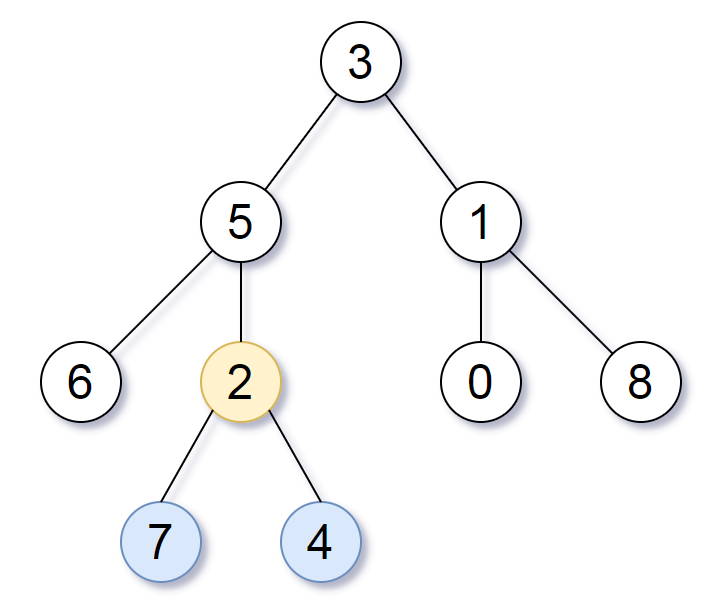
Given the root of a binary tree, return the lowest common ancestor of its deepest leaves.
Recall that:
- The node of a binary tree is a leaf if and only if it has no children
- The depth of the root of the tree is
0. if the depth of a node isd, the depth of each of its children isd + 1. - The lowest common ancestor of a set
Sof nodes, is the nodeAwith the largest depth such that every node inSis in the subtree with rootA.
Example 1:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4] Output: [2,7,4] Explanation: We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram. The nodes coloured in blue are the deepest leaf-nodes of the tree. Note that nodes 6, 0, and 8 are also leaf nodes, but the depth of them is 2, but the depth of nodes 7 and 4 is 3.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: [1] Explanation: The root is the deepest node in the tree, and it's the lca of itself.
Example 3:
Input: root = [0,1,3,null,2] Output: [2] Explanation: The deepest leaf node in the tree is 2, the lca of one node is itself.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 1000]. 0 <= Node.val <= 1000- The values of the nodes in the tree are unique.
Note: This question is the same as 865: https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes/
Companies:
Facebook, Microsoft
Related Topics:
Hash Table, Tree, Depth-First Search, Breadth-First Search, Binary Tree
Similar Questions:
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-deepest-leaves/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
int maxDepth = -1, target = 0, cnt = 0;
void count(TreeNode *root, int d) {
if (!root) return;
if (d > maxDepth) {
target = 1;
maxDepth = d;
} else if (d == maxDepth) ++target;
count(root->left, d + 1);
count(root->right, d + 1);
}
TreeNode *find(TreeNode *root, int d) {
if (!root) return NULL;
int before = cnt;
auto left = find(root->left, d + 1);
if (left) return left;
auto right = find(root->right, d + 1);
if (right) return right;
if (d == maxDepth) ++cnt;
return before == 0 && cnt == target ? root : NULL;
}
public:
TreeNode* lcaDeepestLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
count(root, 0);
return find(root, 0);
}
};The lowest ancester is the highest node whose left and right subtrees have the same height.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-deepest-leaves/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
pair<TreeNode*, int> dfs(TreeNode *root, int d = 0) { // latest node which has equal depth in left and right sub-trees; the corresponding height
if (!root) return {nullptr, d};
const auto &[left, ld] = dfs(root->left, d + 1);
const auto &[right, rd] = dfs(root->right, d + 1);
if (ld > rd) return {left, ld};
if (ld < rd) return {right, rd};
return {root, ld};
}
public:
TreeNode* lcaDeepestLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root).first;
}
};