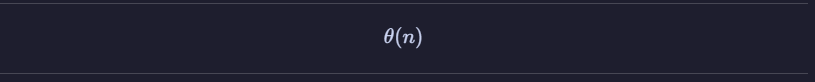
LinkSort is a sorting algorithm implemented using a doubly linked list with a head and tail. This algorithm is particularly effective for sorting arrays that are expanding, meaning that as the array is traversed, each newly accessed value is either the lowest or the highest compared to the previous values. The best-case time complexity is Omega(n), while the worst-case time complexity is O(n^2). The space complexity is Theta(n) .
During my Algorithms class, I remembered how I was sorting a deck of Cards when I was a Kid, in which I'll build a sorted deck gradually by putting each new card either at the begining/end or in between. That's how I was inpsired to start creating this Algorithm.
The LinkSort algorithm works by inserting elements from an array into a doubly linked list in a sorted manner. The steps are as follows:
- Initialize an empty doubly linked list with head and tail pointers.
- Traverse the array and for each element:
- Insert it at the head if it is the smallest value encountered so far.
- Insert it at the tail if it is the largest value encountered so far.
- Insert it between the appropriate nodes if it falls between existing values in the list.
- Once all elements are inserted into the linked list, reconstruct the sorted array from the linked list.
The best use case for LinkSort is when dealing with an expanding array where each newly accessed value is either the smallest or the largest compared to previously accessed values. This characteristic ensures that the algorithm operates close to its best-case time complexity of Omega(n).
Below is the List of available implementations of the LinkSort algorithm:
| Language | State of Implementation | Package or Code | Installation script |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | Code Implemented | Code | |
| C++ | Code Implemented | Code | |
| Dart | Code Implemented (A package will be added in the future) | Code | |
| JavaScript | Code Implemented (A package will be added in the future) | Code |
input: A[1...n], head <- null, tail <- null.
output: A sorted Array.
insertFirst(value: integer)
newNode = new node
newNode.data = value
newNode.prev = null
newNode.next = null
if head is null then
head = newNode
tail = newNode
else
newNode.next = head
head.prev = newNode
head = newNode
end if
insertLast(value: integer):
newNode = new node
newNode.data = value
newNode.next = null
newNode.prev = null
tail.next = newNode
newNode.prev = tail
tail = newNode
insertInBetween(value: integer)
newNode = new node
newNode.data = value
newNode.next = null
newNode.prev = null
temp = head
while temp.next is not null and temp.data <= value and value < temp.next.data do
temp = temp.next
end while
newNode.next = temp.next
newNode.prev = temp
if temp.next is not null then
temp.next.prev = newNode
end if
temp.next = newNode
if newNode.next is null then
tail = newNode
end if
reconstructArray(A: array of integers)
temp = head
for i from 0 to length(A)-1 do
A[i] = temp.data
temp = temp.next
end for
linkSort(A: array of integers)
n = length(A)
// Initialize the doubly linked list with the first element
head = CreateNode(A[0])
tail = head
// Traverse the array and insert each element into the linked list
for k from 1 to n-1 do
if A[k] >= tail.data then
InsertLast(A[k])
else if A[k] <= head.data then
InsertFirst(A[k])
else
InsertBetween(A[k])
end if
end for
// Replace the array with the sorted values from the linked list
ResetArray(A)
To use the LinkSort algorithm, follow these steps:
- Define an array of integers.
- Call the
linkSortfunction with the array as the argument. - The array will be sorted in place.
Example (in C++):
int main() {
int array[] = {5, 3, 2, 10, 9, 0, -10, 8, 8, 1, 10, 30, 44, 31, 22};
const int size = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
linkSort(array);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
cout << array[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}LinkSort is an efficient sorting algorithm for specific types of data sets, particularly those that expand in a manner where each new element is either the smallest or the largest seen so far. The use of a doubly linked list allows for flexible and efficient insertion of elements in their correct order, achieving optimal performance in favorable scenarios.
All Contributions, whether a language Implementation, improvement, or issues are Welcome, but please adhere to Github's common Guidelines.