Contact : [email protected]
You can install the latest version of the package by cloning the repository and via the setup.py script (pip install .)
- You can install gwaihir by typing
pip install -U gwaihirin your command line. A stable version from the master branch uploaded to pypi.org will be used (https://pypi.org/project/gwaihir/) - Otherwise, you can install the latest commit of the package by cloning this repository and typing
pip install .in the terminal (you must be in the same directory as thesetup.pyscript), this will allow you to have the latest updates.
Here is a link to a poster that tries to present Gwaihir: Poster_Gwaihir.pdf
To increase the width of the cells in Jupyter Notebook:
from IPython.core.display import display, HTML
display(HTML("<style>.container { width:75% !important; }</style>"))To avoid automatic cell scrolling:
%%javascript
IPython.OutputArea.prototype._should_scroll = function(lines) {
return false;
}To open the GUI:
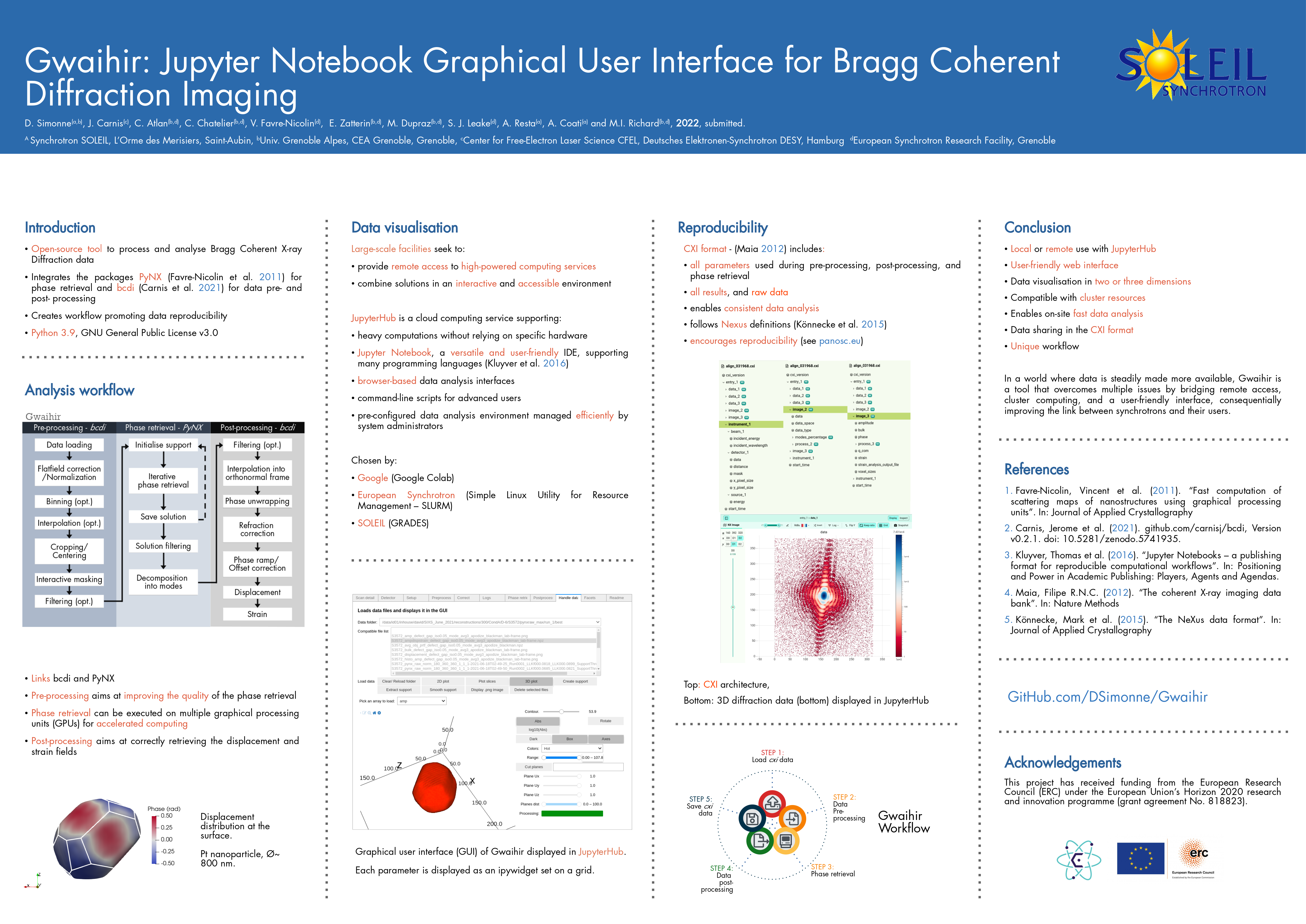
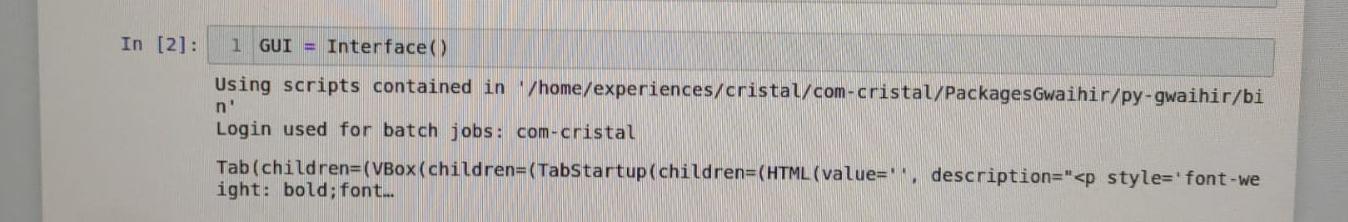
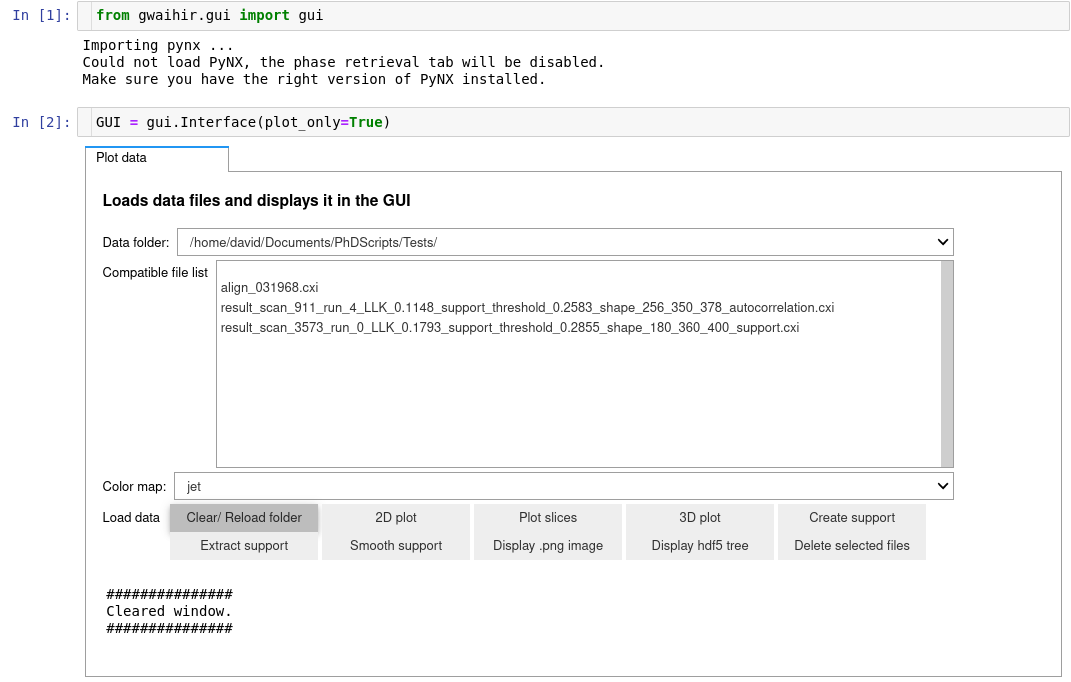
from gwaihir.gui import Interface
GUI = Interface()preprocessing.mp4
phase_retrieval.mp4
handle_data.mp4
postprocessing.mp4
An example file can be downloaded at: https://www.dsimonne.eu/Attachments/align_031968.cxi
The first time you install gwaihir, it is possible that when you open the Interface, you only see some text printed, or the content of the readme tab, but you cannot interact with anything. This is solved by restarting your computer.
Gwaihir only works with the p9 partition at the ESRF, optimized for phase retrieval.
If you want to use it for data analysis, you can install gwaihir and bcdi on rnice.
How to access:
- Web browser: https://jupyter-slurm.esrf.fr/hub/spawn
- Terminal (for advanced users) :
ssh -X <login>@slurm-nice-devel- Ask for a GPU:
srun -N 1 --partition=p9gpu --gres=gpu:1 --time=06:00:00 --pty bash
/usr/bin/python3: your personal environemnt- p9.dev : optimised for BCDI, gwaihir and PyNX, development version,
source /data/id01/inhouse/david/p9.dev/bin/activate - p9.stable : optimised for BCDI, gwaihir and PyNX, stable version,
source /data/id01/inhouse/david/p9.stable/bin/activate - p9.pynx-devel : pynx only, frequently updated :
source /sware/exp/pynx/devel.p9/bin/activate
You are not allowed to modify these environments but you can link a kernel if you wish to use them in jupyter.
To do so:
- Source the environment; e.g.
source /data/id01/inhouse/david/p9.dev/bin/activate - Make sure that:
- you are on slurm
- you requested a GPU
- Create the kernel:
python3 -m ipykernel install --user --name p9.stable
- Documentation
Once you feel confident, you should create your own environment, to avoid sudden updates that may impact your work!
To list the kernels you have installed: jupyter kernelspec list
And to remove them: jupyter kernelspec uninstall <kernelname>
Make sure that you are using the right kernel on your Jupyter Notebook !
- Login into slurm (make sure that you asked for a GPU)
- Open a terminal (new -> terminal)
Enter the following commands (replace <username> with your username, for me it is simonne)
cdssh-keygen -t rsa(press enter when prompted, ~ 3 times)ssh <username>@slurm-nice-devel mkdir -p .sshcat .ssh/id_rsa.pub | ssh <username>@slurm-nice-devel 'cat >> .ssh/authorized_keys'
You should not need a password anymore when login into slurm, make sure it is the case by typing
ssh <username>@slurm-nice-devel
To analyse data recorded at SOLEIL from your personal computer, you can use Jupyter Notebook via GRADES. The documentation is here (accessible on- site via the SOLEIL wifi or with the SOLEIL VPN) : http://confluence.synchrotron-soleil.fr/display/EG/Service%3A+Jupyter+Notebook
- Use this link to open Jupyter Notebook : http://grades-01.synchrotron-soleil.fr/notebook/
- Launch a Terminal (command line) from the upper-right 'New' menu. The system is a Debian 10, so you can enter linux commands there.
PyNX is already installed on GRADES, a version that is out of my control. So you 'just' have to download the bcdi and gwaihir packages by typing pip3 install --proxy=http://195.221.0.35:8080 -U gwaihir bcdi
If you encounter an error with gwaihir or bcdi, it is possible that the pip packages are not up to date. Then you should follow the procedure described below and manually download the packages. Just replace pip install by pip3 install --proxy=http://195.221.0.35:8080, the proxy IP can be 195.221.0.34:8080 or 195.221.0.35:8080 on the ReS (offices and VPN), and 195.221.10.6:8080 or 195.221.10.7:8080 on the REL (beam-lines, RAS).
You can also directly use a virtual machine provided by GRADES
- Go to https://re-grades-01.exp.synchrotron-soleil.fr/qemu-web-desktop/
- Use the SUNset/LDAP id.
- Click on
Createthen onConnect(after 10 sec). - Once the desktop is available, search "gwaihir" in the bottom left menu and execute the program.
- You are now connected to the ruche with an environment that has all the necessary packages, you just need to open a notebook.
A GPU is installed on sixs3, a computer available on the beamline, for phase retrieval.
Please respect the following steps:
- Make sure that you are logged in as
com-sixs - Activate the environment
source_py3.9orsource /home/experiences/sixs/simonne/Documents/py39-env/bin/activate, this environment is protected and you cannot modify it. - Launch
jupyter notebook - Go to the test_data folder and then choose the beamline you want to test
- Follow the instructions in the notebook
A GPU is installed on cristal4, a computer available on the beamline, for phase retrieval.
Please respect the following steps:
- Make sure that you are logged in as
com-cristal - Activate the environment
source_gwaihirorsource /home/experiences/crystal/com-cristal/PackagesGwaihir/py-gwaihir/bin/activate, this environment is protected and you cannot modify it. - Launch
jupyter notebook - Go to the test_data folder and then choose the beamline you want to test
- Follow the instructions in the notebook
- First, I advise you to create a
/Packagesdirectory to keep these. - Secondly, I advise you to create a virtual environment to help with debogging, and so that once everything works, you don't update a package by mistake. To do so please follow the following steps:
mkdir py38-envcd py38-env/python3.8 -m venv .source bin/activate# To activate the environment- Make sure
wheelandsetuptoolsare installed:pip install wheel setuptools pip --upgrade
Then you should create an alias such as: alias source_p9="source /home/user/py38-env/bin/activate"
- If
vtkdoes not install (on the p9 cluster at the ESRF for example), you can type :pip install --trusted-host www.silx.org --find-links http://www.silx.org/pub/wheelhouse vtk, you may also need to remove the version requirements inbcdi/setup.py - If
PyQt5does not install (also on the p9 cluster at the ESRF), you can install it by activating your environment from the rnice cluster.
- Use the latest version
cd /Packagesmkdir PyNX_installcd PyNX_install/curl -O http://ftp.esrf.fr/pub/scisoft/PyNX/pynx-devel-nightly.tar.bz2# Installation details within install-pynx-venv.shsource_p9pip install pynx-devel-nightly.tar.bz2[cuda,gui,mpi]# Install with extras cuda, mpi, cdi- cite
PyNX: high-performance computing toolkit for coherent X-ray imaging based on operators is out: J. Appl. Cryst. 53 (2020), 1404, also available asarXiv:2008.11511
cd /Packagesgit clone https://github.com/DSimonne/gwaihir.gitcd gwaihirsource_p9pip install .- cite
Simonne, D., Carnis, J., Atlan, C., Chatelier, C., Favre-Nicolin, V., Dupraz, M., Leake, S. J., Zatterin, E., Resta, A., Coati, A. & Richard, M. I. (2022). J. Appl. Cryst. 55, 1045-1054.
- Latest version tested : v0.2.8
cd /Packagesgit clone https://github.com/carnisj/bcdi.gitcd bcdisource_p9pip install .- cite
DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.3257616
- Send a thank you email to Fred Picca =D
cd /Packagesgit clone https://salsa.debian.org/science-team/facet-analyser.gitcd facet-analysergit checkoutsudo mk-build-deps -i- Make sure that you have qt installed, for me I had to install
libqt5opengl5-dev(debian-testing) debuild -b- if the package creation fail, try to ignore the test in /debian/rules (line 19)
sudo debi- The package is now installed. You can check the locations of its files with the command
dpkg -L facet-analyser - You should see a file named
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/paraview-5.9/plugins/FacetAnalyser/FacetAnalyser.so - Now launch
/usr/bin/paraview(if not installed yet, good luck, refer tohttps://www.paraview.org/Wiki/ParaView:Build_And_Install#Installing) - In paraview, go to Tools > Manage Plugins > Load New
- Here type the path to the plugin that was printed with the
dpkg -L facet-analysercommand. - Feel free to add it to
/usr/bin/pluginso that it is loaded automatically. - cite
Grothausmann, R. (2015). Facet Analyser : ParaView plugin for automated facet detection and measurement of interplanar angles of tomographic objects. March.
- cxi viewer
- superpose mask and data or support and object in plot