Example:
Here you will find a template to run a Hornet node on a kubernetes clusters.
Or you can deploy using a helm chart available here, but first you must configure the config.json as shown below.
A few things to take into account:
- This configuration uses NodePort. Another alternative is hostNetwork but this will not work well on a real cluster.
- Storage persistence in the example below is using hostPath. For real deployments use other "cloud-native" storage-classes.
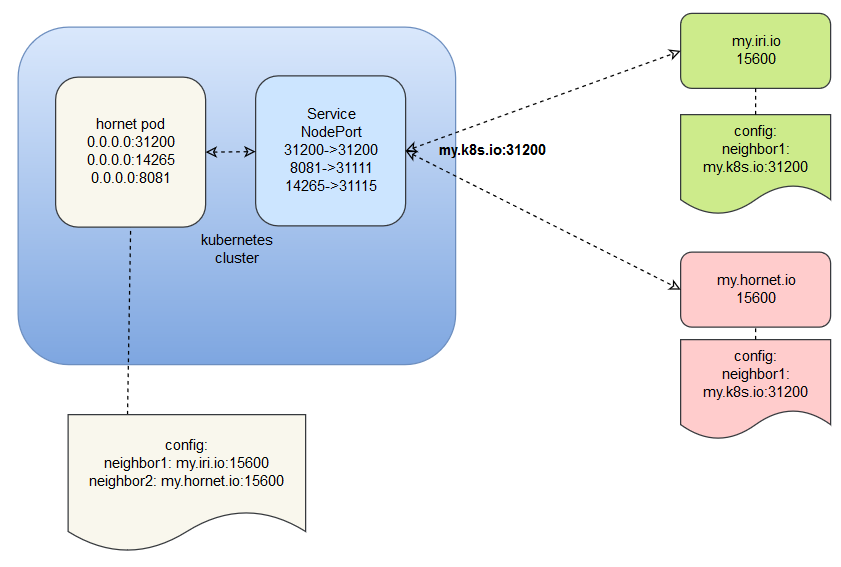
- The peering port in the config.json must match the NodePort, else other nodes will get a conflict in between what is advertised by the k8s hornet node and the port with which it was added.
Check configurations examples and modify according to your needs.
These can be used at the Prepare stage.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: hornet-pv
labels:
type: local
spec:
storageClassName: manual
capacity:
storage: 20Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
hostPath:
path: "/mnt/data"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: hornet-claim
spec:
storageClassName: manual
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 20Gi
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hornet
namespace: hornet
labels:
app: hornet
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hornet
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hornet
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 240
hostNetwork: false
containers:
- name: hornet
image: "iotaledger/hornet:latest"
ports:
- name: dashboard
protocol: TCP
containerPort: 8081
- name: api
protocol: TCP
containerPort: 14265
- name: peering
protocol: TCP
containerPort: 31200
- name: autopeering
protocol: UDP
containerPort: 31201
livenessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 15600
initialDelaySeconds: 120
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 2
failureThreshold: 2
readinessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 15600
initialDelaySeconds: 20
timeoutSeconds: 2
periodSeconds: 10
failureThreshold: 2
command:
- "/bin/sh"
- "-ec"
- |
cp -- /app/config/*.json /app/
mkdir -p /app/db/snapshot /app/db/mainnetdb /app/db/coordinator
exec /sbin/tini -s -- /app/hornet -c config
volumeMounts:
- name: db
mountPath: "/app/db"
- name: mainconfig
mountPath: "/app/config"
securityContext:
fsGroup: 39999
volumes:
- name: db
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: hornet-claim
- name: mainconfig
secret:
secretName: hornet-config
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: hornet-service
namespace: hornet
spec:
selector:
app: hornet
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 14265
nodePort: 31115
name: api
- protocol: TCP
port: 8081
nodePort: 31111
name: dashboard
- protocol: TCP
port: 31200
nodePort: 31200
name: peering
- protocol: UDP
port: 31201
nodePort: 31201
name: autopeering
type: NodePort- First create a namespace
hornet(not necessarity, you can usedefaultbut makes sure to edit above yaml examples).
kubectl create namespace hornet- Create the configuration secret by creating a file
config.jsonwith the configuration json from above. As this may contain passwords we put it in a k8s secret:
kubectl create secret --namespace hornet generic hornet-config --from-file=./config.json --from-file=./peering.json --from-file=./profiles.json --from-file=./mqtt_config.json --dry-run -o yaml | kubectl apply -f -Note that we use the above command (--dry-run and apply) so that it is easier to configure the secret and reload/replace it when it was already created.
Chown the hostPath directory (unless you are going to use other persistent volumes):
mkdir -p /mnt/data && chown 39999: /mnt/dataPaste the above yaml spec into a file hornet.yml and configure for your needs. Apply the deployment and service:
kubectl apply -f hornet.ymlCheck logs (you need to get the pod's name via kubectl get pod -n hornet):
kubectl logs -n hornet hornet-xxxxxxxx-xxxxx -fIf you make any changes to config.json you can use the command you've used to create the secret in order to update it.
You will also have to delete the existing pod in order for it to pick up the new changes.
You might have to allow getNeighbors in the config.json, else you need to run the command from within the pod (it doesn't have curl so you'll have to build an image with curl in it).
curl http://127.0.0.1:31115 -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -H 'X-IOTA-API-Version: 1' -d '{"command":"getNeighbors"}'