRandomSampler in pytorch to samples elements randomly from a given list of indices.
We first generate a random number ≤max length of captions, eg 13. Then we use np.where to get all indices of captions
having length =13.
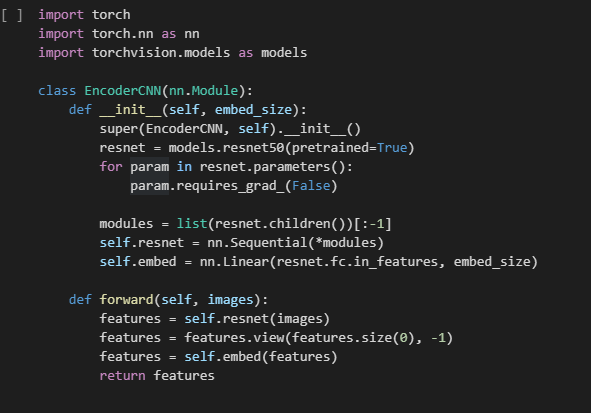
We have apply pre-trained resnet50 to save time. Remember to remove the last FC layer as we are not doing image classification,
we just need to extract feature and connect the feature vector with LSTM in decoder.
Remember to freeze the parameter of the resnet50 otherwise you will destroy the trained-weight.
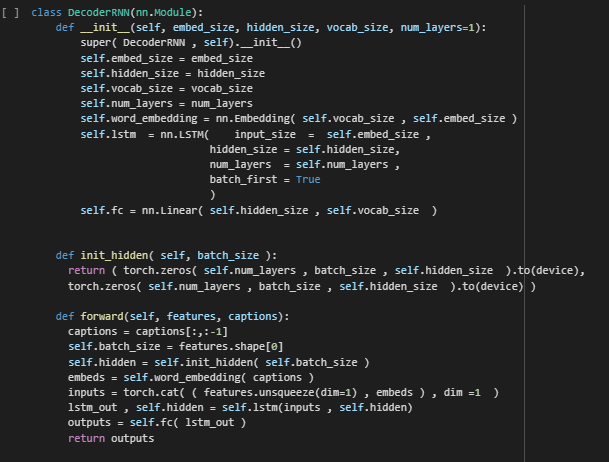
We have already converted text sentence into integer token, now we add a word embedding layer to increase the
representation ability of our model. Don’t forget to concatenate the feature vector(image) and our
embedding matrix(captions) to pass into LSTM
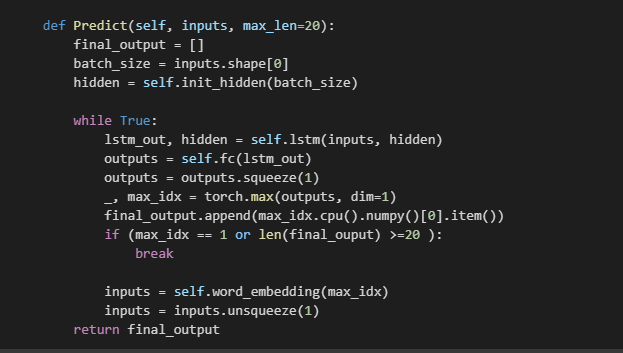
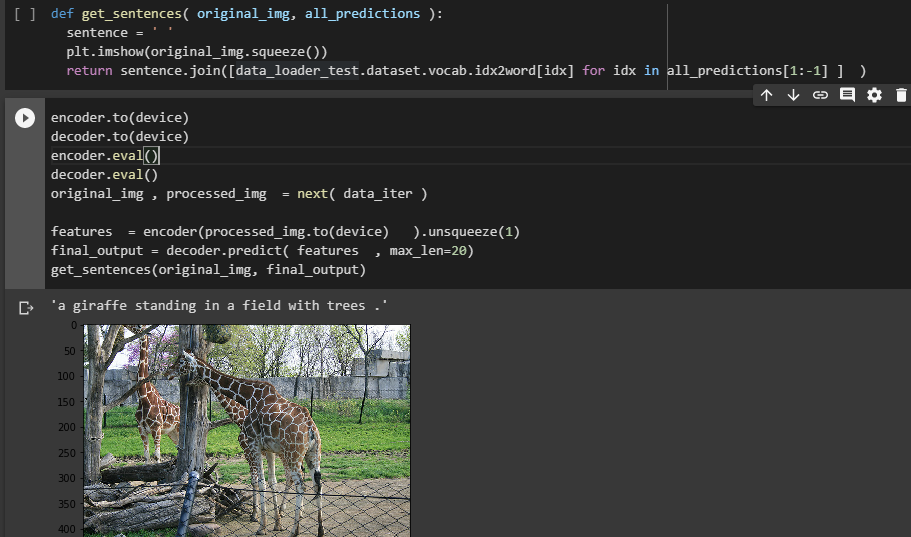
Don’t forget to apply the same image preprocessing steps to the testing image set. The tesing image will go through the same preprocessing steps and feed into the model to output a token, then we map the integer token with the word2idx dictionary to get back the text token. This token also become the input of our model to predict the next token. It loops until our model read the token.