- 简介
- 简单的 netty 应用程序
- Netty 的组件和设计
- 传输
- ByteBuf
- ChannelHandler
- ChannelPipeline 接口
- EventLoop 和线程模型
- 引导
- 编解码器
- 预置的 ChannelHandler 和编解码器
- ctx.write() 和 channel().write() 的区别
-
Channel:传入和传出数据的载体,它可以连接或者断开连接。
-
回调:操作完成后通知相关方。
-
Future:提供了另一种在操作完成时通知应用程序的方式。
-
事件和 ChannelHandler
当一个 socket 建立好之后,Thread 会把这个连接请求交给 Selector,Selector 会不断去遍历所有的 Socket,一旦有一个 Socket 建立完成,它就会通知 Thread,然后 Thread 处理完数据在返回给客户端,这个过程是不阻塞的。
Echo 客户端和服务器之间的交互是非常简单的;在客户端建立一个连接之后,它会向服务 器发送一个或多个消息,反过来,服务器又会将每个消息回送给客户端。
所有的 netty 服务器都需要以下两个部分:
- 一个 ChannelHandler,实现服务器对接受的客户端的数据的处理
- 引导服务器:配置服务器的启动代码,将服务器绑定到它要监听连接请求的端口上
Echo 服务器需要实现 ChannelInboundHandler 方法,定义响应入站事件的方法。
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf in = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("server reveived: " + in.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
ctx.write(in);//将接受到的消息回传给发送者
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();//关闭channel
}
}ChannelHandler 有助于保持业务逻辑与网络处理代码的分离。
- 服务器监听端口;
- 配置 Channel,将有关的入站事件消息通知给 EchoServerHandler。
public class EchoServer {
private final int port;
public EchoServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 1) {
System.err.println(
"Usage: " + EchoServer.class.getSimpleName() +
" <port>");
}
int port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
new EchoServer(port).start();
}
public void start() throws Exception {
final EchoServerHandler serverHandler = new EchoServerHandler();
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//nio传输的channel
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(serverHandler);//将serverHandler添加到自Channel的ChannelPipeline
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind().sync();//异步绑定到服务器,阻塞直到绑定成功
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
}Echo 客户端的功能:
- 连接到服务器;
- 发送消息;
- 接收服务器发送的消息;
- 关闭连接。
客户端也需要实现 ChannelInboundHandler,用于处理数据。
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class EchoClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//当被通知的channel是活跃的时候发送消息
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Netty rocks!", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
/**
* 每当接收数据就会调用此方法,服务器发送的数据可能被分块接收
*/
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
System.out.println("client received: " + byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));//接收的消息
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}客户端使用主机和端口参数来连接远程地址。
public class EchoClient {
private final String host;
private final int port;
public EchoClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
public void start() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//适用于nio传输的channel类型
.remoteAddress(new InetSocketAddress(host, port))
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(
new EchoClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect().sync();//连接到远程节点,阻塞等待
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();//阻塞直到channel关闭
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();//关闭线程池并释放所有的资源
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 2) {
System.err.println(
"Usage: " + EchoClient.class.getSimpleName() +
" <host> <port>");
return;
}
String host = args[0];
int port = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
new EchoClient(host, port).start();
}
}在服务器端,使用mvn clean package构建项目,然后在 idea 中配置 Edit Configurations,带参数运行服务器程序。
同理,客户端进行同样的配置,注意带多个参数的运行配置,参数中间使用空格隔开。
先运行服务器程序,在运行客户端程序,服务端接收到客户端发出的消息,控制台输出:server reveived: Netty rocks!,然后服务端将消息回传客户端,客户端控制台输出:client received: Netty rocks!,之后客户端便退出。
Channel -- Socket;
EventLoop -- 控制流、多线程处理、并发;
ChannelFuture -- 异步通知;
ChannelHandler -- 处理出站和入站数据;
Netty 的Channel 接口所提供的API,大大地降低了直接使用Socket 类的复杂性。
EventLoop 用于处理连接的生命周期中所发生的事件。
Channel 和 EventLoop 的关系:Channel 会被注册到 EventLoop 上,在整个生命周期内使用 EventLoop 处理 io 事件。
一个EventLoop 在它的生命周期内只和一个Thread 绑定;
一个Channel 在它的生命周期内只注册于一个EventLoop;
一个EventLoop 可能会被分配给一个或多个Channel;
一个给定 Channel 的I/O 操作都是由相同的Thread 执行的,实际上消除了对于同步的需要。
Netty 中所有 io 操作都是异步的,ChannelFuture 接口用于在操作完成时得到通知。
ChannelHandler 的方法是由网络事件触发的。典型用途:
- 将数据从一种格式转换为另一种格式
- 提供异常的通知
- 提供Channel 变为活动的或者非活动的通知
- 提供当Channel 注册到EventLoop 或者从EventLoop 注销时的通知
- 提供有关用户自定义事件的通知
一些适配器类提供了 ChannelHandler 接口中的所有方法的默认实现。
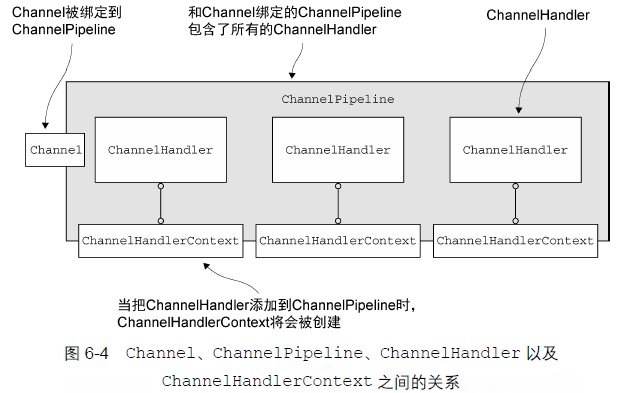
提供了 ChannelHandler 链的容器。当 Channel 被创建时,会被自动分配到它专属的 ChannelPipeline。
每一个事件都会流经 ChannelPipeline,被 ChannelHandler链处理,每一个 ChannelHandler 处理完数据会负责把事件传递给下一个 ChannelHandler,它们的顺序即是它们被安装的顺序。
从客户端应用程序角度来看,如果事件从客户端传递到服务端,那么称之为出站事件,反之则是入站事件。从服务端角度来看则相反。Netty 能区分 ChannelInboundHandler 和 ChannelOutboundHandler 实现,并确保数据在能在具有相同类型的 ChannelHandler 之间传递。
当ChannelHandler 被添加到ChannelPipeline 时,它将会被分配一个ChannelHandlerContext,其代表了ChannelHandler 和ChannelPipeline 之间的绑定。虽然这个对象可以被用于获取底层的Channel,但是它主要还是被用于写出站数据。
作用是给 ChannelPipeline 安装 ChannelHandler。
ChannelHandler 安装到 ChannelPipeline 的过程:
- 一个 ChannelInitializer 的实现被注册到了 ServerBootstrap;
- 当ChannelInitializer.initChannel()方法被调用时,ChannelInitializer 将在 ChannelPipeline 中安装ChannelHandler;
- ChannelInitializer 将它自己从ChannelPipeline 中移除。
Bootstrap 连接远程主机和端口,有一个 EventLoopGroup;ServerBootstrap 绑定到一个本地端口,有两个 EventLoopGroup。
Netty 为所有的传输提供了通用的 API,使得从阻塞传输到非阻塞传输的转换变得更加简单。
public class NettyNioServer {
public void server(int port) throws Exception {
final ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hi!\r\n",
Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();//oio-->nio
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//oio-->nio
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(buf.duplicate())
.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
});
}
});
//绑定服务器以接受连接
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind().sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
}只需要改动 SocketChannel 和 EventLoopGroup。
每个 ChannelHandler 都会分配一个 ChannelPipeline 和 ChannelConfig。ChannelConfig 包含了该 Channel 的所有配置设置,并且支持热更新。
可以通过向 ChannelPipeline 添加 ChannelHandler 实例来增加应用程序的功能。
Channel 被注册到选择器 Selector 后,当 Channel 状态发生变化时可以得到通知。可能的状态变化有:
- 新的 Channel 已被接受并且就绪;
- Channel 连接已经完成;
- Channel 有已经就绪的可供读取的数据;
- Channel 可用于写数据。
零拷贝(zero-copy)是一种目前只有在使用NIO 和Epoll 传输时才可使用的特性。它使你可以快速 高效地将数据从文件系统移动到网络接口,而不需要将其从内核空间复制到用户空间,其在像FTP 或者 HTTP 这样的协议中可以显著地提升性能。它只能传输文件的原始内容,不能传输加密或者压缩的文件。
用于 Linux 的本地非阻塞传输。Netty为Linux提供了一组NIO API,其以一种和它本身的设计更加一致的方式使用epoll,并且以一种更加轻量的方式使用中断。
Java NIO 提供了ByteBuffer 作为它的字节容器,但是这个类使用起来过于复杂,而且也有些繁琐。Netty 的ByteBuffer 替代品是ByteBuf,一个强大的实现,既解决了JDK API 的局限性,又为网络应用程序的开发者提供了更好的API。
Upooled 工具类提供了静态的辅助方法来创建未池化的 ByteBuf 实例。
| 状态 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ChannelUnregistered | Channel 已创建,但还未注册到 EventLoop |
| ChannelRegistered | Channel 已注册到了 EventLoop |
| ChannelActive | Channel 已经连接到它的远程节点,可以接受和发送数据 |
| ChannelInactive | Channel 没有连接到远程节点 |
正常的生命周期:
ChannelRegistered -> ChannelActive -> ChannelInactive -> ChannelUnregistered
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| handlerAdded | 把ChanneHandler添加到ChannelPipeline时被调用 |
| handlerRemoved | 从ChannelPipeline中移除ChannelHandler时被调用 |
| exceptionCaught | 处理过程中在ChannelPipeline中有错误产生时被调用 |
处理入站数据以及各种状态变化。
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| channelRead | 从Channel读取数据时被调用 |
| channelReadComplete | 从Channel上一个读操作完成时被调用 |
| channelWritablityChanged | Channel 的可写状态发生改变时被调用 |
| userEventTriggered | 当ChannelnboundHandler.fireUserEventTriggered()方法被调用时被调用,因为一个POJO 被传经了ChannelPipeline |
ReferenceCountUtil 释放消息资源:
@Sharable
public class DiscardHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}SimpleChannelInboundHandler 会自动释放资源,所以不应该存储指向任何消息的引用供将来使用,因为这些引用都将会失效。
public class SimpleDiscardHandler
extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Object> {
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
Object msg) {
// No need to do anything special
}
}ChannelOutboundHandler 一个强大的功能是可以按需推迟操作或者事件。
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| bind(ChannelHandlerContext, SocketAddress, ChannelPromise) | 当请求将Channel绑定到本地地址时被调用 |
| connect(ChannelHandlerContext, SocketAddress, ChannelPromise) | 当请求连接到远程节点时被调用 |
| close(ChannelHandlerContext, ChannelPromise) | 当请求关闭Channel时被调用 |
| deregister(ChannelHandlerContext, ChannelPromise) | 当请求将Channel 从它的EventLoop 注销时被调用 |
| read(ChannelHandlerContext) | 当请求从Channel 读取更多的数据时被调用 |
| flush(ChannelHandlerContext) | 当请求通过Channel 将入队数据冲刷到远程节点时被调用 |
| write(ChannelHandlerContext, Object, ChannelPromise) | 当请求通过Channel 将数据写到远程节点时被调用 |
ChannelPromise 是 ChannelFuture 的一个子类,ChannelOutboundHandler 中的大部分方法都需要一个 ChannelPromise参数,以便在操作完成时得到通知。
ChannelHandlerAdapter 提供了实用方法 isSharable(),如果其对应的实现被标注成 @Sharable,那么这个方法将返回true,表示它可以被添加到多个 ChannelPipeline 中。
共享 ChannelHandler 一个常见的用途是用于收集跨越多个 channel 的统计信息。
idea 配置 edit configuration -- vm options -- -Dio.netty.leakDetectionLevel=ADVANCED
每一个新创建的 Channel 都将会被分配一个新的 ChannelPipeline,这项关联是永久性的;Channel 既不能附加另外一个ChannelPipeline,也不能分离其当前的。
ChannelHandlerContext 使得 ChannelHandler 能够和它的 ChannelPipeline 以及其他的 ChannelHandler 交互。
ChannelHandler 可以通过添加、删除或者替换其他的ChannelHandler 来实时地修改ChannelPipeline 的布局。
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| addFirst/addBefore/addAfter/addLast | 将 ChannelHandler 添加到 ChannelPipeline |
| remove | 移除 |
| replace | 替换 |
ChannelPipeline 的用于访问ChannelHandler 的操作:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| get | 返回ChannelHandler |
| context | 返回和ChannelHandler绑定的ChannelHandlerContext |
| names | 返回所有的ChannelHanlder名称 |
ChannelHandlerContext 代表了ChannelHandler 和ChannelPipeline 之间的关联,每当有ChannelHandler 添加到ChannelPipeline 中时,都会创建ChannelHandlerContext。
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| fireChannelRead | 触发对下一个ChannelInboundHandler的channelRead()方法的调用 |
| alloc | 返回相关联的Channel所配置的ByteBufAllocator |
| bind | 绑定到给定的SocketAddress,并返回ChannelFuture |
入站异常:在 ChannelInboundHandler 实现 exceptionCaught 方法。
出站异常:
1.添加ChannelFutureListener 到ChannelFuture
ChannelFuture future = channel.write(someMessage);
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete (ChannelFuture f){
if (!f.isSuccess()) {
f.cause().printStackTrace();
f.channel().close();
}
}
});2.添加ChannelFutureListener 到ChannelPromise:
public class OutboundExceptionHandler extends ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg,
ChannelPromise promise) {
promise.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) {
if (!f.isSuccess()) {
f.cause().printStackTrace();
f.channel().close();
}
}
});
}
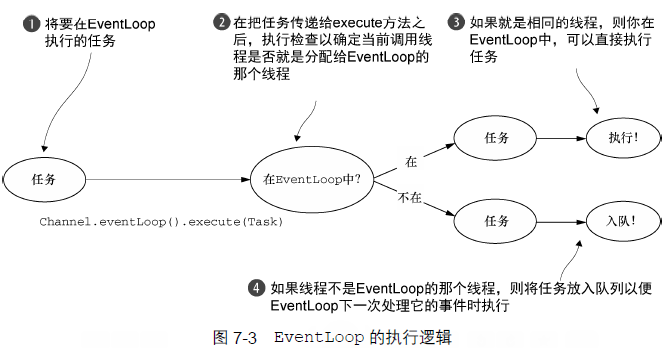
}EventLoop 构建在 java.util.concurrent 和 io.netty.channel 之上。EventLoop 继承了 ScheduledExecutorService。EventLoop 由一个永远不会改变的 Thread 驱动,同时任务可以直接提交给 EventLoop 实现。EventLoop 可能服务于多个 Channel。
Netty4中所有的 io 操作和事件都由 EventLoop 的 Thread 处理。Netty3只保证入站事件在 EventLoop(io 线程)执行,所有出站事件都由调用线程处理,可能是 io 线程或者别的线程,因此需要在 ChannelHandler 中对出站事件进行同步。
Netty 4 中所采用的线程模型,通过在同一个线程中处理某个给定的EventLoop 中所产生的所有事件,解决了这个问题。这提供了一个更加简单的执行体系架构,并且消除了在多个ChannelHandler 中进行同步的需要
使用 EventLoop 调度任务:
Channel ch = ...
ScheduledFuture<?> future = ch.eventLoop().schedule(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//逻辑
}
}, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);周期性任务:
Channel ch = ...
ScheduledFuture<?> future = ch.eventLoop().scheduleAtFixedRate(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//逻辑
}
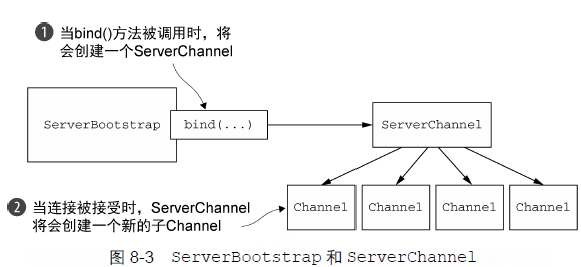
}, 60, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDES);配置 netty 应用程序,使它运行起来。服务器使用一个父 Channel 接受来自客户端的连接,并创建子 Channel 以用于它们之间的通信。客户端只需要一个 Channel 完成所有的网络交互。
引导类是 cloneable 的,在引导类实例上调用 clone() 就可以创建多个具有类似配置或者完全相同配置的 Channel。
BootStrap 类被用于客户端或者使用了无连接协议的应用程序中。
在基类AbstractBootstrap有handler方法,目的是添加一个handler,监听Bootstrap的动作。
在服务端的ServerBootstrap中增加了一个方法childHandler,它的目的是添加handler,用来监听已经连接的客户端的Channel的动作和状态。
handler在初始化时就会执行,而childHandler会在客户端成功connect后才执行。
在 handler 传入 ChannelInitializer 的实现类,重写 initChannel 方法,在这个方法中添加多个 ChannelHandler。
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//适用于nio传输的channel类型
.remoteAddress(new InetSocketAddress(host, port))
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(
new EchoClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect().sync();//连接到远程节点,阻塞等待
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();//阻塞直到channel关闭
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();//关闭线程池并释放所有的资源
}关闭 EventLoopGroup,它将处理任何挂起的事件和任务,随后释放所有活动的线程。
Future<?> future = group.shutdownGracefully();//释放所有资源,关闭Channel
// block until the group has shutdown
future.syncUninterruptibly();数据格式转化。编码器操作出站数据,解码器处理入站数据。继承自 ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter。数据编码或者解码完就会被传入 ChannelPipeline 的下一个 ChannelHandler。
ByteToMessageDecoder、ReplayingDecoder:将字节解码为消息。
MessageToMessageDecoder:将消息解码为另一种消息。
public class ToIntegerDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
@Override
public void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in,
List<Object> list) throws Exception {
if (in.readableBytes() >= 4) {
list.add(in.readInt());
}
}
}调用 readInt() 方法前需要验证输入的 ByteBuf 是否具有足够的数据。
类型参数S 指定了用于状态管理的类型,其中Void 代表不需要状态管理。
public class ToIntegerDecoder2 extends ReplayingDecoder<Void> {
@Override
public void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in,
List<Object> list) throws Exception {
list.add(in.readInt());
}
}如果没有足够的字节可用,这个readInt()方法的实现将会抛出一个Error,将在基类中被捕获并处理。当有更多的数据可供读取时,该decode()方法将会被再次调用。
并不是所有的ByteBuf 操作都被支持,如果调用了一个不被支持的方法,将会抛出一个UnsupportedOperationException;ReplayingDecoder 稍慢于ByteToMessageDecoder。如果使用ByteToMessageDecoder 不会引入太多的复杂性,那么选用它。
两种消息格式的转换。
public class IntegerToStringDecoder extends MessageToMessageDecoder<Integer> {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Integer integer, List<Object> list) throws Exception {
list.add(String.valueOf(integer));
}
}解码器缓冲大量的数据以至于耗尽可用的内存,可以设置一个最大字节数的阈值,如果超出该阈值,则手动抛出一个TooLongFrameException。
消息编码为字节;消息编码为消息。
public class ShortToByteEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<Short> {
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Short msg, ByteBuf out)
throws Exception {
out.writeShort(msg);
}
}public class IntegerToStringEncoder extends MessageToMessageEncoder<Integer> {
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Integer msg
List<Object> out) throws Exception {
out.add(String.valueOf(msg));
}
}结合一个解码器和编码器可能会对可重用性造成影响。
结合了 ByteToMessageDecoder 和 MessageToByteEncoder。
定义:public abstract class MessageToMessageCodec<INBOUND_IN,OUTBOUND_IN>
可以实现一个编解码器,而又不必直接扩展抽象的编解码器类。
public class CombinedChannelDuplexHandler<I extends ChannelInboundHandler,
O e xtends ChannelOutboundHandler>ByteToCharDecoder 类:
public class ByteToCharDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf, List<Object> list) throws Exception {
while (byteBuf.readableBytes() >= 2) {
list.add(byteBuf.readChar());
}
}
}CharToByteEncoder 类:
public class CharToByteEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<Character> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Character character, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
byteBuf.writeChar(character);//向byteBuf写入基本类型的值
}
}编解码器类:
public class CombinedByteCharCodec extends CombinedChannelDuplexHandler<ByteToCharDecoder, CharToByteEncoder> {
public CombinedByteCharCodec() {
super(new ByteToCharDecoder(), new CharToByteEncoder());//将委托实例传递给父类
}
}Java 提供了 javax.net.ssl 支持 SSL/TSL,用以实现数据安全。
添加 SSL/TLS 支持:
public class SslChannelInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
private final SslContext context;
private final boolean startTls;
public SslChannelInitializer(SslContext context, boolean startTls) {
this.context = context;
this.startTls = startTls;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
SSLEngine engine = context.newEngine(channel.alloc());//alloc返回channel所配置的ByteBufAllocator
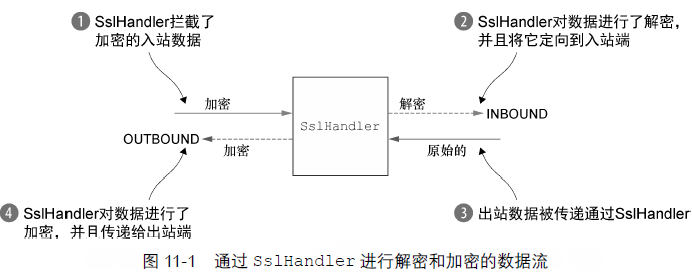
channel.pipeline().addFirst("ssl",
new SslHandler(engine, startTls));//大多数情况SslHandler是第一个ChannelHandler
//这确保了所有其他的ChannelHandler处理数据之后,才会进行加密。
}
}完整的 HTTP 请求(FullHttpRequest)包括请求头信息、若干个 HTTPContent 和 LastHttpContent。
完整的 HTTP 响应(FullHttpResponse)包括响应头信息、若干个 HTTPContent 和 LastHttpContent。
所有类型的 HTTP 消息都实现了 HttpObject 接口。
HTTP 编解码器:HttpRequestEncoder、HttpResponseEncoder、HttpReqeustDecoder 和 HttpResponseDecoder。
HttpResponseDecoder:将字节解码为 HttpResponse、HttpContent 和 LastHttpContent。
public class HttpPipelineInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
private final boolean client;
public HttpPipelineInitializer(boolean client) {
this.client = client;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
if (client) {
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new HttpResponseDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new HttpRequestEncoder());
} else {
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new HttpRequestDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new HttpResponseEncoder());
}
}
}判断是否是客户端,如果是客户端,则添加 HttpResponseDecoder 对服务器响应进行解码。
由于 HTTP 请求和响应可能由多个部分组成,需要将它们聚合成完整的消息。Netty 提供了一个聚合器,可以将多个消息部分合并成 FullHttpRequest 或者 FullHttpResponse 消息。
自动聚合 HTTP 的消息片段:
public class HttpAggregarotInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
private final boolean isClient;
public HttpAggregarotInitializer(boolean isClient) {
this.isClient = isClient;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
if (isClient) {
pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpClientCodec());
} else {
pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpServerCodec());
}
pipeline.addLast("aggregator", //最大消息大小是512kb
new HttpObjectAggregator(512*1024));
}
}HttpServerCodec 里面组合了HttpResponseEncoder和HttpRequestDecoder。
HttpClientCodec 里面组合了HttpRequestEncoder和HttpResponseDecoder。
当使用HTTP 时,建议服务器端开启压缩功能以尽可能多地减小传输数据的大小。Netty 为压缩和解压缩提供了ChannelHandler 实现,它们同时支持gzip 和deflate 编码。
自动压缩 HTTP 消息:
public class HttpCompressionInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
private final boolean isClient;
public HttpCompressionInitializer(boolean isClient) {
this.isClient = isClient;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
if (isClient) {
pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpClientCodec());
pipeline.addLast("decompressor",
new HttpContentDecompressor());//处理来自服务器的压缩内容
} else {
pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast("compressor",
new HttpContentCompressor());//服务器端压缩数据
}
}
}启动 HTTPS 只需要将 SslHandler 添加到 ChannelPipeline。
public class HttpsCodecInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
private final SslContext context;
private final boolean isClient;
public HttpsCodecInitializer(SslContext context, boolean isClient) {
this.context = context;
this.isClient = isClient;
}
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
SSLEngine engine = context.newEngine(channel.alloc());
pipeline.addFirst("ssl", new SslHandler(engine));//添加SslHandler之后可以使用https
if (isClient) {
pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpClientCodec());
} else {
pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpServerCodec());
}
}
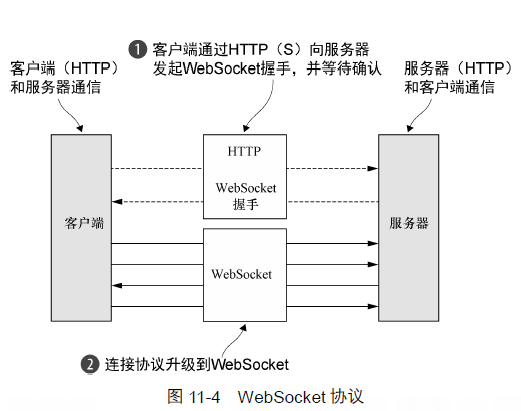
}WebSocket 在客户端和服务器之间提供了真正的双向数据交换。
WebSocketFrame 类型:
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| BinaryWebSocketFrame | 二进制数据帧 |
| TextWebSocketFrame | 文本数据帧 |
| ContinuationWebSocketFrame | 二进制和文本数据帧结合体 |
| CloseWebSocketFrame | 控制帧:一个close请求、关闭的状态码以及关闭的原因 |
| PingWebSocketFrame | 控制帧:请求一个PongWebSocketFrame |
| PongWebSocketFrame | 控制帧:对PingWebSocketFrame请求的响应 |
WebSocketServerProtocolHandler 处理协议升级握手,以及三种控制帧--Close、Ping 和 Pong。Text和Binary数据帧将会被传递给下一个 ChannelHandler 进行处理。
public class WebSocketServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
channel.pipeline().addLast(
new HttpServerCodec(),
new HttpObjectAggregator(65536),
new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/websocket"),//升级握手
new TextFrameHandler(),
new BinaryFrameHandler(),
new ContinuationFrameHandler());
}
public static final class TextFrameHandler extends
SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, TextWebSocketFrame textWebSocketFrame) throws Exception {
//handle text frame
}
}
public static final class BinaryFrameHandler extends
SimpleChannelInboundHandler<BinaryWebSocketFrame> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, BinaryWebSocketFrame binaryWebSocketFrame) throws Exception {
//handle binary frame
}
}
public static final class ContinuationFrameHandler extends
SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ContinuationWebSocketFrame> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ContinuationWebSocketFrame continuationWebSocketFrame) throws Exception {
//handle continuation frame
}
}
}要想为WebSocket 添加安全性,只需要将SslHandler 作为第一个ChannelHandler 添加到ChannelPipeline 中。
用于空闲连接以及超时的 ChannelHandler。
发送心跳:
public class IdleStateHandlerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
//60s没有接受或发送数据,IdelStateHandler会使用IdleStateEvent调用fireUserEventTriggered()
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(
0, 0, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
pipeline.addLast(new HeartbeatHandler());
}
public static final class HeartbeatHandler extends
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
//发送到远程节点的心跳信息
private static final ByteBuf HEARTBEAT_SEQUENCE =
Unpooled.unreleasableBuffer(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(
"HEARTBEAT", CharsetUtil.ISO_8859_1));
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) {
//连接空闲时间太长时,发送心跳消息,并在发送失败时关闭该连接
ctx.writeAndFlush(HEARTBEAT_SEQUENCE.duplicate())
.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} else {
super.userEventTriggered(ctx, evt);//传递给下一个ChannelInboundHandler
}
}
}
}使用 IdleStateHandler 测试远程节点是否还活着,失活时关闭连接释放资源。
基于分隔符的协议的解码器
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder | 使用自定义分隔符提取帧的通用解码器 |
| LineBasedFrameDecoder | 提取由行尾符分隔的解码器,速度比DeimiterBasedFrameDecoder快 |
分隔符提取帧:
public class LineBasedHandlerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
//提取帧,并传给下一个ChannelHandler
pipeline.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(64*1024));
pipeline.addLast(new FrameHandler());//接收数据帧
}
public static final class FrameHandler extends
SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
//处理LineBasedFrameDecoder传进的帧
}
}示例:1.每个帧都由换行符(\n)分隔;2.每个帧由一系列的元素组成,每个元素都由的单个空格字符分隔;3.一个帧内容代表一个命令,定义为一个命令名称后面跟着数目可变的参数。
public class CmdHandlerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
static final byte SPACE = (byte)' ';
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new CmdDecoder(64 * 1024));
pipeline.addLast(new CmdHandler());
}
public static final class Cmd {
private final ByteBuf name;
private final ByteBuf args;
public Cmd(ByteBuf name, ByteBuf args) {
this.name = name;
this.args = args;
}
public ByteBuf getName() {
return name;
}
public ByteBuf getArgs() {
return args;
}
}
public static final class CmdDecoder
extends LineBasedFrameDecoder {
public CmdDecoder(int maxLength) {
super(maxLength);
}
@Override
protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf buffer) throws Exception {
ByteBuf frame = (ByteBuf) super.decode(ctx, buffer);
if (frame == null) {
return null;
}
//查找第一个空格字符的索引,空格前是命令名称,后面是参数
int index = frame.indexOf(frame.readerIndex(),
frame.writerIndex(), SPACE);
return new Cmd(frame.slice(frame.readerIndex(), index),
frame.slice(index + 1, frame.writerIndex()));
}
}
public static final class CmdHandler extends
SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Cmd> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Cmd cmd) throws Exception {
//处理cmd
}
}
}基于长度的协议的解码器:
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| FixedLengthFrameDecoder | 提取固定长度的帧 |
| LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder | 根据帧头部中的长度值提取帧;该字段的偏移量以及长度在构造函数中指定 |
变长帧:
public class LengthBasedInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeLine = channel.pipeline();
//帧起始的前8字节是帧长度
pipeLine.addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(64 * 1024, 0, 8));
pipeLine.addLast(new FrameHandler());
}
public static class FrameHandler extends
SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
//处理帧
}
}
}当写大型数据到远程节点时,如果连接速度比较慢,数据依然不断的往内存写,可能导致内存耗尽。利用 NIO 的零拷贝特性,可以消除将文件内容从文件系统移动到网络栈的复制过程。应用程序需要做的就是实现一个 FileRegion 的接口。
利用零拷贝特性(FileRegion)来传输一个文件的内容。
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(File);
FileRegion region = new DefaultFileRegion(in.getChannel(), 0, file.length());
channel.writeAndFlush(region).addListener(
new ChannelFuture(region).addListener(
new ChannelFutureListener() {
}
)
);https://blog.csdn.net/lalalahaitang/article/details/81563830