#OpenStack Nova README
OpenStack Nova provides a cloud computing fabric controller, supporting a wide variety of virtualization technologies, including KVM, Xen, LXC, VMware, and more. In addition to its native API, it includes compatibility with the commonly encountered Amazon EC2 and S3 APIs.
OpenStack Nova is distributed under the terms of the Apache License, Version 2.0. The full terms and conditions of this license are detailed in the LICENSE file.
Nova primarily consists of a set of Python daemons, though it requires and integrates with a number of native system components for databases, messaging and virtualization capabilities.
To keep updated with new developments in the OpenStack project follow @openstack on Twitter.
To learn how to deploy OpenStack Nova, consult the documentation available online.
For information about the different compute (hypervisor) drivers supported by Nova, read this page on the wiki
In the unfortunate event that bugs are discovered, they should be reported to the appropriate bug tracker. If you obtained the software from a 3rd party operating system vendor, it is often wise to use their own bug tracker for reporting problems. In all other cases use the master OpenStack bug tracker.
Developers wishing to work on the OpenStack Nova project should always base their work on the latest Nova code, available from the master GIT repository.
Developers should also join the discussion on the mailing list.
Any new code must follow the development guidelines detailed in the HACKING.rst file, and pass all unit tests. Further developer focused documentation is available at docs.openstack.org/developer/nova/
For information on how to contribute to Nova, please see the contents of the CONTRIBUTING.rst file.
-- End of broadcast
#VirtualBox Driver for Nova
More and more people are interested in cloud computing and OpenStack but many of them give it up because they can’t test or interact with this kind of infrastructure. This is mostly a result of either high costs of hardware or the difficulty of the deployment in a particular environment.
In order to help the community to interact more with cloud computing and learn about it, Cloudbase Solutions has come up with a simple VirtualBox driver for OpenStack. VirtualBox allows you to set up a cloud environment on your personal laptop, no matter which operating system you’re using (Windows, Linux, OS X). It also gets the job done with a free and familiar virtualization environment.
##Hypervisor Support Matrix
| Feature | Status | VirtualBox |
|---|---|---|
| Attach block volume to instance | optional | ❗ |
| Detach block volume from instance | optional | ❗ |
| Evacuate instances from host | optional | ❌ |
| Guest instance status | mandatory | ✅ |
| Guest host status | optional | ✅ |
| Live migrate instance across hosts | optional | ❌ |
| Launch instance | mandatory | ✅ |
| Stop instance CPUs | optional | ✅ |
| Reboot instance | optional | ✅ |
| Rescue instance | optional | ❌ |
| Resize instance | optional | ✅ |
| Restore instance | optional | ✅ |
| Service control | optional | ❌ |
| Set instance admin password | optional | ❌ |
| Save snapshot of instance disk | optional | ✅ |
| Suspend instance | optional | ✅ |
| Swap block volumes | optional | ❌ |
| Shutdown instance | mandatory | ✅ |
| Resume instance CPUs | optional | ✅ |
| Auto configure disk | optional | ❌ |
| Instance disk I/O limits | optional | ❌ |
| Config drive support | choice | ❌ |
| Inject files into disk image | optional | ❌ |
| Inject guest networking config | optional | ❌ |
| Remote desktop over RDP | choice | ✅ |
| View serial console logs | choice | ❌ |
| Remote desktop over SPICE | choice | ❌ |
| Remote desktop over VNC | choice | ✅ |
| Block storage support | optional | ✅ |
| Block storage over fibre channel | optional | ❌ |
| Block storage over iSCSI | condition | ✅ |
| CHAP authentication for iSCSI | optional | ✅ |
| Image storage support | mandatory | ✅ |
| Network firewall rules | optional | ❌ |
| Network routing | optional | ❌ |
| Network security groups | optional | ❌ |
| Flat networking | choice | ✅ |
| VLAN networking | choice | ❌ |
More information regarding this features can be found on the following pages: Nova Support Matrix and Hypervisor Support Matrix.
##VirtualBox supported features
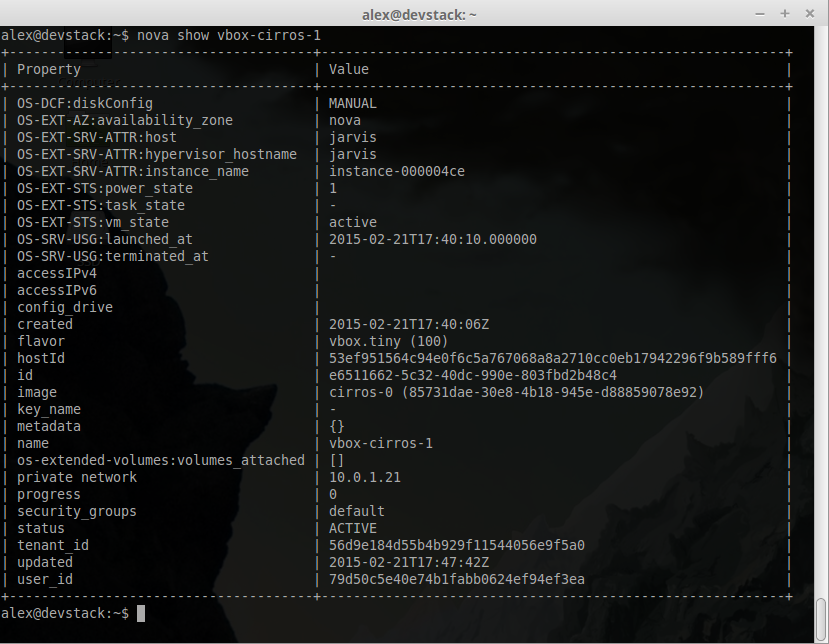
###Guest instance status Provides a quick report on information about the guest instance, including the power state, memory allocation, CPU allocation, number of vCPUs and cumulative CPU execution time.
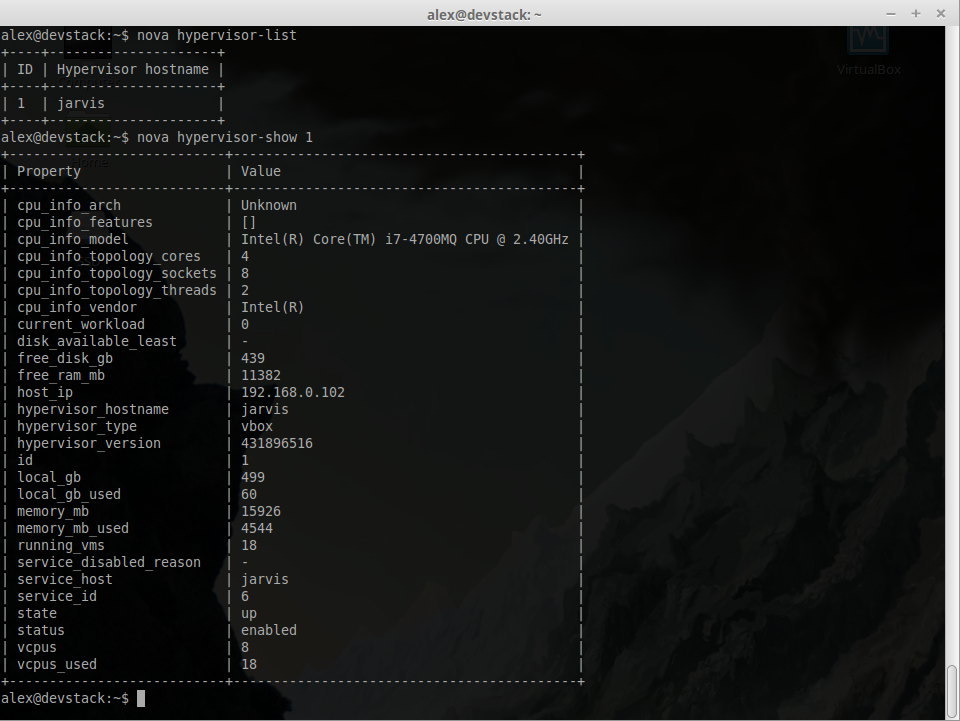
~ $ nova instance_name show###Guest host status Provides a quick report of available resources on the host machine.
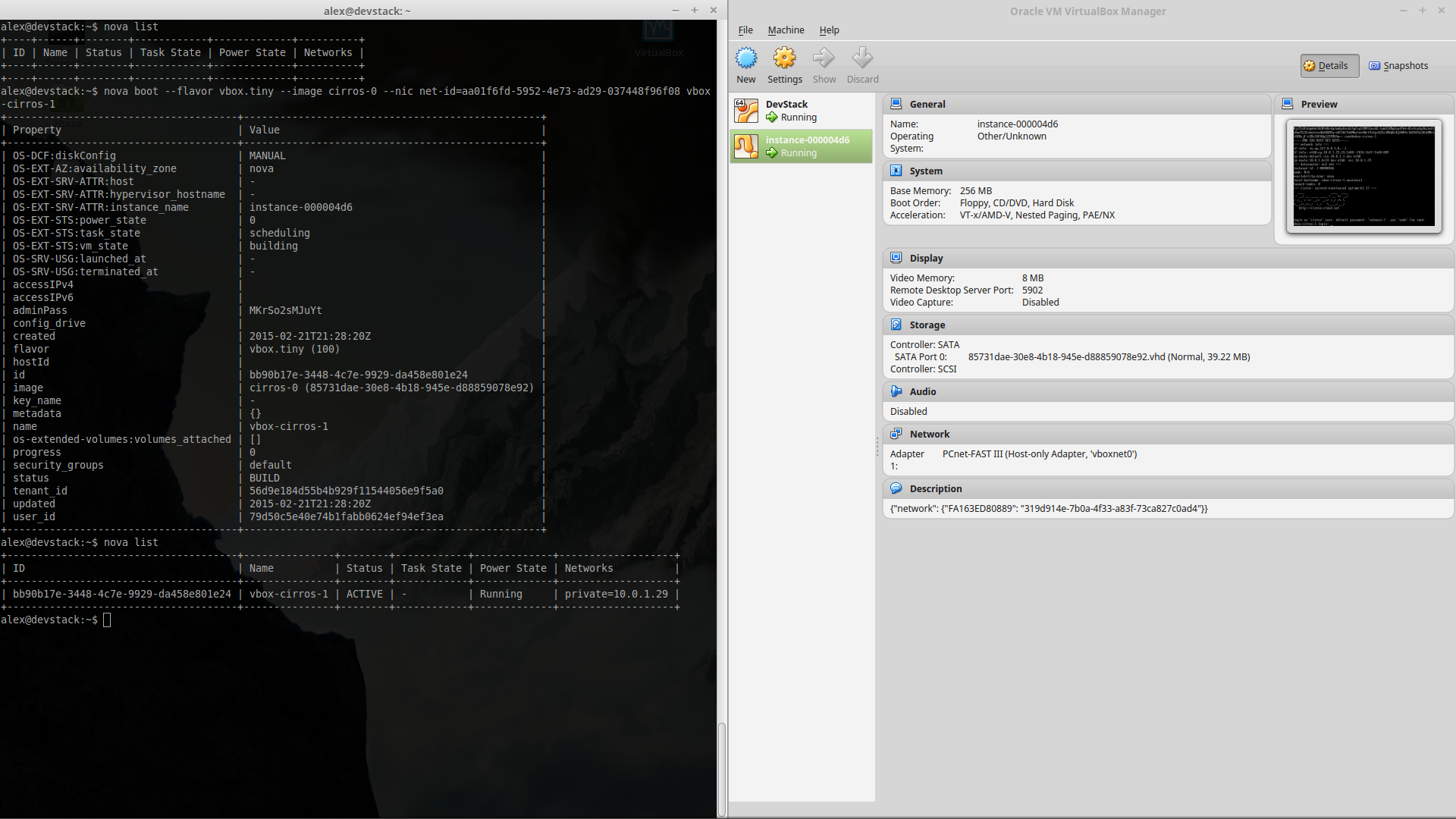
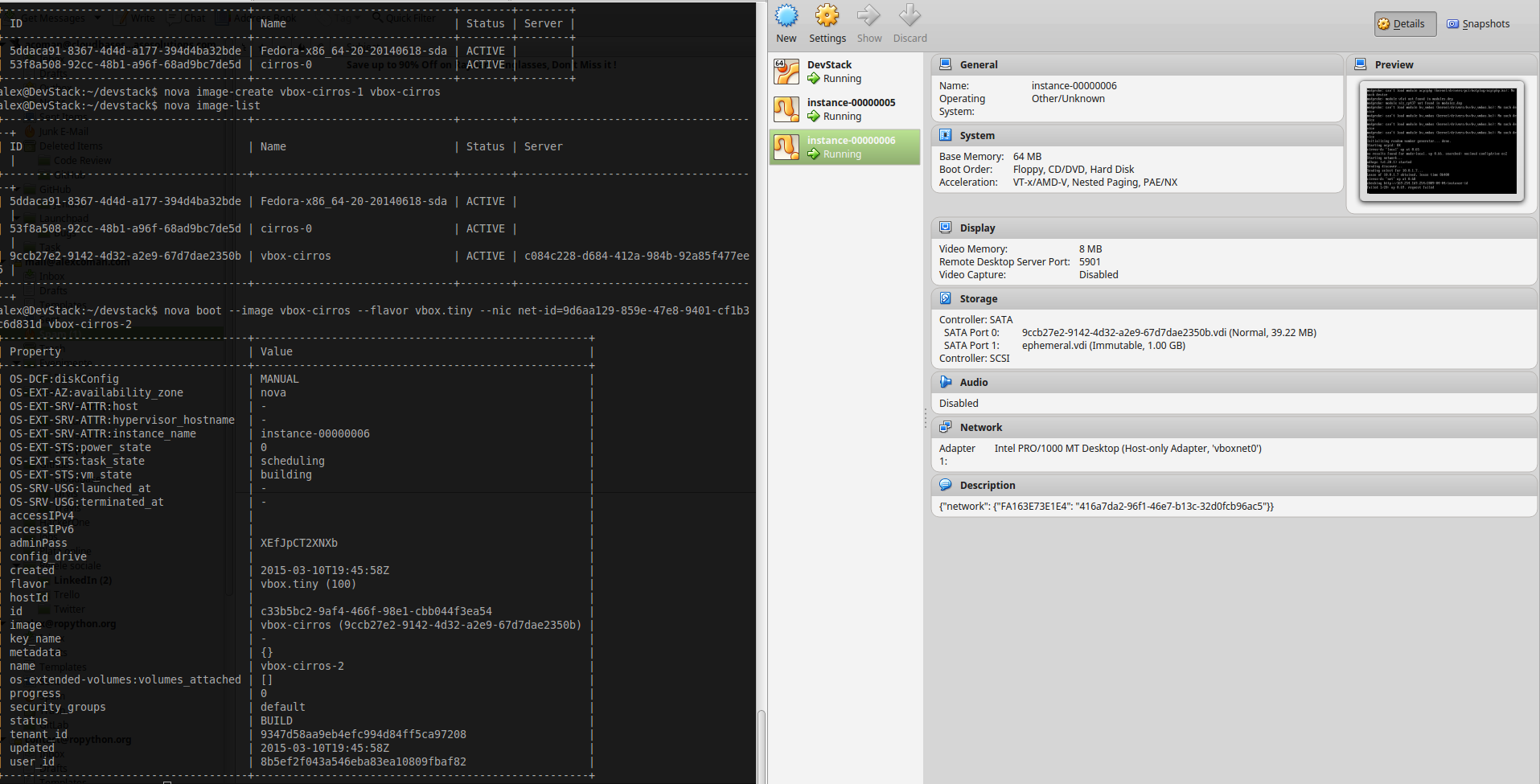
~ $ nova hypervisor-show hypervisor_id###Launch instance Create a new instance(virtual machine) on the virtualization platform.
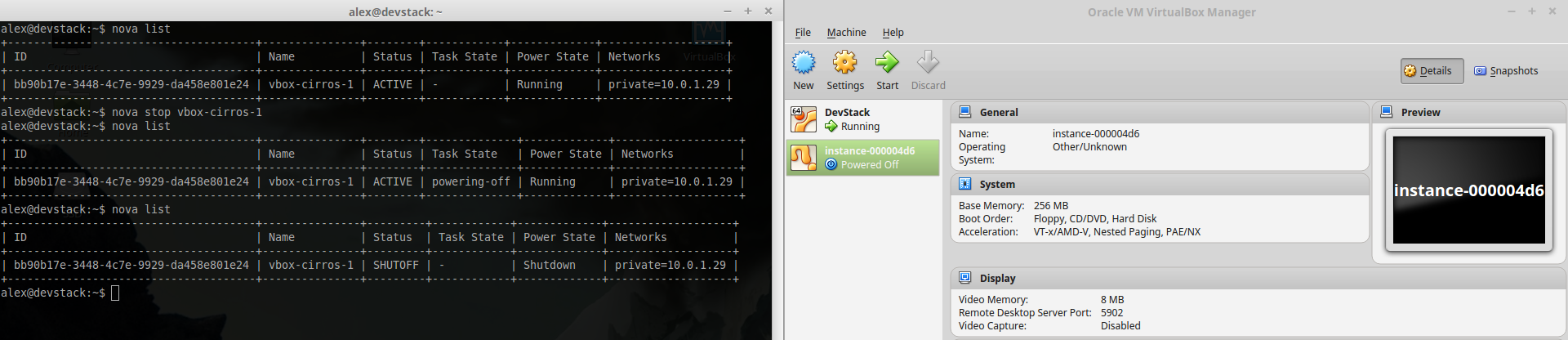
###Shutdown instance
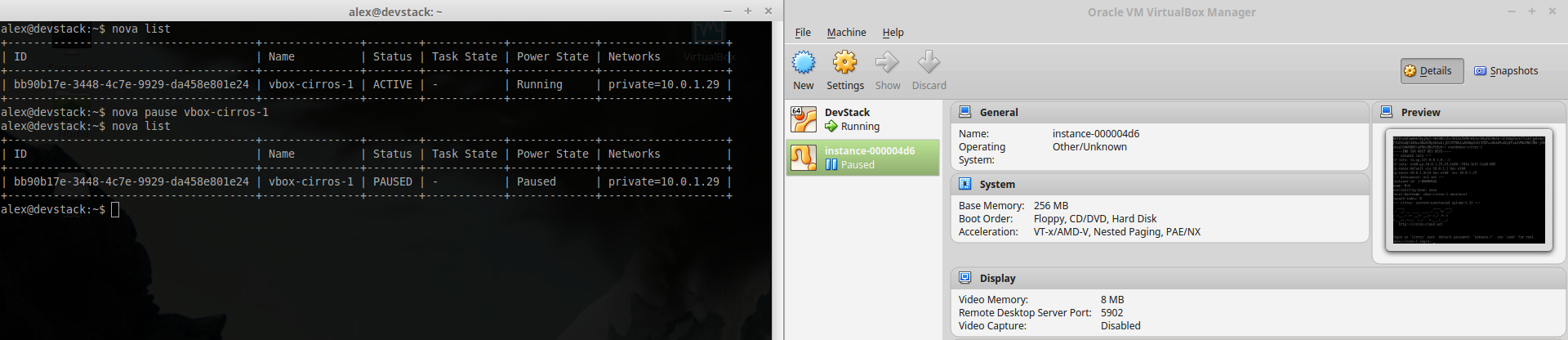
~ $ nova stop instance_name###Stop instance CPUs Stopping an instances CPUs can be thought of as roughly equivalent to suspend-to-RAM. The instance is still present in memory, but execution has stopped.
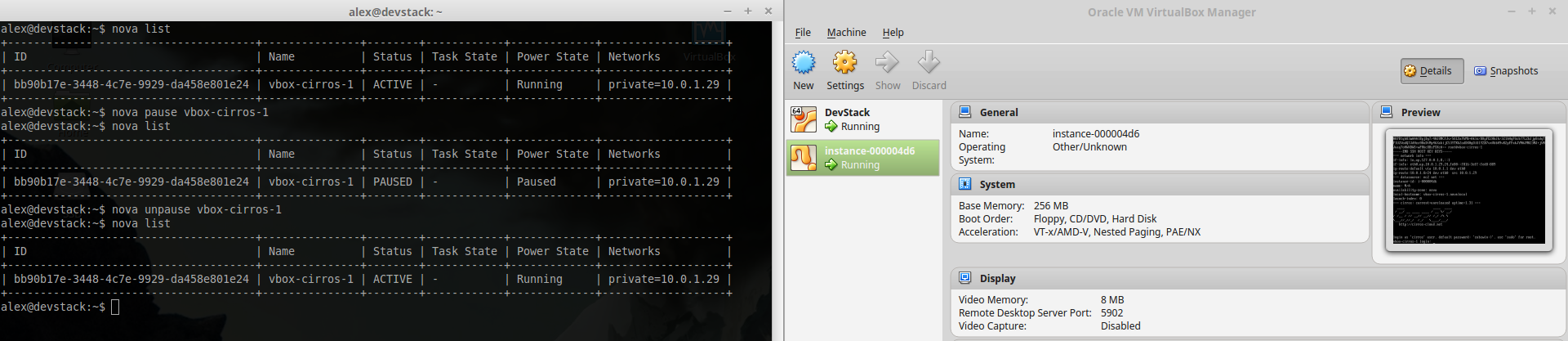
~ $ nova pause instance_name###Resume instance CPUs
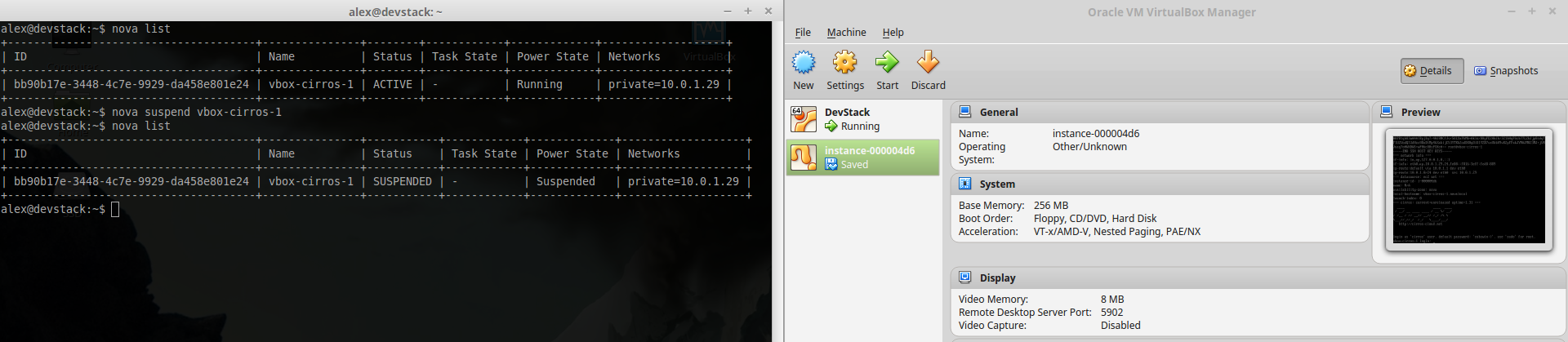
~ $ nova unpause instance name###Suspend instance Suspending an instance can be thought of as roughly equivalent to suspend-to-disk. The instance no longer consumes any RAM or CPUs, with its live running state having been preserved in a file on disk. It can later be restored, at which point it should continue execution where it left off.
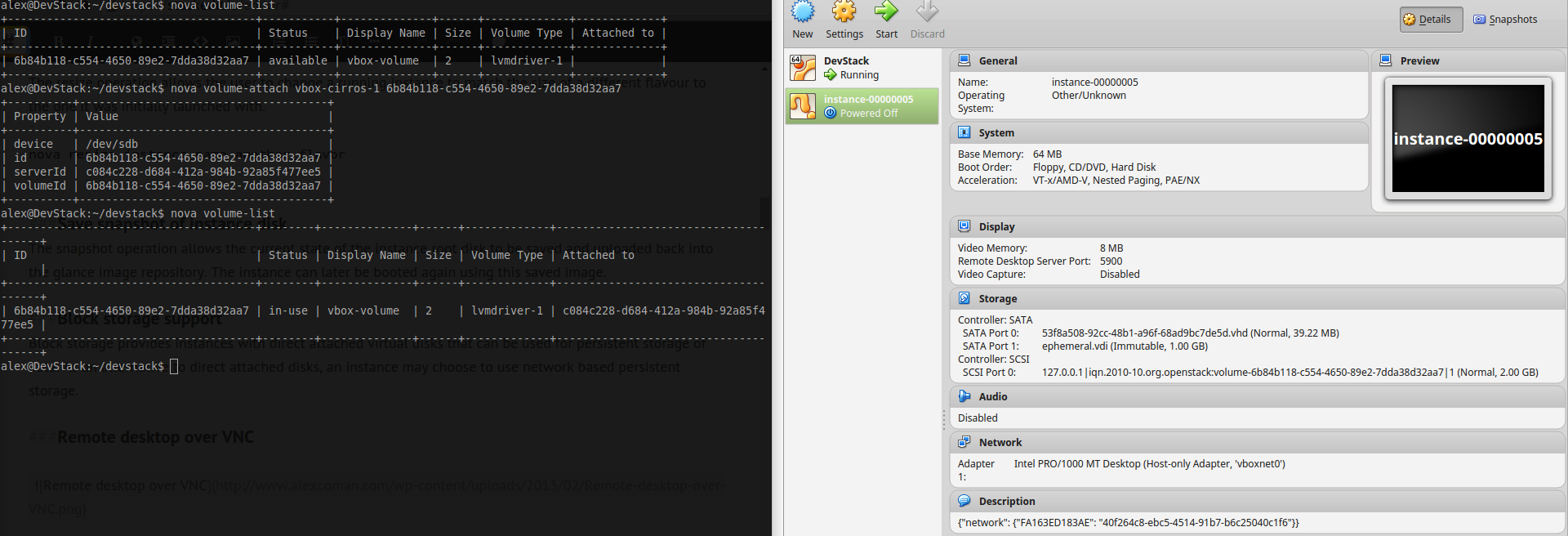
~ $ nova suspend instance_name###Save snapshot of instance disk The snapshot operation allows the current state of the instance root disk to be saved and uploaded back into the glance image repository. The instance can later be booted again using this saved image.
###Block storage support Block storage provides instances with direct attached virtual disks that can be used for persistent storage of data. As an alternative to direct attached disks, an instance may choose to use network based persistent storage.
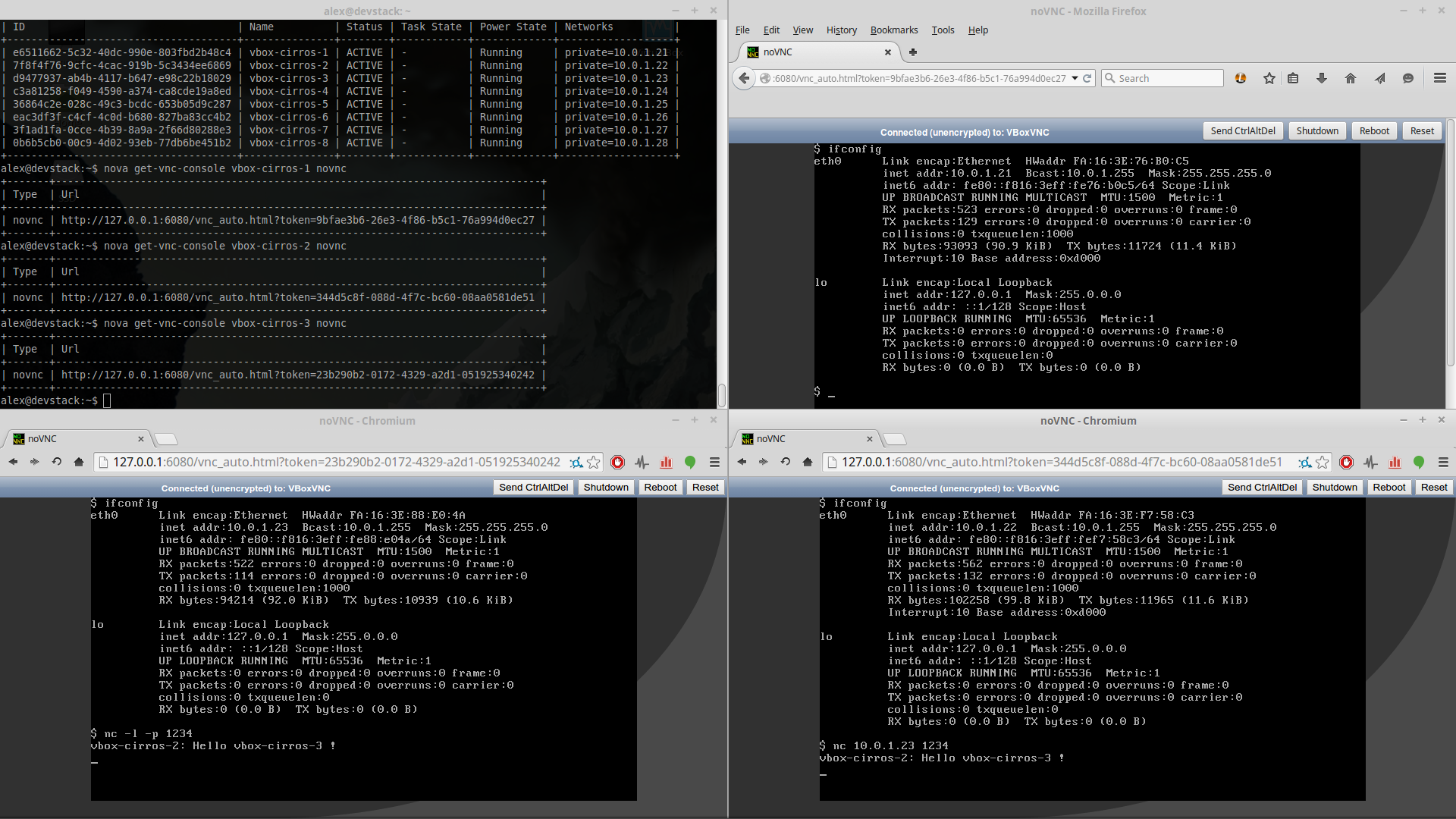
###Remote desktop over VNC
Note: In order to use this feature the VNC extension pack for VirtualBox must be installed. You can list all the available extension package running the following command:
~ $ VBoxManage list extpacksExtension Packs: 2
Pack no. 0: Oracle VM VirtualBox Extension Pack
Version: 4.3.20
Revision: 96996
Edition:
Description: USB 2.0 Host Controller, Host Webcam, VirtualBox RDP, PXE ROM with E1000 support.
VRDE Module: VBoxVRDP
Usable: true
Why unusable:
Pack no. 1: VNC
Version: 4.3.18
Revision: 96516
Edition:
Description: VNC plugin module
VRDE Module: VBoxVNC
Usable: true
Why unusable:
##Setting up the environment
###DevStack
####Create Virtual Machine
- Processors:
- Number of processors: 2
- Number of cores per processor 1
- Memory: 4GB RAM (Recommended)
- HDD - SATA - 20 GB Preallocated
- Network:
- Network Adapter 1: NAT
- Network Adapter 2: Host Only
- Network Adapter 3: Nat
- Operating system - Ubuntu Server 14.04 (Recommended)
####Update System
~ $ sudo apt-get update
~ $ sudo apt-get upgrade####Install openssh-server, git, vim, openvswitch-switch
~ $ sudo apt-get install -y git vim openssh-server openvswitch-switch####Edit network Interfaces
~ $ sudo vim /etc/network/interfacesIMPORTANT: This is a template. Please use your own settings.
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5).
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
# The management interface
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet manual
up ip link set eth1 up
up ip link set eth1 promisc on
down ip link set eth1 promisc off
down ip link set eth1 down
# The public interface
auto eth2
iface eth2 inet manual
up ip link set eth2 up
down ip link set eth2 downIMPORTANT: After you edit /etc/network/interfaces the network service should be restarted.
~ $ sudo service network restart~ $ sudo ovs-vsctl add-br br-eth1
~ $ sudo ovs-vsctl add-port br-eth1 eth1
~ $ sudo ovs-vsctl add-br br-ex
~ $ sudo ovs-vsctl add-port br-ex eth2####Clone devstack
~ $ cd
~ $ git clone https://github.com/openstack-dev/devstack.git
~ $ cd devstack####Change local.conf
~ $ sudo vim ~/devstack/local.confIMPORTANT: The following config file is a template. Please use your own settings.
[[local|localrc]]
HOST_IP=10.0.2.15
DEVSTACK_BRANCH=stable/kile
DEVSTACK_PASSWORD=Passw0rd
#Services to be started
enable_service rabbit
enable_service mysql
enable_service key
enable_service n-api
enable_service n-crt
enable_service n-obj
enable_service n-cond
enable_service n-sch
enable_service n-cauth
enable_service n-novnc
disable_service n-net
enable_service neutron
enable_service q-svc
enable_service q-agt
enable_service q-dhcp
enable_service q-l3
enable_service q-meta
enable_service q-lbaas
enable_service q-fwaas
enable_service q-metering
enable_service q-vpn
enable_service horizon
enable_service g-api
enable_service g-reg
enable_service cinder
enable_service c-api
enable_service c-vol
enable_service c-sch
enable_service c-bak
disable_service s-proxy
disable_service s-object
disable_service s-container
disable_service s-account
disable_service heat
disable_service h-api
disable_service h-api-cfn
disable_service h-api-cw
disable_service h-eng
disable_service ceilometer-acentral
disable_service ceilometer-collector
disable_service ceilometer-api
disable_service tempest
# To add a local compute node, enable the following services
disable_service n-cpu
disable_service ceilometer-acompute
IMAGE_URLS+=",https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cloudbase/ci-overcloud-init-scripts/master/scripts/devstack_vm/cirros-0.3.3-x86_64.vhd.gz"
HEAT_CFN_IMAGE_URL="https://www.cloudbase.it/downloads/Fedora-x86_64-20-20140618-sda.vhd.gz"
Q_PLUGIN=ml2
Q_ML2_PLUGIN_MECHANISM_DRIVERS=openvswitch
Q_ML2_TENANT_NETWORK_TYPE=vlan
PHYSICAL_NETWORK=physnet1
OVS_PHYSICAL_BRIDGE=br-eth1
OVS_BRIDGE_MAPPINGS=physnet1:br-eth1
OVS_ENABLE_TUNNELING=False
ENABLE_TENANT_VLANS=True
TENANT_VLAN_RANGE=500:2000
GUEST_INTERFACE_DEFAULT=eth1
PUBLIC_INTERFACE_DEFAULT=eth2
FLOATING_RANGE=172.24.4.0/27
FIXED_RANGE=10.0.1.0/24
NETWORK_GATEWAY=10.0.1.1
CINDER_SECURE_DELETE=False
VOLUME_BACKING_FILE_SIZE=50000M
LIVE_MIGRATION_AVAILABLE=False
USE_BLOCK_MIGRATION_FOR_LIVE_MIGRATION=False
LIBVIRT_TYPE=kvm
API_RATE_LIMIT=False
DATABASE_PASSWORD=$DEVSTACK_PASSWORD
RABBIT_PASSWORD=$DEVSTACK_PASSWORD
SERVICE_TOKEN=$DEVSTACK_PASSWORD
SERVICE_PASSWORD=$DEVSTACK_PASSWORD
ADMIN_PASSWORD=$DEVSTACK_PASSWORD
SCREEN_LOGDIR=/opt/stack/logs/screen
VERBOSE=True
LOG_COLOR=False
SWIFT_REPLICAS=1
SWIFT_HASH=66a3d6b56c1f479c8b4e70ab5d2014f6
KEYSTONE_BRANCH=$DEVSTACK_BRANCH
NOVA_BRANCH=$DEVSTACK_BRANCH
NEUTRON_BRANCH=$DEVSTACK_BRANCH
SWIFT_BRANCH=$DEVSTACK_BRANCH
GLANCE_BRANCH=$DEVSTACK_BRANCH
CINDER_BRANCH=$DEVSTACK_BRANCH
HEAT_BRANCH=$DEVSTACK_BRANCH
TROVE_BRANCH=$DEVSTACK_BRANCH
HORIZON_BRANCH=$DEVSTACK_BRANCH
TROVE_BRANCH=$DEVSTACK_BRANCH
REQUIREMENTS_BRANCH=$DEVSTACK_BRANCH
[[post-config|$NEUTRON_CONF]]
[database]
min_pool_size = 5
max_pool_size = 50
max_overflow = 50More information regarding local.conf can be found on Devstack configuration.
~ $ vim ~/.bashrcAdd this lines at the end of file.
export OS_USERNAME=admin
export OS_PASSWORD=Passw0rd
export OS_TENANT_NAME=admin
export OS_AUTH_URL=http://127.0.0.1:5000/v2.0####Run stack.sh
~ $ cd ~/devstack
~ $ ./stack.shIMPORTANT: If the scripts doesn't end properly or something else goes wrong, please unstack first using ./unstack.sh script.
####Disable Firewall
~ $ sudo ufw disable####Create a Flat Network (if not exists)
-
Remove the current network setup.
neutron router-interface-delete router1 $SUBNETID1 neutron router-gateway-clear router1 neutron router-delete router1 neutron net-delete private neutron net-delete public -
Create private network/subnetwork
neutron net-create private --provider:network_type flat --provider:physical_network physnet1 neutron subnet-create private 10.0.1.0/24 --gateway 10.0.1.1 --dns_nameservers list=true 8.8.8.8
-
Create public network/subnetwork
neutron net-create public --router:external=True neutron subnet-create public 172.24.4.0/27 --gateway 172.24.4.1 --enable_dhcp=False --dns_nameservers list=true 8.8.8.8
-
Create and setup router
neutron router-create router1 neutron router-interface-add router1 $SUBNETID1 neutron router-gateway-set router1 $EXTNETID1
####Change current version of nova and neutron
For the moment the Nova Driver and Neutron Agent for VirtualBox are not included in the current version of OpenStack. In order to use them we must change the version of nova and neutron installed by DevStack.
Change the nova version used:
~ $ cd /opt/stack/nova
~ $ git remote add vbox $NOVA_FORK
~ $ git fetch vbox
~ $ git checkout -t vbox/virtualbox_driver
~ $ sudo python setup.py installChange the neutron version used:
~ $ cd /opt/stack/neutron
~ $ git remote add vbox $NOVA_FORK
~ $ git fetch vbox
~ $ git checkout -t vbox/virtualbox_agent
~ $ sudo python setup.py installChange mechanism drivers:
~ $ cd /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2
~ $ vim ml2_conf.iniAdd vbox in the following line: mechanism_drivers = openvswitch,vbox
####Port forwarding In order to access services from the DevStack virtual machine from the host machine we need to forward the to host.
For each used port we need to run one of the following commands:
# If the virtual machine is in power off state.
VBoxManage --modifyvm DevStack [--natpf<1-N> [<rulename>],tcp|udp,[<hostip>],
<hostport>,[<guestip>],<guestport>]
# If the virtual machine is running
VBoxManage --controlvm DevStack natpf<1-N> [<rulename>],tcp|udp,[<hostip>],
<hostport>,[<guestip>],<guestport> |
For example the required rules for a compute node can be the following:
# Message Broker (AMQP traffic) - 5672
~ $ VBoxManage controlvm DevStack natpf1 "Message Broker (AMQP traffic), tcp, 127.0.0.1, 5672, 10.0.2.15, 5672"
# iSCSI target - 3260
~ $ VBoxManage controlvm DevStack natpf1 "iSCSI target, tcp, 127.0.0.1, 3260, 10.0.2.15, 3260"
# Block Storage (cinder) - 8776
~ $ VBoxManage controlvm DevStack natpf1 "Block Storage (cinder), tcp, 127.0.0.1, 8776, 10.0.2.15, 8776"
# Networking (neutron) - 9696
~ $ VBoxManage controlvm DevStack natpf1 "Networking (neutron), tcp, 127.0.0.1, 9696, 10.0.2.15, 9696"
# Identity service (keystone) - 35357 or 5000
~ $ VBoxManage controlvm DevStack natpf1 "Identity service (keystone) administrative endpoint, tcp, 127.0.0.1, 35357, 10.0.2.15, 35357"
# Image Service (glance) API - 9292
~ $ VBoxManage controlvm DevStack natpf1 "Image Service (glance) API, tcp, 127.0.0.1, 9292, 10.0.2.15, 9292"
# Image Service registry - 9191
~ $ VBoxManage controlvm DevStack natpf1 "Image Service registry, tcp, 127.0.0.1, 9191, 10.0.2.15, 9191"
# HTTP - 80
~ $ VBoxManage controlvm DevStack natpf1 "HTTP, tcp, 127.0.0.1, 80, 10.0.2.15, 80"
# HTTP alternate
~ $ VBoxManage controlvm DevStack natpf1 "HTTP alternate, tcp, 127.0.0.1, 8080, 10.0.2.15, 8080"
# HTTPS - 443
~ $ VBoxManage controlvm DevStack natpf1 "HTTPS, tcp, 127.0.0.1, 443, 10.0.2.15, 443"More information regarding Openstack default ports can be found on Appendix A. Firewalls and default ports.
##Setting up nova-compute
###Clone nova
~ $ cd
~ $ git clone -b virtualbox_driver $NOVA_FORK###Install nova & requirements
~ $ cd nova
~ $ pip install -r requirements.txt
~ $ python setup.py install###Configuration VirtualBox Nova Driver have the following custom config options:
[virtualbox]
| Config option | Default value | Short description |
|---|---|---|
| remote_display | False | Enable or disable the VRDE Server. |
| retry_count | 3 | The number of times to retry to execute command. |
| retry_interval | 1 | Interval between execute attempts, in seconds. |
| vboxmanage_cmd | VBoxManage | Path of VBoxManage. |
| vrde_unique_port | False | Whether to use an unique port for each instance. |
| vrde_module | Oracle VM VirtualBox Extension Pack | The module used by VRDE Server. |
| vrde_port | 3389 | A port or a range of ports the VRDE server can bind to. |
| vrde_require_instance _uuid_as_password | False | Use the instance uuid as password for the VRDE server. |
| vrde_password_length | None | VRDE maximum length for password. |
| wait_soft_reboot_seconds | 60 | Number of seconds to wait for instance to shut down after soft reboot request is made. |
[rdp]
| Config option | Default value | Short description |
|---|---|---|
| encrypted_rdp | False | Enable or disable the rdp encryption. |
| security_method | RDP | The security method used for encryption. (RDP, TLS, Negotiate). |
| server_certificate | None | The Server Certificate. |
| server_private_key | None | The Server Private Key. |
| server_ca | None | The Certificate Authority (CA) Certificate. |
IMPORTANT: The following config file is an exemple of nova_compute.conf. Please use your own settings.
[DEFAULT]
verbose=true
debug=true
use_cow_images=True
allow_resize_to_same_host=true
vnc_enabled=True
vncserver_listen = 127.0.0.1
vncserver_proxyclient_address = 127.0.0.1
novncproxy_base_url=http://127.0.0.1:6080/vnc_auto.html
# [...]
[cinder]
endpoint_template=http://127.0.0.1:8776/v2/%(project_id)s
[virtualbox]
#On Windows
#vboxmanage_cmd=C:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage.exe
remote_display = true
vrde_module = VNC
vrde_port = 5900-6000
vrde_unique_port = true
vrde_password_length=20
vrde_require_instance_uuid_as_password=True
[rdp]
enabled=false
#encrypted_rdp=true
#security_method=RDP
#server_certificate=server_cert.pem
#server_private_key=server_key_private.pem
#server_ca=ca_cert.pem
#html5_proxy_base_url=http://127.0.0.1:8000/More information regarding compute node configuration can be find on the following pages: List of compute config options and Nova compute
###Start up nova-compute
~ $ nova-compute --config-file nova_compute.conf