Supporting repository for article "Software Evaluation for 'de novo' Detection of Transposons"
Datasets used for testing the TE de novo detection tools:
| Dataset | Sequences | Length | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human genome | chromosome 21 | 46.7 Mb | GRCh38 |
| Zebrafish | chromosome 1 | 137.5 Mb | GRCz11 |
| Fruit fly | whole genome | 137.6 Mb | dm6 |
| Simulated data | simulation | 100.1 Mb | - |
Requirements:
- Python 3.x
- Biopython
- NumPy
- PyYAML
Scripts to simulate a DNA sequence with TEs with different degrees of divergency and fragmentation. It uses a configuration file to specify the type and number of copies of each TE, the level of divergency and fragmentation. The output is a fasta file with a randomly generated sequences with randomly located TEs, and a GFF file reporting the coordinates and divergency of the TEs.
random_sequence_TEs.py : script needs config.yml and the files specified there (repeats_list and repeats.fa). Outputs a fasta sequence with random TEs and an annotation file (GFF).
random_nest_TEs.py : script run after random_sequence_TEs.py, requires the same files. Outputs a fasta sequences with nested TEs and an updated GFF file.
repeats_list : configuration file with a row for each TE and 9 columns:
- id_of_TE : this must be the id of a sequence from the repeats.fa file
- number_of_repeats : how many copies of the TE are expected
- %_identity : percent of divergency expected among the copies of these TEs
- std_dev : standard deviation of the percent of identity
- %_indels : percent of indels expected in these TEs
- has_TSD? : boolean value that allows a to simulate a short random TSD for the TEs
- real_length : real length of the original TE from the file repeats.fa
- %_fragmentation : percent of copies that are fragmented
- %_nested : percent of copies that can be nested
config.yml : configuration file in YAML format with prefixes for the output, size of base sequence, location of repeats_list and fasta files, gc_content and seed (optional).
- prefix: this is the prefix used for the initial output with simple TEs
- prefix_nest : prefix used for the sequences with nested TEs
- seq_length : length of the base sequence, previous to the TE insertions
- rep_fasta : fasta file with the sequences of the TEs that are going to be inserted in the base sequence
- rep_list : configuration file that specifies the properties of the TEs being added
- seed : a seed value for reproducibility of the results
- gc_content : percent of GC content expected in the base sequence, before adding the TEs.
repeats.fa : fasta file with the TE sequences that are going to be used in this simulation. The id of the sequences must be the same as the one in the repeats_list file.
First run inserts TEs in base sequence:
e.g.: ./random_sequence_TEs.py (expects repeats.fa, config.yml and repeats_list in the same directory)
output: prefix_out_repeats.gff, prefix_out_repeats.fasta (only modified repeats), prefix_out_sequence.fasta (full sequence)
Next run nests TEs in the previous sequence:
e.g.: ./random_nest_TEs.py (expects repeats.fa, config.yml, repeats_list, prefix_out_repeats.gff in the same directory)
output: prefix_out_repeats_nest.gff, prefix_out_sequence_nest.fasta (full sequence)
- As an example a RepeatMasker output can be transformed into a GFF file using the following command:
awk 'OFS="\t" {print $5, "software_tool", "any_key", $6, $7, ".", "." , ".", "ID="$10"_"$11}' rmasker.output > rmasker.gff- Then, to avoid reporting twice overlaped regions, they must be merged (for example using bedtools merge command) :
bedtools merge -i rmasker.gff -c 2,3,7,8,9 -o distinct | awk 'OFS="\t" {print $1, $4, $5, $2, $3, $6, $7, $8}' | sed 's/ID=//2g' > rmasker.merged.gff
repeat_analysis.py : script that compares the gff of an annotation to a reference and outputs the percent annotated for each entry, a global confusion matrix and the Matthews Correlation Coefficient
e.g.: ./repeat_analysis.py reference.gff repeats.gff 41500000 (genome size in nucleotides)
Requirements:
- R 3.4.x
- ggplot2
- gridExtra
- yaml
gff_tracks/gff_tracks.R : Main file that generates the plots. gff_tracks/config.yml : Configuration file, must be in the same directory as gff_tracks.R.
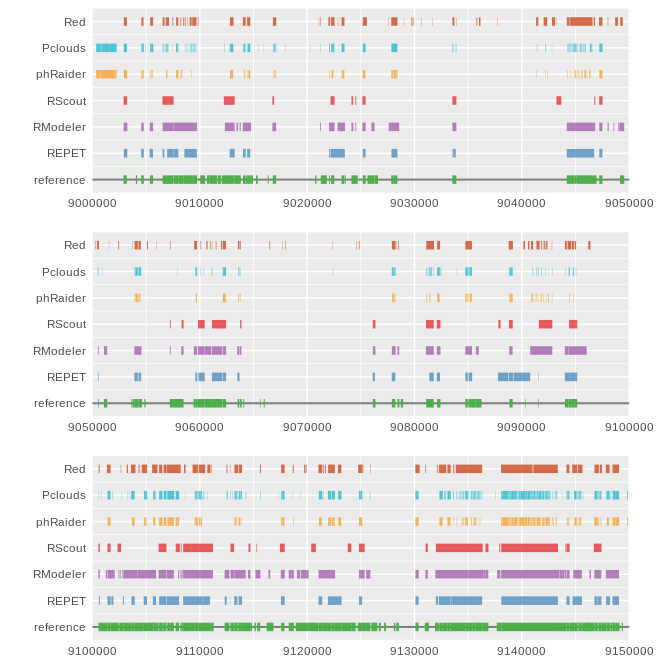
This script allows to plot coordinates from a GFF file as colored line segments in a track. Multiple tracks can be used to plot coordinates from multiple GFF files, and alos multiple plots are allowed.
Important: The GFF files must have only the lines from the coordinates that are going to be plotted, as the script expects only the informative lines.
The idea behind this kind of plot is to have a fast visual comparison of different results obtained by different software tools on the same dataset.
The config.yml file must be used to setup the location of the GFF files, and customize the plots. The parameters necessary to set in config.yml are:
- gff : the list of GFF files to plot
- labels : this are the labels of the plot but need to be the same as the "source" or 2nd column of a GFF file, must be in the same order as the GFF files set before.
- colors: list of color for each GFF file coordinates, it follows the order of the GFF files set before.
- coor:
- start : initial coordinate from the GFF
- step : length of the sequences to be plotted
- repeat : how many plots are shown, also how many steps are plotted
e.g.: Rscript gff_tracks.R (expects config.yml in the same directory)
output: plot.png
Fig 1. Plot generated using this script. It uses seven different GFF files, one for each track and allows a simple comparions of results coming from different software tools.