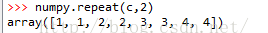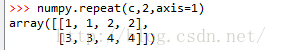repeat
参数的意义:axis=None,时候就会flatten当前矩阵,实际上就是变成了一个行向量
axis=0,沿着y轴复制,实际上增加了行数
axis=1,沿着x轴复制,实际上增加列数
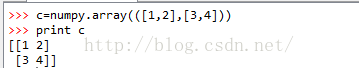
repeats可以为一个数,也可以为一个矩阵,具体区别我们从以下实例中就会发现 以下各个实例都是使用了矩阵c:
实例1:
实例2:
实例3:
实例4:
flatten
>>> a = np.array([[1,2], [3,4]])
>>> a.flatten()
array([1, 2, 3, 4])
>>> a.flatten('F') #按竖的方向降
array([1, 3, 2, 4]) array和asarray都可以将结构数据转化为ndarray,但是主要区别就是当数据源是ndarray时,array仍然会copy出一个副本,占用新的内存,属于深拷贝。但asarray不会,属于浅拷贝。、
>>> a=[(1,2,3),(4,5,6)]
>>> a=np.asarray(a)
>>> print(a)
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
>>> b=[(1,2,3),(4,5)]
>>> b=np.asarray(b)
>>> b.shape
(2,)
>>> print(b)
[(1, 2, 3) (4, 5)]
>>> print(a.shape)
(2, 3)
>>> c=[(1,2,3),(4,5,6)]
>>> c=np.asarray(c)
>>> c.shape
(2, 3)If x is a multi-dimensional array, it is only shuffled along its
first index.
Returns
-------
out : ndarray
Permuted sequence or array range.
Examples
--------
>>> np.random.permutation(10)
array([1, 7, 4, 3, 0, 9, 2, 5, 8, 6])
>>> np.random.permutation([1, 4, 9, 12, 15])
array([15, 1, 9, 4, 12])
>>> arr = np.arange(9).reshape((3, 3))
>>> np.random.permutation(arr)
array([[6, 7, 8],
[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5]])