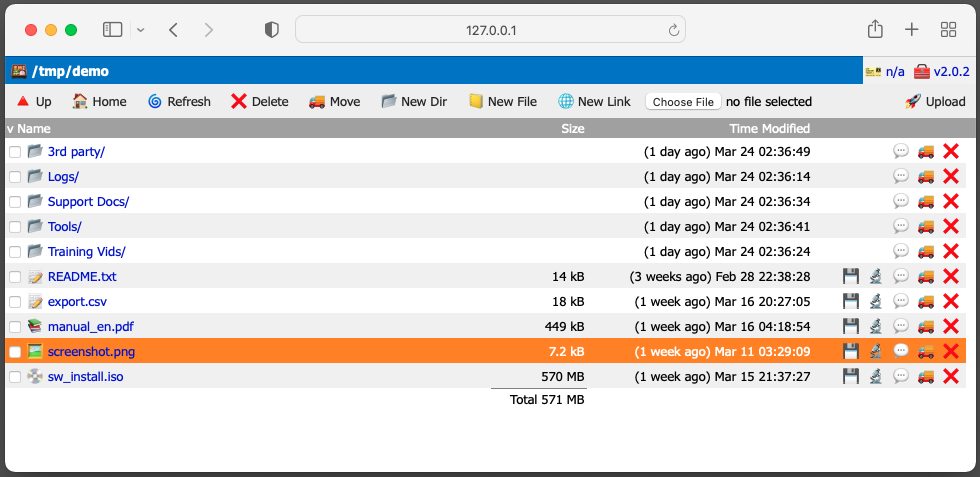
WFM is a lightweight web based file management application. It allows to perform regular file and folder operations such as upload, download, rename, delete files and organize directory tree structure using standard web browser. Text, markup and markdown files can be edited directly in the browser.
An integrated GIT client can track and auto commit all file change operations into a GIT repository.
This app was initially used as a web front end for an FTP server. However since you can edit html and markdown documents over the web and there is a GIT backed version control, you can think and use WFM as a small Content Management System (CMS).
WFM can also be used as a personal cloud, for taking notes, managing files, bookmarks or as a front end of a NAS servers.
This program is written using portable C code and compiles natively for many flavors of Unix. It runs as a cgi-bin application on most httpd servers and does not require PHP, Perl, Python or any other interpreted language. It's a single binary application with all icons embedded inside. It's very small and lightning fast. I runs on resource constrained embedded computers or legacy systems. For compatibility with older browsers it outputs certified HTML 4.01. JavaScript is completely optional and only used for non-essential luxuries. Tested using BrowserStack.
WFM begun its life around 1994 as a Perl CGI script for CERN httpd server to allow uploading and managing customer logs by field support engineers over the web and as a front end to FTP servers. Later rewritten in C language, when CGIC library and Apache httpd were released. Up to 2015 WFM has been a closed source commercial application, used for lighweight document management and supported by a few companies. WFM is now released as open source.
WFM binary is self-contained including all icons/images. You only need to copy the compiled wfm binary (with any name) to your cgi execution directory, usually cgi-bin. Include a config file of the same name as the binary file plus .cfg extension. Example:
/home/user/web/cgi-bin
wfm
wfm.cfg
Edit the .cfg file according to your needs.
Point your browser to http://x.x.x.x/cgi-bin/wfm and you are done.
This application was designed with multiple instances in mind. An instance is made by copying or linking WFM binary with a different name. In a more advanced configuration different instances can suexec to different users.
In basic form each instance reads it's configuration file of instance name + .cfg extension from the current working directory. For example if you decide to use "ftpadmin" as name of the executable (or link) it will read file named "ftpadmin.cfg" for the configuration. Below is a simple, self-explanatory configuration file example:
# tagline or application name
tagline=Snake Oil File Exchange
# home directory, typically local directory on the server or SMB/NFS mount
directory=/home/user/wfmdata
# recursively calculate directory sizes - only enable if you have
# fast disk (eg. SSD), large cache or a small directory tree structure
#recursive-du=true
# large file set makes the move dialog display only a reduced directory tree
# instead of a complete tree from the whole repository
#large-file-set=true
# favicon / application icon, must be one of the embedded/compiled icon files
# by default wfmicon.gif
#favicon=home.gif
# When clicking on txt file - edit instead of download by default
#txt-default-edit=true
# Edit any file as it was txt
#edit-any-file=false
# optional browser url prefix - aka "external link" - if defined, file
# names will be glued to it giving option to be opened directly with the
# external link button without going through cgi routines
#browser-url=http://x.x.x.x/files/
#browser-url=ftp://x.x.x.x/pub/
# access lists
# acl format is access-type=level:check, one per line
# type is either access-ip, access-md5pw or access-htauth
# level is ro|rw
# check is ip address, username or * for any ip or user
# md5 format is username:md5hashof(username:password)
# to generate this use: echo -n "foo:bar" | md5
# htauth is for http basic/digest auth, use username or * for any user
# htauth requires externally (httpd) defined auth and require directive
access-ip=ro:*
access-ip=rw:127.0.0.1
# guest / guest
access-md5pw=ro:guest:d3c3b5cb55d3c6d0c6122eedccc3dcf3
# admin / password
access-md5pw=rw:admin:73eff6386ce2091b5ca702fc007e1da9
access-htauth=ro:*
access-htauth=rw:admin
If you use mixed readonly and readwrite access then then in order to authenticate click on the lock sign on right side of the top status bar.
For enterprise users LDAP/Active Directory is supported.
Refer to mod_authnz_ldap
with basic / digest authentication. To allow a specific LDAP group or DN use
Require ldap-group
or Require ldap-dn
and access-htauth=:rw:* in wfm.cfg.
Copyright (c) 1994-2018 by Antoni Sawicki
Copyright (c) 2018-2019 by Google LLC
Copyright (c) 1996-2011 by Thomas Boutell and Boutell.Com, Inc.
Copyright (c) 2002 by Aladdin Enterprises
Copyright (c) 1999-2009 by Paul Johnston
Copyright (c) 2010 by Yusuke Kamiyamane
WFM implemented by Antoni Sawicki
CGIC Library by Thomas Boutell
Server Side RFC 1321 implementation by L. Peter Deutsch
Client Side RFC 1321 implementation by Paul Johnston
Icons by Yusuke Kamiyamane
URL Encoding routines by Fred Bulback
Web browser testing by BrowserStack