- Overview
- Requirements and notes
- What this module affects
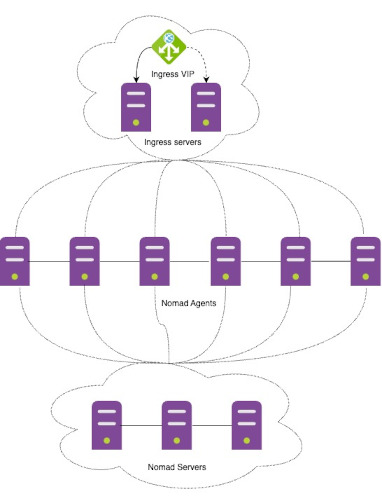
- Architecture diagram
- Usage and examples
- NICs management
- Firewall
- Add CNIs to Nomad
- Register your services to Consul
- Limitations
- Notes
This module leverages the configuration of the CNI networks, using VXLAN and macvlan network driver on the Nomad agents.
Whilst other CNI operators uses key pair databases to store/retrieve the configurations, this module does two things:
- use your Puppet hieradata backend (whatever it is)
- splits the network in multiple segment, and assigns one segment for each agent. There is a function which can determine the size of the networks based on the number of agents, otherwise the
min_networksparameter can be used to create more networks than necessary (to create room for future cluster expansion, avoiding disruptions).
The module will also create a Bridge interface and a VXLAN interface on each Agent and for each CNI network, and the VXLANs will be interconnected and bridged with the host network.
In addition to the requirements listed in metadata.json, this module requires PuppetDB.
You also need to enable IP forward:
# cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
1The CNI configuration has a stanza for the DNS settings, but these settings are not working for me with Nomad. If needed you can specify the settings for the DNS in Nomad.
- Installs the CNI network plugins (via url)
- Installs configuration/scripts for every CNI network (
/opt/cni/vxlan/.d/{un,mult}icast.d/*.sh) - Creates a Bridge and a VXLAN for every CNI network (managed via custom script)
- Optionally, segregates and interconnects CNIs (by default they're open and interconnected)
basic usage
include nomad_cniif you want to change the download URL and you want to specify the version to install:
class { 'nomad_cni':
cni_version => '1.5.0',
cni_base_url => https://server.example.org/cni/,
}agent_regex will only match nodes within the same Puppet environment. Alternatively you can use agent_list to supply a list of nomad agents.
Using the following resource declaration you can setup two CNI networks, using the unicast vxlan technology:
nomad_cni::bridge::unicast::v4 {
default:
agent_regex => 'nomad0';
'cni1':
network => '192.168.1.0/24';
'cni2':
network => '172.16.2.0/22';
}Multicast would work much better, but in my environment it wasn't reliable. Feel free to experiment and contribute to this module.
in most cases it is unlikely to use all the IPs on the same Agent. For instance a 24 bit network, split by 3 agents, will give 83 IPs per Agent.
You may decide to overcommit the number of networks, to foresee and allow a seamless extension of the Nomad cluster. If you do not use this parameter, when you extend the cluster, the CNI needs to be reconfigured on all the agents, and you'll experience an outage (the containers loose connectivity and need to be respawned).
In the example below the 24 bit network will be split by 10, and it will assign 24 IPs for each network, regardless of the number of agents:
nomad_cni::bridge::unicast::v4 {
default:
min_networks => 10,
agent_regex => 'nomad0';
'cni10':
network => '192.168.3.0/24';
'cni20':
network => '172.16.4.0/22';
}The interfaces are managed using custom scripts, triggered by systemd.
-
Why not using systemd-networkd? In Ubuntu the main interface is already declared in netplan, and it's being ignored by systemd.
-
Why not using netplan? Netplan does not support yet unicast mode for VXLAN and bridge FDB entries.
The firewall settings are applied via the module puppetlabs/firewall.
The rules are being created under a custom chain, so they can be purged without affecting the default chain.
manage_firewall_nat is set to true. This is kind of mandatory. Without this rule the containers won't be able to connect outside.
If your firewall is set to drop connections that are not specifically declared, you can set manage_firewall_vxlan to true, to open UDP port 4789 among the Nomad Agents.
By default all CNIs are interconneccted. CNIs segregation is achieved by setting cni_cut_off to true:
class { 'nomad_cni':
cni_cut_off => true
}If you applied CNI segregation (cni_cut_off set to true), you can interconnect some of them using the following code:
nomad_cni::cni_connect { ['cni1', 'cni2']: }If you need encryption, or you need to interconnect only certain services within the CNI, you could use Consul Connect
The client stanza of the Agent configuration has a section called host_network.
Using the host_network, the job will be registered on Consul using the IP belonging to the host_network and will open a socket only on the host_network.
If you do not follow these steps the socket will be open either on the Agent IP, on the bridge, and on the Container, and you defeat the purpose of using CNI.
This module provides a function that can be used to pass the host_network parameter to VoxPupuli Nomad Module.
Assuming that the Nomad agent is listening on eth0, you can add the following key in your Nomad configuration hash
host_network => nomad_cni::host_network_v4('eth0')as a result, you'll get something like the following in the agent configuration
"host_network": [
{
"public": {
"cidr": "183.184.185.186/22",
"interface": "eth0"
}
},
{
"foo": {
"cidr": "192.168.2.1/24",
"interface": "vxbr11882895"
}
},
{
"bar": {
"cidr": "192.168.3.1/24",
"interface": "vxbr5199537"
}
},
... and so on ...
]If you have dual stack IP configuration, the network that it's not defined will be the default network for your jobs.
If you want to default to your host ipv4, you need to include ipv6 instead, and you can do as following:
host_network => nomad_cni::host_network_v4('eth0', 'v6')If you have a host_network called foo, this is how the network stanza looks like in your job (as you can see, you no longer need to use dynamic ports with CNI isolated networks)
network {
mode = "cni/foo"
port "grafana" {
static = 3000
host_network = "foo"
}
}If you register the service at task level, using the default settings, Nomad will register to Consul the IP of gateway of the CNI (instead of the IP of the container) and the service will be unreachable.
The service block must be defined at group level, and it must contain address_mode = "alloc" either in the service block and in the check block:
service {
name = "test-service-http"
provider = "consul"
address_mode = "alloc"
port = "http"
tags = ["tcp"]
check {
name = "http_tcp_check"
address_mode = "alloc"
type = "tcp"
port = "http"
interval = "5s"
timeout = "2s"
}
}- there is an attempt to use IPv6 in this module, although only IPv4 is currently supported
- maximum supported version of
puppetlabs/firewallis 6.0.0 - changelog not yet handled
- spec test isn't bad but it has limitations, due to reliance on PuppetDB
- feel free to test, contribute and raise issues