Bool is a project that uses Hamcrest matchers to provide a clean way to write conditionals and making them readable even for your clients.
Note that apart from cleaning your code, it forces you to maintain the level of abstraction of methods without having to populate your classes with a list of methods that are composed by one line returning a boolean value like next example:
...
if(areResultsAvailable(messages)) {
...
}
private boolean areResultsAvailable(List<String> messages) {
return messages.size()>0;
}From Hamcrest documentation we can read that
Hamcrest it is not a testing library: it just happens that matchers are very useful for testing.
Hamcrest is used in many projects, JUnit for asserting tests (most of us have use it in this way), or Mockito. But as previous cite said, Hamcrest can be also used outside testing scope, Lambdaj is an example, and Bool is another one.
To use Bool you only have to add it to classpath.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.lordofthejars</groupId>
<artifactId>bool</artifactId>
<version>0.9.0</version>
</dependency>All required methods are provided as static methods in the class Bool:
import static com.lordofthejars.bool.Bool.*;Let's explore a simple example to see the differences between using an if as usually and with Bool project:
String name = "Alex";
if(isAlex(name) {
...
}
private boolean isAlex(String name) {
return "Alex".equals(name);
}you can use Hamcrest directly in condition without using Bool, but see that readability is not improved:
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
if(equalTo("Alex").matches(name)) {
...
}and finally using Bool:
if(the(name, is(equalTo("Alex")))) {
...
}Note that the important word here is the, which receives the element to compare and a matcher (similar to assertThat method). See in previous example how condition has been improved so much.
Another place where Bool improves readability is with not operator (!).
if you want to return if name is not Alex, you should add a new method with ! operator which does not help us too much in improving the code legibility.
if(isNotAlex(name) {
...
}
private boolean isAlex(String name) {
return "Alex".equals(name);
}
private boolean isNotAlex(String name) {
return !isAlex(name)
}But with Bool:
if(the(name, is(not(equalTo("Alex"))))) {
...
}Bool is also useful when you are dealing with collections. Because you can use any matcher from Hamcrest project you can implement conditions that would require some work if you didn't use Bool, in a few seconds, see next example:
List ages = Arrays.asList(21, 25, 30);
if(areAllPersonsAdult(ages)) {
...
}
private boolean areAllPersonsAdult(List<Integer> ages) {
for(int age:ages) {
if(age < 18) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}To something like:
List ages = Arrays.asList(21, 25, 30);
if(the(ages, is(everyItem(greaterThan(18))))) {
..
}But also with arrays are improved so much, when you want to compare two arrays you cannot do by using equals method directly but using Arrays.equals method. But Hamcrest matchers deals with this problem, hiding this details from developers so we can compare arrays safely.
byte[] name = "alex".getBytes();
if(the(name, is(equalTo("Alex".getBytes())))) {
...
}And of course you can use all matchers you can imagine like contains, empty, containsInAnyOrder, ...
Let's complicate things a bit more.
Normally, our conditions contain more than one clause. For example, the name should be Alex or Ada. For covering this case, be and is keyword is also available. is keyword provides a better readability to your conditions, but can conflict with Hamcrest "is" method. So be is also provided. You can use any of them.
if(the(name, be(equalTo("Alex")).or(be(equalTo("Ada"))))) {
...
}and is also valid, but remember that the is method is from Bool class not the Hamcrest one.
if(the(name, is(equalTo("Alex")).or(is(equalTo("Ada"))))) {
...
}be matcher also contains and operation too.
But sometimes rules are more complex and imply more than one variable. For solving this cases, we must use twice the the keyword. So for example if name should be "Alex" and surname "Soto":
String name = "Alex";
String surname = "Soto";
if(the(name, be(equalTo("Alex")).and(the(surname, equalTo("Soto"))))) {
...
}Note that be keyword is only mandatory when we want to concatenate conditions.
As final notes, you can even use matchers defined in Lambdaj project, and a pretty example could be to compare a property of a class:
private class Person {
private String name;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
if(the(person, having(on(Person.class).getName(), is(equalTo("Alex"))))) {
...
}And also you can use Bool in unit tests by using shouldBe method. For example a valid assertion could be:
assertThat(the(name, shouldBe(equalTo("Alex")).and(shouldBe(startsWith("A")))), is(true));It seems reasonable that using Bool performance should be worst than using native conditions. But I have to say that I have been pleasantly surprised by the performance of Bool and Hamcrest matchers.
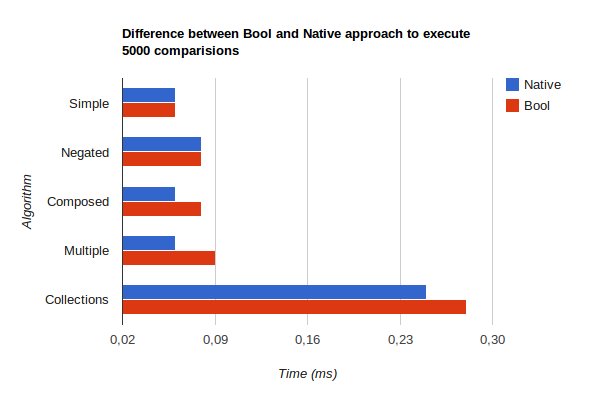
I have run 5000 times some examples provided in documentation. For example one single condition, one condition negated, two conditions over the same attribute with and keyword, two attributes being compared with one condition, and one collection comparison. And the results are the next ones:
PerformanceTests.native_simple_comparision: [measured 50000 out of 50001 rounds, threads: 1 (sequential)]
round: 0.00 [+- 0.00], round.gc: 0.00 [+- 0.00], GC.calls: 0, GC.time: 0.00, time.total: 0.06, time.warmup: 0.00, time.bench: 0.06
PerformanceTests.bool_simple_comparision: [measured 50000 out of 50001 rounds, threads: 1 (sequential)]
round: 0.00 [+- 0.00], round.gc: 0.00 [+- 0.00], GC.calls: 0, GC.time: 0.00, time.total: 0.06, time.warmup: 0.00, time.bench: 0.06
PerformanceTests.native_simple_negated_comparision: [measured 50000 out of 50001 rounds, threads: 1 (sequential)]
round: 0.00 [+- 0.00], round.gc: 0.00 [+- 0.00], GC.calls: 1, GC.time: 0.01, time.total: 0.08, time.warmup: 0.00, time.bench: 0.08
PerformanceTests.bool_simple_negated_comparision: [measured 50000 out of 50001 rounds, threads: 1 (sequential)]
round: 0.00 [+- 0.00], round.gc: 0.00 [+- 0.00], GC.calls: 1, GC.time: 0.00, time.total: 0.08, time.warmup: 0.00, time.bench: 0.08
PerformanceTests.native_composed_comparision: [measured 50000 out of 50001 rounds, threads: 1 (sequential)]
round: 0.00 [+- 0.00], round.gc: 0.00 [+- 0.00], GC.calls: 0, GC.time: 0.00, time.total: 0.06, time.warmup: 0.00, time.bench: 0.06
PerformanceTests.bool_composed_comparision: [measured 50000 out of 50001 rounds, threads: 1 (sequential)]
round: 0.00 [+- 0.00], round.gc: 0.00 [+- 0.00], GC.calls: 0, GC.time: 0.00, time.total: 0.08, time.warmup: 0.00, time.bench: 0.08
PerformanceTests.native_multi_values_composed_comparision: [measured 50000 out of 50001 rounds, threads: 1 (sequential)]
round: 0.00 [+- 0.00], round.gc: 0.00 [+- 0.00], GC.calls: 0, GC.time: 0.00, time.total: 0.06, time.warmup: 0.00, time.bench: 0.06
PerformanceTests.bool_multi_values_composed_comparision: [measured 50000 out of 50001 rounds, threads: 1 (sequential)]
round: 0.00 [+- 0.00], round.gc: 0.00 [+- 0.00], GC.calls: 0, GC.time: 0.00, time.total: 0.09, time.warmup: 0.00, time.bench: 0.09
PerformanceTests.native_collection_comparision: [measured 50000 out of 50001 rounds, threads: 1 (sequential)]
round: 0.00 [+- 0.00], round.gc: 0.00 [+- 0.00], GC.calls: 1, GC.time: 0.01, time.total: 0.25, time.warmup: 0.00, time.bench: 0.25
PerformanceTests.bool_collection_comparision: [measured 50000 out of 50001 rounds, threads: 1 (sequential)]
round: 0.00 [+- 0.00], round.gc: 0.00 [+- 0.00], GC.calls: 3, GC.time: 0.01, time.total: 0.28, time.warmup: 0.01, time.bench: 0.27
Note that using simple conditions the time is the same, and is after we start creating more complex condition expressions that the performance is a bit reduced.
You can find the performance test in com.lordofthejars.bool.performance.PerformanceTests
Please keep in mind that the border between writing clean and readable code and something unintelligible is very thin. You can start creating a complex chaining of calls train wreck so no one can understand the real meaning of the condition. One good practice to avoid this case is splitting complex chaining calls into multiple variables and then the final calls are executed inside the if (or inside a method which extracts all this logic). But anyway if you found creating a really complex condition, think about the correctness of this logic before coding it, because maybe you are providing to a condition a heavy responsibility.
Also note that you can use Bool in all of your conditions, but where you really take the full power is in conditions that represents important rules for your business.
- Email: asotobu at gmail.com
- Blog: Lord Of The Jars
- Twitter: @alexsotob
- Github: Bool Github
And any suggestion, improve, or bug don't hesitate to open an issue.