-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
Home
Hyperion is an engine designed to launch and monitor user defined components using YAML configuration files.
Inspired by vdemo and TMuLE (see vdemo and TMuLE assessment)
Hyperion (like TMuLE) is written in Python and utilizes the tmux library for python to start components in detached sessions. For each host defined in the components a master session is created, in which each component will be started in a window.
Hyperion is planned to support various modes, but currently the main developing focus is set on the 'run' and the 'slave' mode:
hyperion --config systems/demo.yaml run
The run mode will initialize the configured system with the executing host as controlling instance. The the used components will be copied to the hosts they will be run on and a GUI to start, monitor and stop components will show.
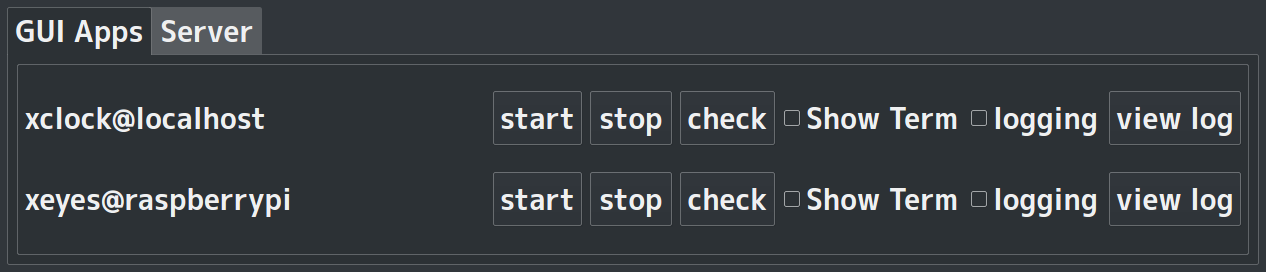 Image: Screenshot of the current GUI prototype (September 2018)
Image: Screenshot of the current GUI prototype (September 2018)
hyperion --config components/top.yaml slave
The slave mode will search for an already running tmux slave session on the executing host and start one, if it's not found. Then only the specified component will be started a new window within the slave session.
hyperion --config components/top.yaml slave --kill
When the optional kill argument is provided, the window belonging to the specified component is searched in the slave session and if found, a SIGINT signal is sent to the running program and after that the window is killed.
hyperion --config systems/demo.yaml validate
The validation mode parses the dependencies specified in the component configuration files and checks whether they are all met makes sure the directed dependency graph is acyclic (no circular dependencies) to check if starting all components with their dependencies is possible. Errors (unmet and circular dependencies) are displayed on the cli. If the configuration is valid, a list showing the order for a full system start is printed on the cli.
hyperion --config components/top.yaml validate --visual
by specifying the visual argument, the command will generate an image of the the dependency graph (highlighting errors). Please note: if a circular dependency error is detected, the graph will be incomplete because the algorithm won't be able to iterate through the remaining nodes!

Image: Graph generated with the sample components (October 2018)
hyperion --config systems/demo.yaml edit
The editor mode is planned to provide an editor GUI to create and edit components, groups and systems. The main idea is, to prevent misconfiguration by wrong by syntax errors in the configuration files and to help configure run dependencies (see dependency feature). Maybe this feature will integrate the validation mode.
An initial structure for the system components has been chosen: YAML file format. (may be subject to change)
Additionally an initial effort to model the component lifecycle has been made.
EMPTY