Description
Consider Stack Overflow for getting support using TensorBoard—they have
a larger community with better searchability:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/tensorboard
Do not use this template for for setup, installation, or configuration
issues. Instead, use the “installation problem” issue template:
https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorboard/issues/new?template=installation_problem.md
To report a problem with TensorBoard itself, please fill out the
remainder of this template.
Environment information (required)
Please run diagnose_tensorboard.py (link below) in the same
environment from which you normally run TensorFlow/TensorBoard, and
paste the output here:
Sorry for that I cannot copy terminal from my remote desktop, so the screenshot is attached here:

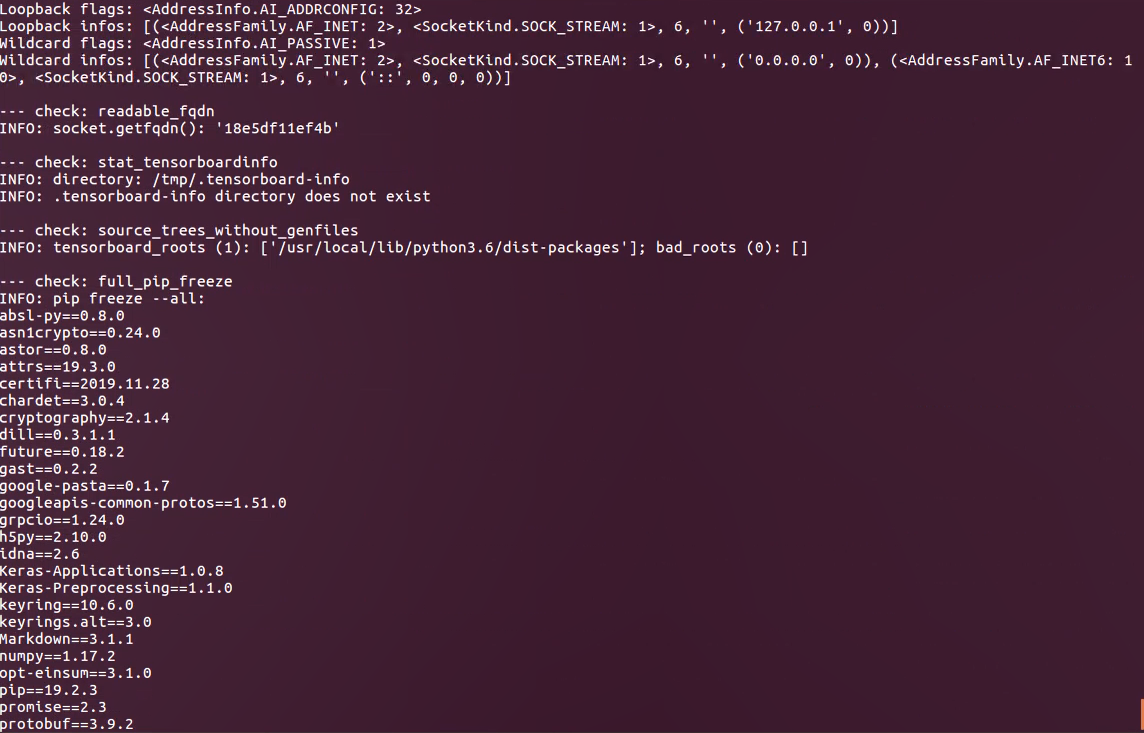
For browser-related issues, please additionally specify:
- Browser type and version (e.g., Chrome 64.0.3282.140):
- Screenshot, if it’s a visual issue:
Issue description
I am trying to get profiler result of my custom training loop. My complex training loop(larger model, larger datasets) is stuck and then killed. Please note that I only run profiler for one epoch:
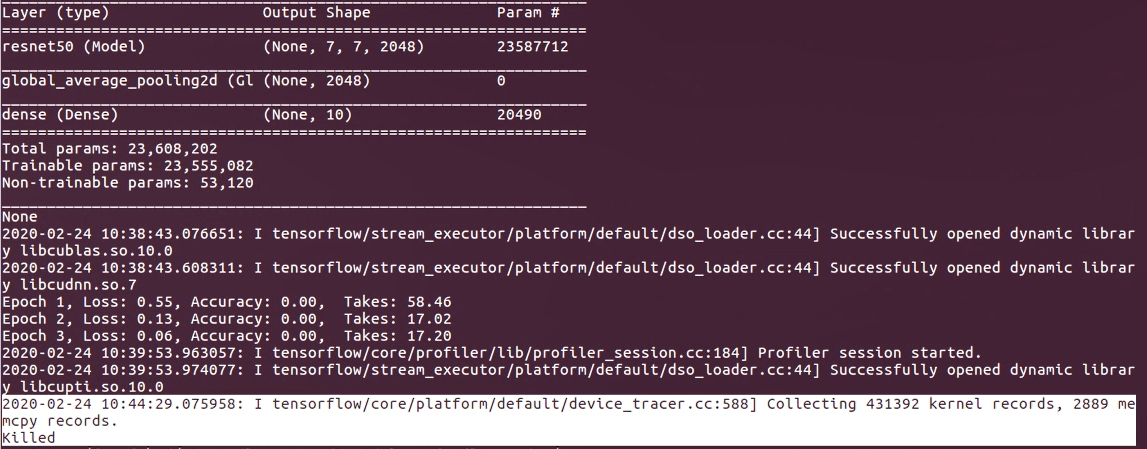
In this case for comparison, I tried training on a simple traing loop(mnist datasets, simple model). Profiler works but takes much longer time. 146s/epoch vs 1.8s/epoch:
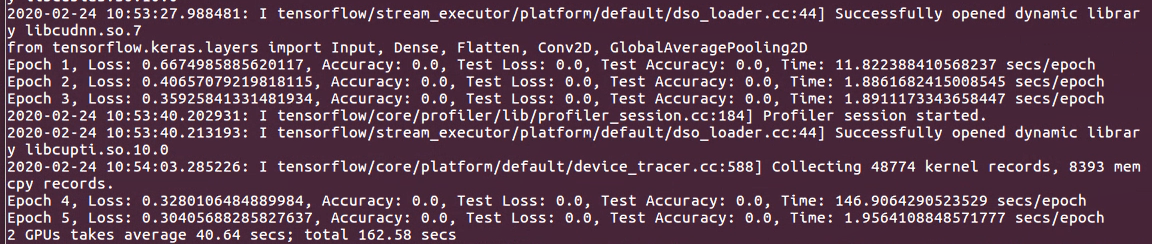
Why does profiler slow down the runtime greatly in custom training loop while keras callbacks doesn't???
Please note that the code is copied from tf official tutorial from the TF website combined with distributed custom training loop and profiler.Code is attached as below:
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
# Import TensorFlow
import tensorflow as tf
# Helper libraries
import numpy as np
import os
import time
from tensorflow.python.eager import profiler
from datetime import datetime
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Flatten, Conv2D, GlobalAveragePooling2D
fashion_mnist = tf.keras.datasets.fashion_mnist
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
# Adding a dimension to the array -> new shape == (28, 28, 1)
# We are doing this because the first layer in our model is a convolutional
# layer and it requires a 4D input (batch_size, height, width, channels).
# batch_size dimension will be added later on.
train_images = train_images[..., None]
test_images = test_images[..., None]
# Getting the images in [0, 1] range.
train_images = train_images / np.float32(255)
test_images = test_images / np.float32(255)
setting_GPUs_num = 2
devices = ["/gpu:"+str(i) for i in range(setting_GPUs_num)]
strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy(devices)
print ('Number of devices: {}'.format(strategy.num_replicas_in_sync))
BUFFER_SIZE = len(train_images)
BATCH_SIZE_PER_REPLICA = 128
GLOBAL_BATCH_SIZE = BATCH_SIZE_PER_REPLICA * strategy.num_replicas_in_sync
EPOCHS = 5
times = []
train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((train_images, train_labels)).shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(GLOBAL_BATCH_SIZE)
test_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((test_images, test_labels)).batch(GLOBAL_BATCH_SIZE)
train_dist_dataset = strategy.experimental_distribute_dataset(train_dataset)
test_dist_dataset = strategy.experimental_distribute_dataset(test_dataset)
def create_model():
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)
])
return model
def assemble_model(num_classes, model_name='MobileNetV2'):
import tensorflow as tf
base_model = tf.keras.applications.ResNet50(input_shape=(224,224,3),
weights='imagenet',
include_top=False)
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
base_model,
GlobalAveragePooling2D(),
Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax')
])
model.trainable = True
return model
# Create a checkpoint directory to store the checkpoints.
checkpoint_dir = './training_checkpoints'
checkpoint_prefix = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, "ckpt")
with strategy.scope():
# Set reduction to `none` so we can do the reduction afterwards and divide by
# global batch size.
loss_object = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(
from_logits=True,
reduction=tf.keras.losses.Reduction.NONE)
def compute_loss(labels, predictions):
per_example_loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)
return tf.nn.compute_average_loss(per_example_loss, global_batch_size=GLOBAL_BATCH_SIZE)
with strategy.scope():
test_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='test_loss')
train_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(
name='train_accuracy')
test_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(
name='test_accuracy')
# model and optimizer must be created under `strategy.scope`.
with strategy.scope():
model = create_model()
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(optimizer=optimizer, model=model)
with strategy.scope():
def train_step(inputs):
images, labels = inputs
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
predictions = model(images, training=True)
loss = compute_loss(labels, predictions)
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, model.trainable_variables))
train_accuracy.update_state(labels, predictions)
return loss
def test_step(inputs):
images, labels = inputs
predictions = model(images, training=False)
t_loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)
test_loss.update_state(t_loss)
test_accuracy.update_state(labels, predictions)
current_time = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
train_log_dir = 'logs/custom_train_loop/' + current_time + '/train'
train_summary_writer = tf.summary.create_file_writer(train_log_dir)
with strategy.scope():
# `experimental_run_v2` replicates the provided computation and runs it
# with the distributed input.
@tf.function
def distributed_train_step(dataset_inputs):
per_replica_losses = strategy.experimental_run_v2(train_step,
args=(dataset_inputs,))
return strategy.reduce(tf.distribute.ReduceOp.SUM, per_replica_losses,
axis=None)
@tf.function
def distributed_test_step(dataset_inputs):
return strategy.experimental_run_v2(test_step, args=(dataset_inputs,))
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
# TRAIN LOOP
if epoch == 3:
profiler.start()
start = time.time()
total_loss = 0.0
num_batches = 0
for x in train_dist_dataset:
total_loss += distributed_train_step(x)
num_batches += 1
train_loss = total_loss / num_batches
with train_summary_writer.as_default():
tf.summary.scalar('loss', train_loss, step=epoch)
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', train_accuracy.result(), step=epoch)
# TEST LOOP
for x in test_dist_dataset:
distributed_test_step(x)
test_loss.reset_states()
train_accuracy.reset_states()
test_accuracy.reset_states()
if epoch == 3:
profiler_result = profiler.stop()
profiler.save(train_log_dir, profiler_result)
end = time.time()
if epoch != 1:
times.append(end-start)
template = ("Epoch {}, Loss: {}, Accuracy: {}, Test Loss: {}, "
"Test Accuracy: {}, Time: {} secs/epoch")
print (template.format(epoch+1, train_loss,
train_accuracy.result()*100, test_loss.result(),
test_accuracy.result()*100, end-start))
print("{} GPUs takes average {:.2f} secs; total {:.2f} secs".format(setting_GPUs_num,
sum(times)/(EPOCHS-1), sum(times)))