(Can also be useful for CCSK)
CCSP mnemonics for CISSP-passers.
CISSP-mnemonics | CCSP-Mnemonics
- CCSP Exam Cram by Zete Zerger
- CCSP OPT book
- FREE (ISC)² CCSP Quiz/Test
- CCSP by Alukos
- CSA Security Guidance (recommended by Reddit)
- Cloud Computing Security Considerations – by ACSC – brief CSA Security Guidance for beginners.
- FREE (ISC)² CCSP Flashcards [These may or may not be useful]
- (wishlist of resources I didn't have)
(Similar to ISO 17789:2014, but don't worry about it)
-
On-demand self-service – service
self -
Broad network access – broad access over internet or WAN
-
Resource pooling – Resources are somewhere in that cloud pool (within chosen geographic location)
Swimming pool with resources... somewhere -
Rapid elasticity – (Repeat) (cloud) solution is like an elastic band – can scale up and scale down as needed. Elasticity implies scalability
-
Measured service – pay exactly the measured amount
-
Scalability – app/solution can "scale up" well for thousands of inputs or clients
-
Elasticity – (cloud) solution is like an elastic band – can scale up and scale down as needed. Elasticity implies scalability
-
Cloud bursting – Hybrid cloud elasticity (bursting)
-
Multitenancy – Sharing tenements (resources) with everyone, including Communists, Anarchists, and crooks
- On-prem – Your datacenter
- Private – CSP only services you (CSP is your Sugar Baby) – Expensive.
- Community – (U.S. Intelligence) Community Cloud – cloud for those who share a mission!
- Hybrid – Your infrastructure 🖤 CSP's cloud. Uses data portability technology and is hard to configure well.
- Public – CSP's cloud for everyone, including crooks. Multitenancy.
- TEE – Trusted Execution Environment (≈ TCB)
- TPM/vTPM – Internal hardware for TEE/TCB (+ Secure Boot)
- HSM – External dongle/card for TEE/TCB (+ Secrets Management)
- Dedicated HSM – BEST Secrets Management. Better than any vTPM.
- Confidential Computing – protect data in use (e.g. in RAM).
- Quantum computing – protect secrets by watching for observer's principle/effect.
- Service – service-app only (not user)
- Shared – shared by team
- Lowest
- TPM, HSM [Cryptographic modules]
- (TPM, HSM) + Tamper-proof
- (TPM, HSM) + (Tamper-proof) + Self-destruct on attack
- Lowest
- For cryptographic modules that protect sensitive information
- For physical contractors to prevent physical tampering
- Tamper-proof control where the data on the device is automatically erased if it detects a physical attack
- Mnemonic 1: Low adoption of crypto in the physical world due to auto-erase
- Mnemonic 2: Low amount of crypto will cause physical ASIC to self-destruct
- Type 1 – Bare metal (hardware)
- Type 2 – Software
Mnemonic: Hardware first, then software
- 1-3: Something you know, something you have, something you are,
- 4-5: Somewhere you are, something you do
- (Comply with) Policy
- (Expected) Behavior
- (Standard and secure) Transport
- (Exchange is) Syntactic (and thus Understandable)
- (Data meaning is) Semantic
- Governance – Policy & Central control
- Orchestration – manage workloads
- Scheduling – Orchestrate on automatic schedule
- Distributed Resource Scheduling – VMWare-proprietary schedule optimization
- Scheduling – Orchestrate on automatic schedule
- Migration – from on-prem to cloud
The cloud data lifecycle consists of:
- Create
- Store
- Use
- Share
- Archive
- Destroy
- Letters: CS US AD
- Mnemonic: CompSci (of) US (created) ActiveDirectory
- Mnemonic 2: Cloud SUS ActiveDirectory
- RAW – Direct hands-on low-level access some drive (including access to S.M.A.R.T. and drive firmware!). Access directly:
You → Drive. Direct access means "Direct responsibility" for data remanence caused and found. - Volume-storage – High-level, abstracted ("abstractioned"), indirect, access to a (likely virtual) drive in a cluster:
You → Cluster of drives → (Subcluster of drives? It's a cloud architecture after all) → Drive- File-storage – Store files in an abstract vacuum – like on Cisco devices.
- Block-storage – Store blocks of data like on hard drives – you can orchestrate filesystems, NTFS Master File Tables, folders, files, file attributes etc.
- Ephemeral – RAM, RAMDisk (ephemeral volume), SWAP/Pagefile, temporarily LiveCD (whether RAM or HDD) destroyed after a session.
- Long-Term – HDD RAID or LTO tapes for use after session (for example, for work on next day and backup)
- Archival – (likely a subset of long-term storage) – good for archiving, but very slow data retrieval (hours/days).
- Structured – SQL Database
- Semi-structured – CSV, JSON, XML. Additionally, most often: Emails, HTML.
- Unstructured – Files and everything else
Just a KISS term: "Store data in many places"
A bit like RAID, can be used to achieve diametrically opposed goals:
- Availability (by orchestrating multiple copies of data), and
- [
Two-person control] Multi-person control (by splitting data into many pieces – thus potentially jeopardizing availability),
(Rough unofficial order)
- First, eDiscover your data.
- Prioritize and categorize – thus label the data.
- After labeling, tag the data.
- For CCSP: Tags for DLP; Labels for classification. (Tags explain the data, labels show sensitivity)
- After the data is tagged, set up DLP policies.
- Deploy DLP.
- Let DLP train on data. (you can assist, but for CCSP: DLP will work fine on its own)
- Anonymization – Remove sensitive data and make the subject anonymous (like a hacker group). Can be required by GDPR.
- Masking – Permanently mask and damage data, sub-options:
- Randomize – meaningful parts of data replaced with meaningless random data
- Hash –
Tim Abdiukovbecomes0x3CFDFAC8 - Shuffle – Everyone's data is shuffled, rendering data dirty and meaningless
- Mask – Card number
**** **** **** 9608expiry09/25cvv*** - Delete – Delete
- Tokenization – split sensitive and non-sensitive tables, use meaningless tokens to uniquely identify subjects where needed.
- IRM System – Internet (Requires) RSA Management – Protect sensitive data in transit.
Not to be confused with DRM
(same as CISSP, plus):
- Cloud site – much more cost-effective than hot site, however, takes longer to reallocate to. Is a viable replacement to Hot and Warm sites.
- 99.671%
- 99.741%
- 99.982%
- 99.995%
TIERS1234
123456789
-----6789
TIER
4321
9876
Cloud IR framework by CSA. Based on NIST 800-61,
4 stages of Incident Response,
- Preparation
- Detection & Analysis
- Containment, Eradication and Recovery
- Post-mortem
(Reminiscent of CISSP's DRMRRRL (DRM RRR L))
- Data plane – data traffic
- Control plane – control of low-level data flow configuration
- Management plane – high-level management and reporting
For designing a datacenter
- Ping = Ping to remote access (RDP/SSH)
- Power = Electric Power
- Pipe = ISP/internet/YouTube
(Not-so-serious guide)
- Step 1: Pick a legal heaven location
- Step 2: Redundancy is key
- Step 3: Do all nice things (ISC)² likes (protect people, create plans for a UFO attack)
- Step 4: Add LOTS of cables everywhere
- Step 5: ???????
- Step 6: PROFIT!
 |
|---|
| DREAD is forced away by STRIDE |
- DreaD – Damages (by attacker) – developed by Microsoft – replaced with STRIDE. DREAD is forced away by STRIDE
- STRIDE – Prime model by Microsoft.
- Tampering – always of data, not systems
- PASTA – for code. PASTA (spaghetti) code.
 |
|---|
| ATACMS... I mean ATASM |
- ATASM – Serial ATA (SATA) is serial – ATASM is Serial. Powerfully addresses surface like ATACMS. ATASM is also a metamodel. ATASM – ATA Serial Metamodel.
- Architecture (Analysis)
- Threats (existing: actors, goals)
- Attack Surface (existing)
- Mitigations (existing)
(Architecture Threats – Attack Surface – Mitigations)
- CSA – Cloud Security Alliance (organization)
- SBOM – List software's BOMbay-made libraries.
- SCA – Analytical Actions upon SBOM.
- SCM – Software Configuration Management (software in secure configuration – protect against scummy configurations like
allowlist *.*)
- Dynamic Secrets – JIT secrets.
- KMS – Key Management Service = Secrets Server.
- Planning Analysis (for ongoing project)
- Requirements Analysis (to finish project) [for CCSP: separate phase]
- Define (goals with user)
- Design (map technical control plane)
- Develop (implement)
- Test (verify)
- Deploy/Release/Maintain
PR DDD TD
- Security starts as early as Define stage.
- Security inserts controls at Design stage.
- SOAP – (Endless) SOAP opera of using Microsoft's XML – just like Microsoft's Internet Explorer.
- REST – RESTructured (modern) API using URIs
Neither is an IDS/IPS
- File Activity Monitoring (FAM) – Audit user activities intelligently (on) Files
- Database Activity Monitoring (DAM) – Audit user activities intelligently (on) Databases
- SWG (Secure Web) Gateway/Virtual Security Appliance (VSA) = Virtual Cloud Firewall host. Heavy duty, advanced functionality.
- API Gateway = API WAF/IPS and monitoring
- XML Gateway = XML (SOAP) WAF/IPS and monitoring.
- Crypto-shredding – Secure data deletion with double-encryption. Awesome for cloud.
- Full Disk Encryption (FDE) – BitLocker/dm-crypt
- Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) – encryption/decryption of data at rest, transparent to the legacy app (no app changes required)
- Functional – (rather facts-based) – Does app Function as expected
- Non-Functional – (rather bias-based) – Is the app bulky, too slow, susceptible to DDoS, and has an ugly UI?
- Static (SAST) – Code
- Dynamic (DAST) – Runtime
- IAST – Interactive AST – Agent on backend to show where the error is,
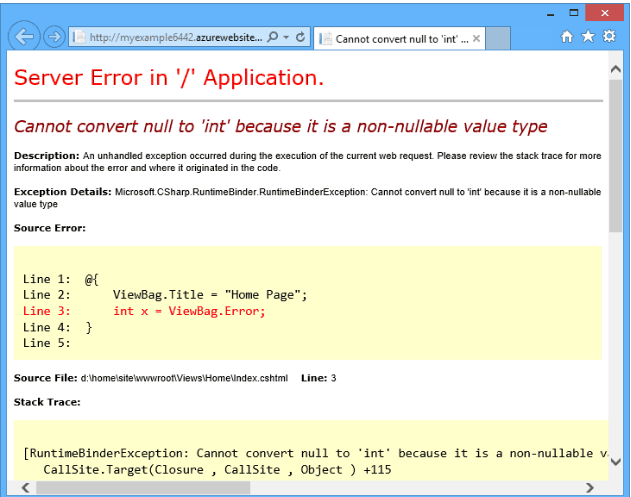 |
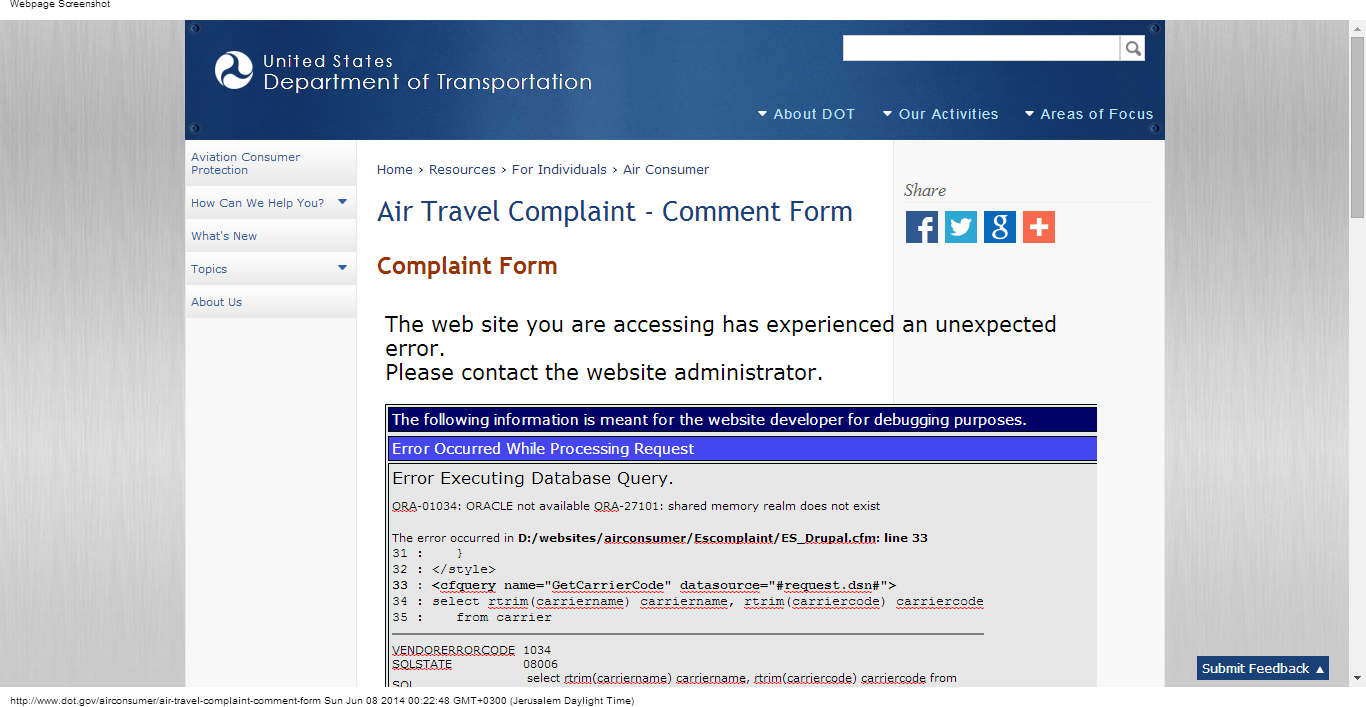 |
|---|---|
| IAST Example | IAST Example |
(taken directly from Alukos + my notes)
- OWASP Application Security – guidelines.
- OWASP's ASVS – AppSec metric Standard for: SAST, DAST, IAST. ASVS has 3 levels.
- Software Assurance Forum for Excellence in Code (SAFECode)
- Abuse Case Testing – (Intentional) misuse case testing (more info).
- (Abuse Case Testing ≈ Misuse Case Testing)
- ISO/IEC 20000-1 – IT Service Management (Directly to Domain 5, like ITILv4)
- Mnemonic 1: SLA downtime should all be 0s
- Mnemonic 2: At 0 years you work in IT Support, at 7 years you work in Security Management
- Mnemonic 3: 0s are for IT staff, 7s (as in Boeing 777) are for Security
- ISO/IEC 27001 – Base.
- ISO/IEC 27002 – Base lite (for gap analysis – fits like LEGO with 27001)
- ISO/IEC 27001 – Base.
- ISO/IEC 27017 – Base + Cloud.
- ISO/IEC 27018 – Base + Cloud + PII. HIGH level of assurance.
- ISO/IEC 27001 – Base.
- ISO/IEC 27701 – Base + Privacy focus
- ISO 17789:2014 –
5670917789 is a go-to number for who must do what in the cloud. (condensed info). - ISO 22301:2019 – Business Continuity management. Just in time for COVID.
- ISO 27036 – Supply Chain Risk Management (SCM/SCRM) for ISO 27001 users.
- ISO 31000 – Overall/general RMF
- ISO 27000-5 – InfoSec RMF
- OWASP CRS – Managed best firewall practices
- Variable – one value for a configuration parameter
- Template – Template.
templatewith many{{variables}}=> CI. - CI – Configuration Item – configuration for one app
- CMDB – Collection of CIs (Configuration Items) – configuration for many apps.
- CMB – Configuration Management Board (not baseline)
- Asset inventory.
- Create baseline.
- Establish a CMB board (like CAB).
- Deploy baselined assets.
- Document approved deviations (if needed).
- VPC – Virtual Private Cloud – cloud 'VLAN/intranet' area
- RDM – Release & Deployment Management (plan/policy)
- Virtual Client ≈ VDI
- CSA Domain 3 – Legal concerns: security, privacy, SLAs.
- NIST IR 8006 – Guidance on DFIR in the cloud.
- ISO/IEC 27037 – Initial: Identify, Collect, Preserve e-evidence (Digital Forensics)
- ISO/IEC 27050 – eDiscovery
- ISO/IEC 27041 – Investigate
- ISO/IEC 27042 – Analyze (evidence)
- ISO/IEC 27043 – Principles & Processes
IAPP – Investigate, Analyze, Principles&Processes
DF-IAPP
37-1233
Also, IAPP – International Association of Privacy Professionals. Another acronym found in CCSP, about similar topics. So, privacy=IAPP. eDiscovery=IAPP.
- CLOUD Act 2018 – FBI can access CLOUD even outside the U.S. (in conflict with GDPR)
- Sentiment Analysis – AI + ML to gain people's Sentiment on social media (Cambridge Analytica targeted Sentiment to Donald Trump)
Trick: Replace "Problem" with "Bad Driver".
Bad Drivers are a Problem – car crashes as a result of their driving are Incidents
All problems bad drivers potentially cause incidents, but not all bad drivers result in incidents.
Trick 2: My boyfriend is a walking problem! He'll eventually beat me down.
(This is optional knowledge, but commonly referenced)
- Designing services for Availability
- Availability Testing
- Availability Monitoring and Reporting
Is to Recover
 |
|---|
| Manage highways & their components! |
- Process Owner ≈ Data Owner
- Process Architect ≈ Data Custodian
- CSI Manager – Mid-level managers who just ensure ITSM (clue: mid-level managers are suckers for fancy job titles)
- Identification service requirements
- Agreement sign-off and service activation
- Service-level monitoring and reporting
- Maintenance of SLM framework
- ITIL "recovery plan" – Detailed master plan for BCP/DRP, can also include data restoration to RPO.
- BCP Strategy – Strategy for business (functions)
- IT Service Continuity – Specific cases continuity plan (i.e., if a specific host failed)
- BCP Invocation Guidelines – Invocation
- Only scan your internal systems
- Don't impact other customers
- Date and time – for detailed scanning
Capacity management of YOUR:
- Business
- Service
- Component
- Stored Communications Act (SCA) 1986 – Stored Communications (Discord, email) are private communications. Dated, but in force.
- GAPP – U.S. Optional (gapped) GDPR
- Privacy Shield – DEAD privacy partnership between the US and EU (For CCSP OPT – still alive)
- BICSI – like SCSI – cables organization
 |
|---|
| Electro NERD |
- NERC/CIP – Electro NERD (and simp)
- SAS 70 – outdated like the 70s SOC 1
- SSAE 16 – outdated SSAE 18
- AICPA (USA) → SSAE → SOC (1/2/3)
- IAASB (EU) → ISAE → ISAE 3402
- ISAE ≈ SSAE
- ISAE 3402 ≈ SSAE SOC 2
- FedRAMP – Federally screened CSPs for being RAMPs
CSA → STAR
CSA STAR – for CSPs. Lightweight assurance method used by CSP, customer, auditor, consultant.
- Self-assessment (internal audit, low assurance)
- Third-party audit (external audit, high assurance)
- Continuous auditing
CSA STAR – SEC (Self, External, Continuous)
- ISMS – Identify and monitor risk
- IISCS – Mitigate risk
Trick: ISMS is a radar that sends SMS, IISCS is a fighter jet with 2 I-shaped harpoon rockets and 2 S-shaped hooks.
 |
 |
|---|---|
| ISMS | IISCS |
- Profile – Risks (profiles) that stand up to the organization.
- Posture – How well organization holds (poses) against risks.
- Appetite = Tolerance – How hungry is the organization to take more risk.
- Treatment = Management
- Data Protection Officer (DPO) – Mandatory compliance officer
- Data Controller = Data Owner (controls data life)
- MSA – Master Services Provided. Masters of Airlines.
- SOW – Slave (small) Jobs Worked-on.
- MOU – Completely different beast – Confirms understanding of each-other's "moo" (talk).
- SLA – Performance Expected
- OLA – Like Windows OLE (internal, under-the-hood) – under-the-hood 'SLA' internal agreement between (C)SP and its brokers.
- NDA – Confidential clauses (SLA is not suitable)
- BPA – BiPlane Joint-Venture agreement
- Viability – Vendor may die like Viacom
- Lock-in – Proprietary infrastructure forces you to stay with vendor
- Lock-out – cannot access living vendor. Can also sometimes mean "Viability".
- PIA – like BIA – Privacy impact analysis.
- Doctrine of Proper Law – properly defines jurisdiction of law applied in a case
- CSA Cloud Controls Matrix (CCMv4) – Cloud Risk Management framework by CSA, mapped to trusted organizations&frameworks like ISO, ISACA, PCI. Simplify regulatory compliance with CSA's prime product!
- Mouthful Trick: ISACA has CISM, CSA has ISACA in CCM
- CSA "Egregious 11" – Top cloud threats
- CSA Checklists – VERY SAFE baseline guides
- CSA CIR – Cloud IR framework by CSA. Based on NIST 800-61.
- CSA Domain 3: Legal Issues – Security guidance of legal issues
- CSA STAR – Lightweight compliance standard. Level 1 – Internal audit. Level 2 – External audit.
- CSA CAIQ – Consensus Assessment Initiative Questionnaire – optional IQ questions to access CSP Security
- anti-DDoS: CDN > CSP's anti-DDoS capabilities
- API anti-DDoS: API Gateway > IPS [API Gateway can help understand DDoS traffic]
- anti-DDoS: Authentication > Scale
- AuthN of (cloud) hosts: Host digital certificates
- SSO – One org (+IDaaS); Federation – 2+ orgs.
 |
|---|
 |
| IPS - IaaS, PaaS, SaaS |
- IaaS – Many hosts Infrastructure. Best if your app really requires complex infrastructure (such as 5 databases, 10 firewalls, etc).
- PaaS – One host. Best if: your app can run on 1 host, and you are concerned about: liability, security, time, and money wasted configuring code and infrastructure. PaaS is much more liability-optimal than IaaS. PaaS is the easiest to administer. PaaS your code – so IaC is PaaS.
- SaaS – Service. Service is the most affordable, has least liability to the customer and the cheapest, but it takes time to configure code to work with SaaS and cloud.
Finally,
- FaaS – serverless (fatherless) IaC, cheaper and simpler than PaaS.