Please see the full documentation at https://inverselight.github.io/ValoMC/
ValoMC is an open source Monte Carlo code that can simulate the passage of visible and near infrared range photons through a medium. The implementation is based on the photon packet method. The simulation geometry is defined using unstructured (triangular or tetrahedral) mesh. The program solves the photon fluence in the computation domain and the exitance at the domain boundary. It is capable of simulating complex measurement geometries with spatially varying optical parameter distributions and supports several types of light sources as well as intensity modulated light. Furthermore, attention is given to ease of use and fast problem set up with a MATLAB (The MathWorks Inc., Natick, MA) interface. The simulation code is written in C++ and parallelized using OpenMP.
ValoMC is being developed by Aleksi Leino, Aki Pulkkinen, Tuomas Lunttila and Tanja Tarvainen at University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland.
If you use ValoMC in your work, please reference it with the following citation:
NEW: Please see the end of this README file for a list of recent changes.
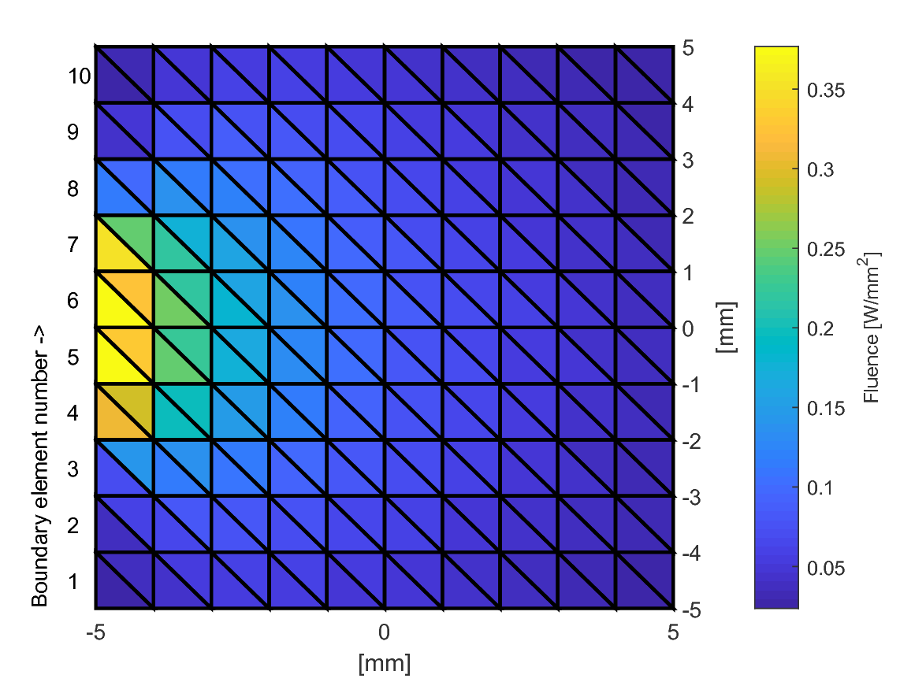
The following MATLAB code snippet sets up and runs a Monte Carlo simulation in a rectangular region
xsize = 10; % width of the region [mm]
ysize = 10; % height of the region [mm]
dh = 1; % discretisation size [mm]
vmcmesh = createRectangularMesh(xsize, ysize, dh);
% Create a light source
% - Set a light source from boundary elements 4 to 7
% - Photons are launched at a random angle so that all angles have a cosinic distribution
vmcboundary.lightsource(4:7) = {'cosinic'};
% Give optical parameters
% - Constant optical parameters are set troughout the medium.
% - Alternatively, optical parameters can set be for each element using indexing
vmcmedium.absorption_coefficient = 0.01; % [1/mm]
vmcmedium.scattering_coefficient = 1.0; % [1/mm]
vmcmedium.scattering_anisotropy = 0.9; % anisotropy parameter g [unitless]
vmcmedium.refractive_index = 1.3; % refractive index [unitless]
% Run the Monte Carlo simulation
solution = ValoMC(vmcmesh, vmcmedium, vmcboundary);
% Plot the solution using MATLAB
patch('Faces',vmcmesh.H,'Vertices',vmcmesh.r,'FaceVertexCData', solution.element_fluence, 'FaceColor', 'flat', 'LineWidth',1.5);
- Obtain the latest source code using git or direct download
git clone https://github.com/InverseLight/ValoMC/
- Open MATLAB and type
addpath('ValoMC/')
where ValoMC/ is the the folder from the zip archive or obtained using git.
- Type
cd ValoMC
compile_vmc_mex
to compile mex files for MATLAB. This assumes that a working C++ compiler has been installed and compiles a serial version of the code. See below on instructions how to obtain a suitable compiler such as GCC and how to compile the parallel version.
You can now run the examples in the examples/ -folder. The next time you use ValoMC, the mex files will be already compiled and you simply need to repeat step 2 to continue using ValoMC.
- Test the installation
Try to run e.g. simpletest.m.
cd examples
simpletest
If you receive error messages, it most likely means the mex compiler has not yet been set up in MATLAB. For instructions how to set up the mex compiler, please refer to MATLAB manual and 'troubleshooting' below.
Messages along the lines 'libstdc++.so.6: version GLIBCXX_3.4.21 not found' most likely means that MATLAB does not support the compiler version. For instructions how to compile the mex files with a specific gcc version, see 'troubleshooting'
CMake is a program that can automatize the compilation process. It can be obtained here. ValoMC can then be installed from command prompt, at 'ValoMC/'
cmake .
cmake --build .
This will build the external executables as well as the mex files. It will try to compile the parallel versions. If problems persist, see below how to compile the external executable and the mex files manually and how to obtain a suitable compiler. To use CMake with a specific compiler, you can use e.g.
cmake -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=/usr/bin/g++-4.9
cmake --build .
The external executable can be used to run ValoMC e.g. on a cluster without MATLAB (see example: 'Generating input for the external executable'). The source code for the external executables are located in 2d/cpp/ and 3d/cpp/. These folders contain Ubuntu makefiles for reference. CMake also builds the external executables. The 2D code can be manually built using
g++ MC2D.cpp -o MC2D.a -O3
The multi-threaded (OpenMP) version can be compiled with
g++ MC2D.cpp -o MC2D.a -O3 -DUSE_OMP -fopenmp
Generalization to other compilers than GNU ones should be straightforward.
Linux (gcc): To compile with OpenMP (multithread) support (from MATLAB prompt, at 'ValoMC/'):
mex -DUSE_OMP cpp/2d/MC2Dmex.cpp COMPFLAGS='\$COMPFLAGS -fopenmp' CXXFLAGS='\$CXXFLAGS -fopenmp' LDFLAGS='\$LDFLAGS -fopenmp'
mex -DUSE_OMP cpp/3d/MC3Dmex.cpp COMPFLAGS='\$COMPFLAGS -fopenmp' CXXFLAGS='\$CXXFLAGS -fopenmp' LDFLAGS='\$LDFLAGS -fopenmp'
Windows (Visual Studio):
mex -DUSE_OMP cpp/2d/MC2Dmex.cpp COMPFLAGS='\$COMPFLAGS /openmp /O2' CXXFLAGS='\$CXXFLAGS ' LDFLAGS='\$LDFLAGS '
mex -DUSE_OMP cpp/3d/MC3Dmex.cpp COMPFLAGS='\$COMPFLAGS /openmp /O2' CXXFLAGS='\$CXXFLAGS ' LDFLAGS='\$LDFLAGS '
To install ValoMC, MATLAB mex system must be set up. It needs to have an external C++ compiler to work.
For example, the TDM gcc compiler can be obtained from this site.
After installation you can use
setenv('MW_MINGW64_LOC','C:\TDM-GCC-64');
mex -setup
to inform MATLAB of the location. Visual Studio can be obtained [here]https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/ For Visual Studio, OpenMP (parallelisation) support can be enabled as follows
mex -DUSE_OMP cpp/2d/MC2Dmex.cpp COMPFLAGS='\$COMPFLAGS /openmp'
To get gcc in Ubuntu you can use
sudo apt-get install g++
sudo apt-get install gcc
in shell. Depending on your MATLAB, it might be necessary to obtain an older version of the compiler. For example, if MATLAB supports g++ 4.9 you can install it by
sudo apt-get install g++-4.9
sudo apt-get install gcc-4.9
and use (from MATLAB prompt, at 'ValoMC/'):
mex -v GCC='/usr/bin/gcc-4.9' -DUSE_OMP cpp/2d/MC2Dmex.cpp COMPFLAGS='\$COMPFLAGS -fopenmp' CXXFLAGS='\$CXXFLAGS -fopenmp' LDFLAGS='\$LDFLAGS -fopenmp'
6.3.2022: A potentially important error was spotted in the 3d code and fixed. Please see this issue and the news section in the frontpage.