This repository contains introductory topics for Convolutional Neural Network and Computer Vision with TensorFlow
CNN, short for, Convolutional Neural Network, is a special kind of neural network which is used for computer vision (detecting patterns in visual data).
Since we are surrounded by cameras, capturing images and videos of every moment, we have huge of amount of data in image (or video format), and to detect patterns and apply algorithms to make a productive use of those type of data, we need specific kind of model architectures to fulfil our need, and that is what Convolutional Neural Network architectures comes into action.
For example, you might want to:
- Classify whether a picture of road contains car 🚗 or bicycle 🚲 or truck 🚛 (we're going to do this)
- Detect whether or not an object appears in an image (e.g did a specific car pass through a security camera?)
In this repo, we're going to follow the TensorFlow modelling workflow we've been following so far whilst learning about how to build and use CNNs.
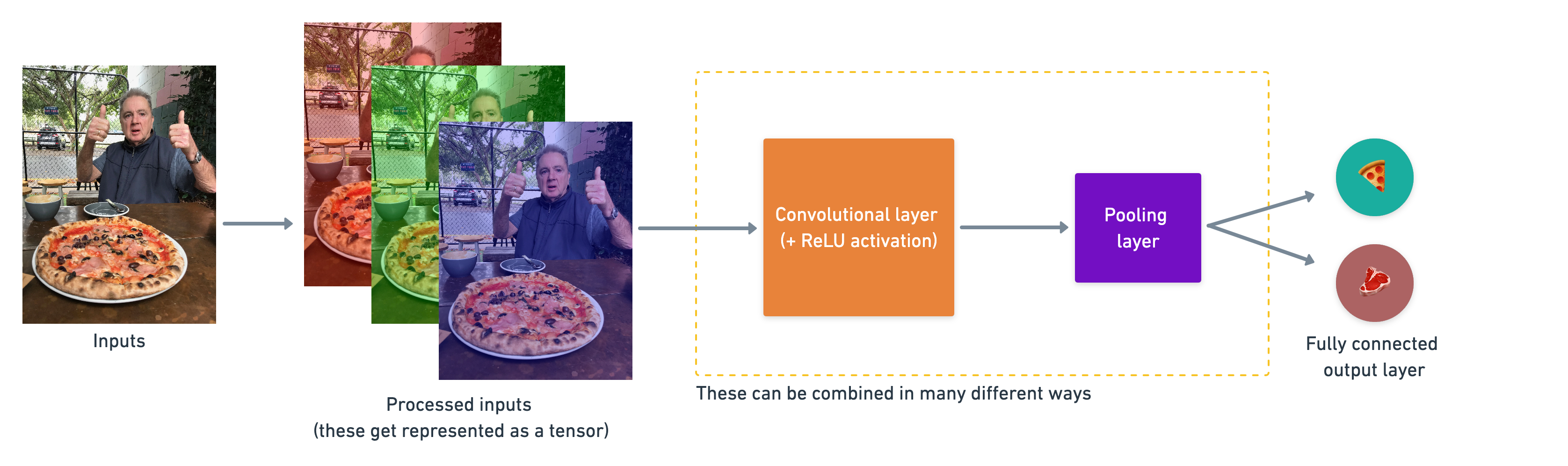
Note: Convolutional Neural Network learn features and patterns by themselves, we don't need to tell them learn this or that feature.
| Hyperparameter/Layer type | What does it do? | Typical Values |
|---|---|---|
| Input image(s) | Target images you'd like to discover patterns in | Whatever you can take a photo(or video) of |
| Input layer | Takes in target images and preprocess them for further layers | input_shape = [batch_size, image_height, image_width, color_channels] |
| Convolution layer | Extracts/learns the most important features from target images | Multiple, can create with tf.keras.layers.ConvXD (X can be multiple values) |
| Hidden activation | Adds non-linearity to learned features (non-straight lines) | Usually ReLU |
| Pooling layer | Reduces the dimensionality of learned image features | Average tf.keras.layers.AvgPool2D or Max tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D |
| Fully Connected layer | Further refines learned features from convolution layers | tf.keras.layers.Dense |
| Output Layer | Takes learned features and outputs them in shape of target labels | output_shape = [number_of_classes] (e.g. 3 for pizza, steak or sushi) |
| Output Activation | Adds non-linearities to output layer | tf.keras.activations.sigmoid (binary classification) or tf.keras.activations.softmax |
Specifically, we're going to go through the follow with TensorFlow:
- Getting a dataset to work with
- Architecture of a convolutional neural network
- A quick end-to-end example (what we're working towards)
- Steps in modelling for binary image classification with CNNs
- Becoming one with the data
- Preparing data for modelling
- Creating a CNN model (starting with a baseline)
- Fitting a model (getting it to find patterns in our data)
- Evaluating a model
- Improving a model
- Making a prediction with a trained model
- Steps in modelling for multi-class image classification with CNNs
- Same as above (but this time with a different dataset)
- Spend 20-minutes reading and interacting with the CNN explainer website.
- What are the key terms? e.g. explain convolution in your own words, pooling in your own words
- Play around with the "understanding hyperparameters" section in the CNN explainer website for 10-minutes.
- What is the kernel size?
- What is the stride?
- How could you adjust each of these in TensorFlow code?
- Take 10 photos of two different things and build your own CNN image classifier using the techniques we've built here.
- Find an ideal learning rate for a simple convolutional neural network model on your the 10 class dataset.
-
Watch: MIT's Introduction to Deep Computer Vision lecture. This will give you a great intuition behind convolutional neural networks.
-
Watch: Deep dive on mini-batch gradient descent by deeplearning.ai. If you're still curious about why we use batches to train models, this technical overview covers many of the reasons why.
-
Read: CS231n Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition class notes. This will give a very deep understanding of what's going on behind the scenes of the convolutional neural network architectures we're writing.
-
Read: "A guide to convolution arithmetic for deep learning". This paper goes through all of the mathematics running behind the scenes of our convolutional layers.
-
Code practice: TensorFlow Data Augmentation Tutorial. For a more in-depth introduction on data augmentation with TensorFlow, spend an hour or two reading through this tutorial.