2020年12月11日,国际知名刊物《eLife》在线发表A gustatory receptor tuned to the steroid plant hormone brassinolide in Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae)一文,该研究成果由中科院动物所昆虫生理与神经遗传学研究组完成。本文第一作者:杨科博士,通讯作者:王琛柱研究员。
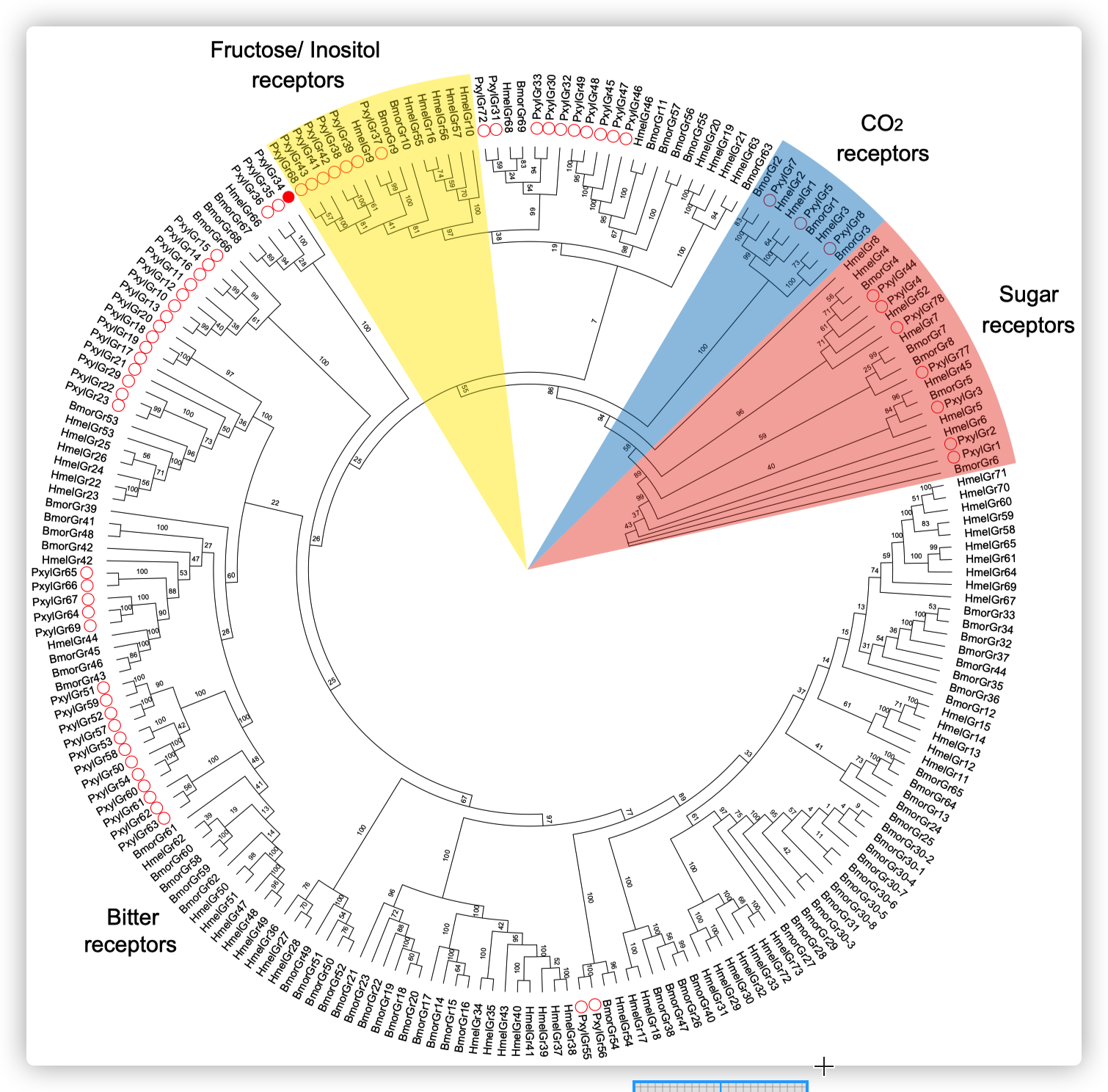
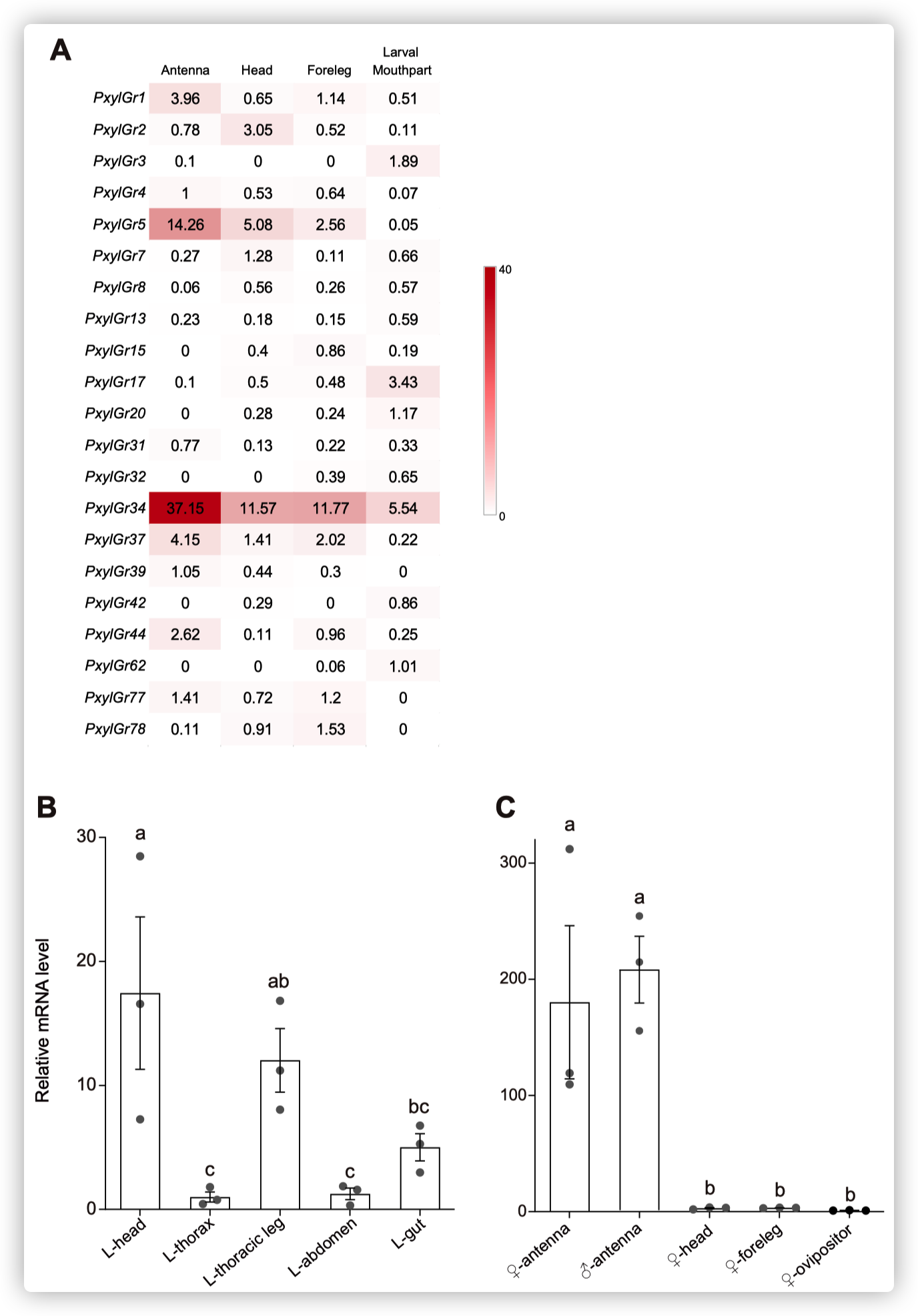
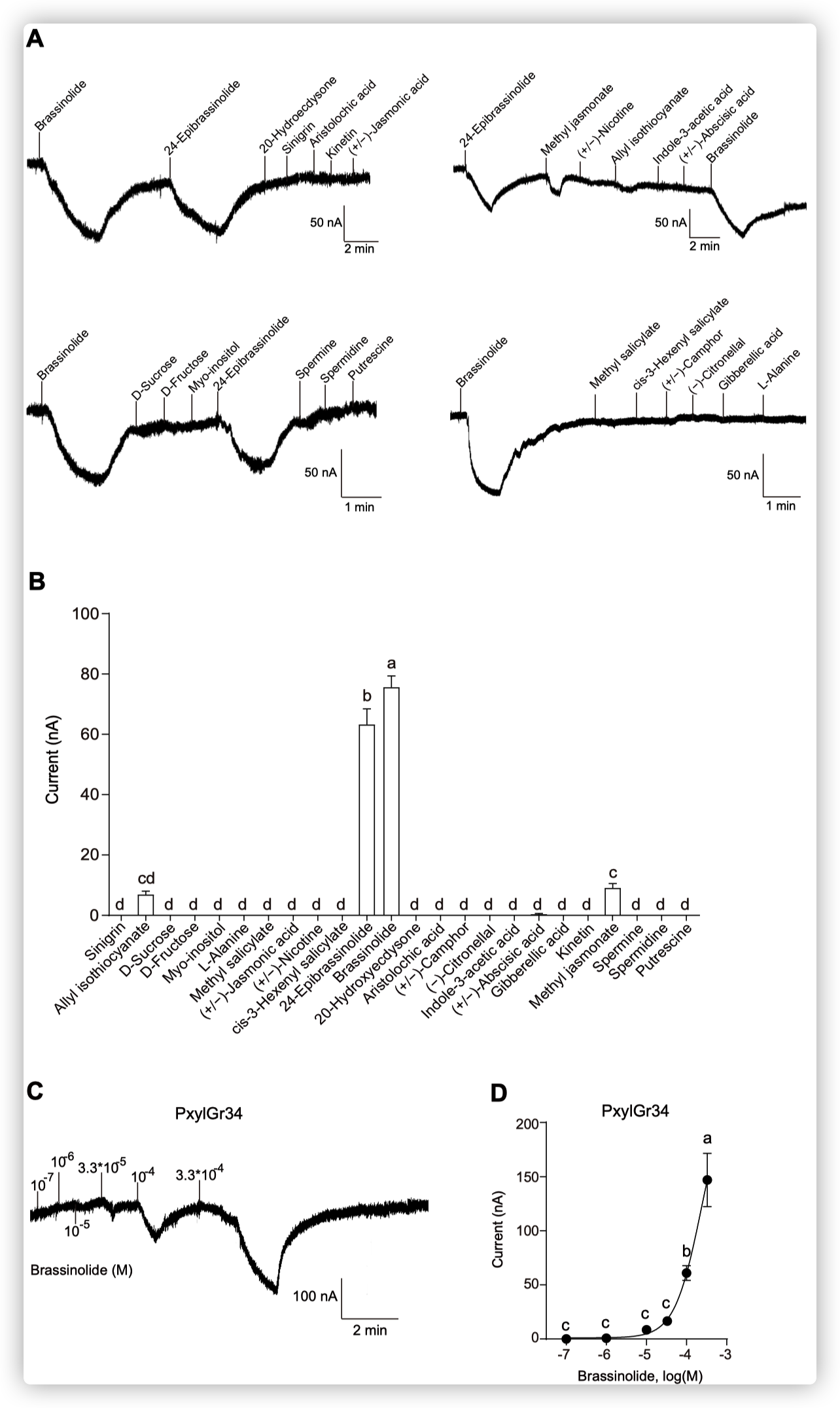
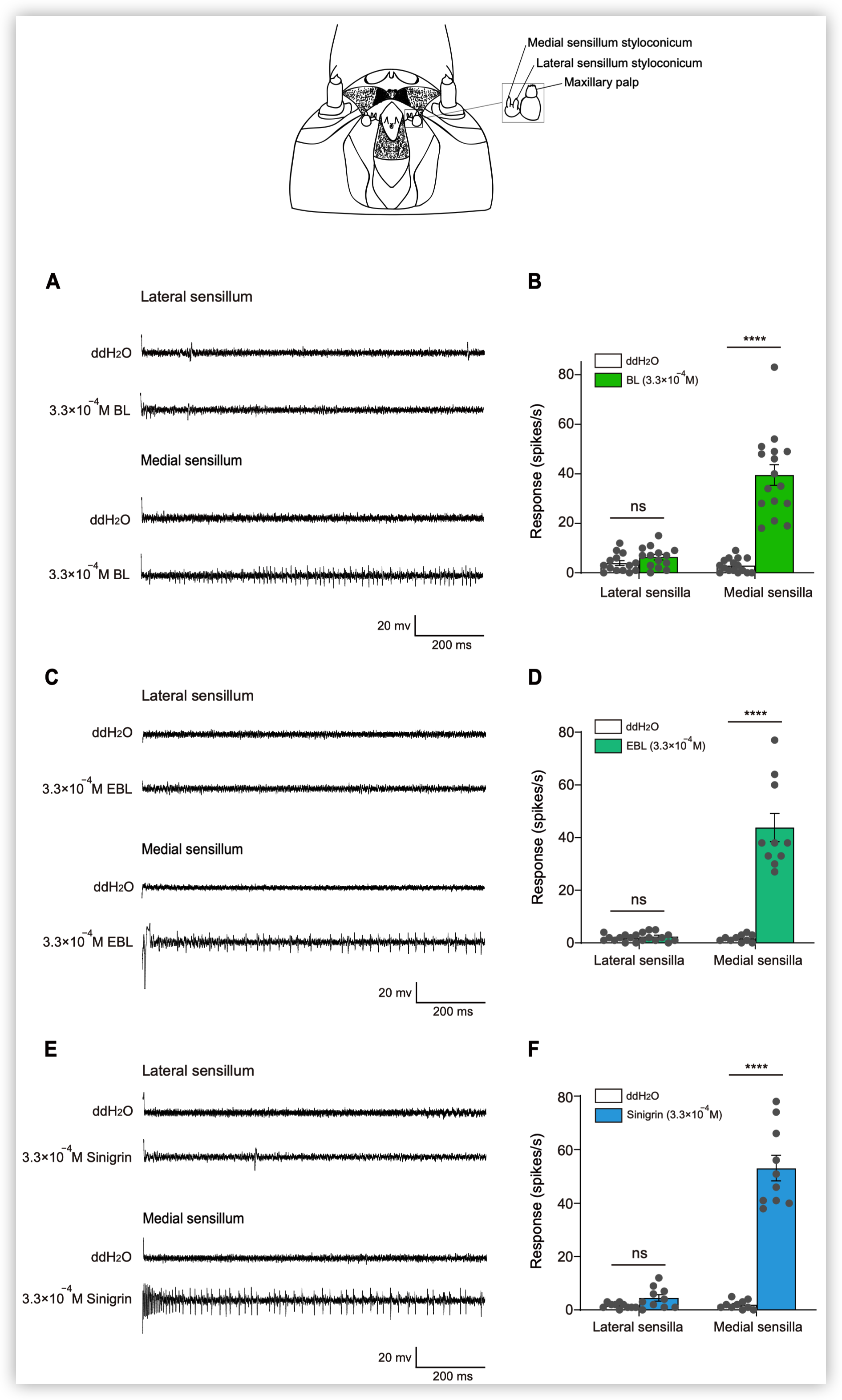
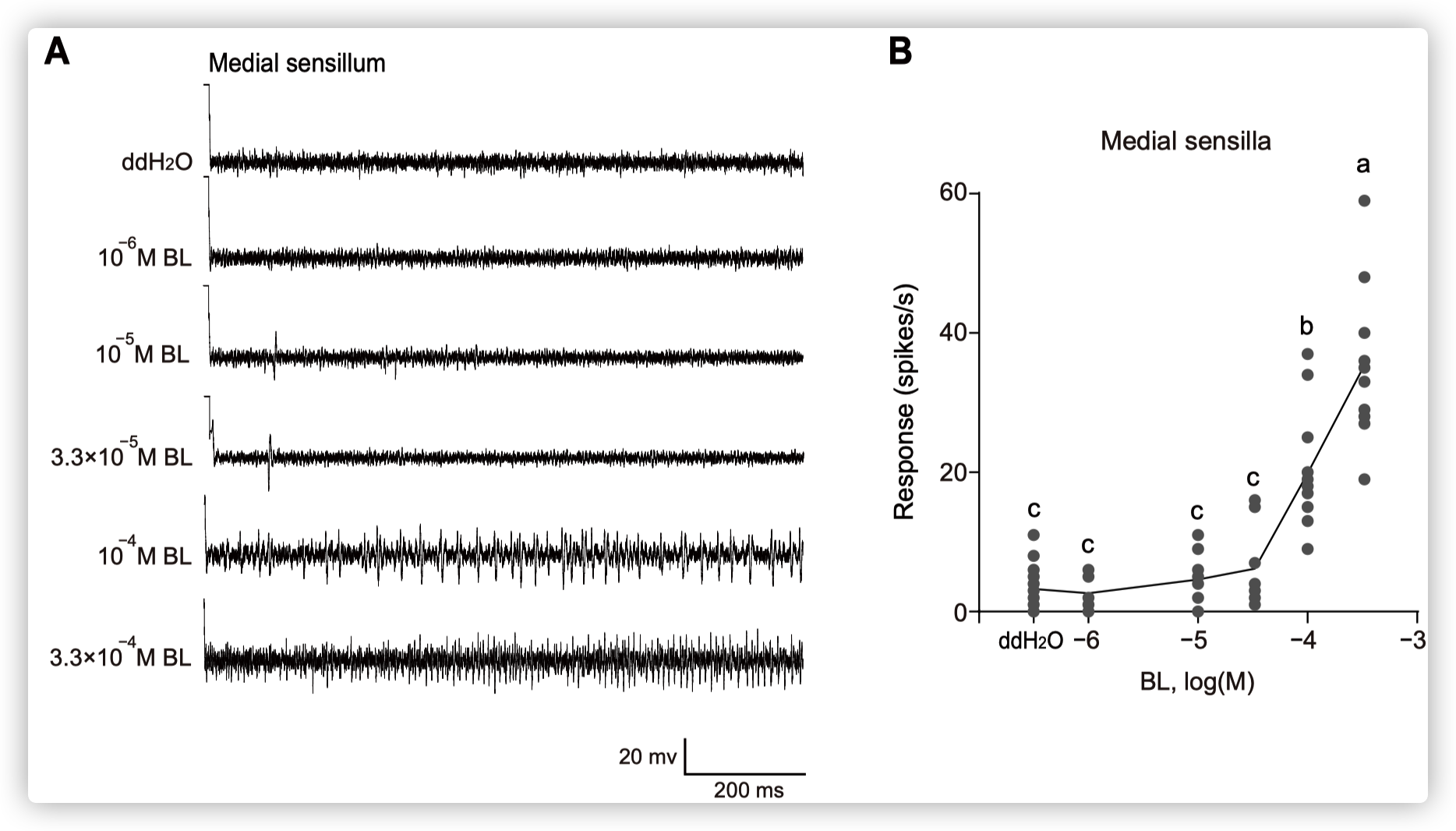
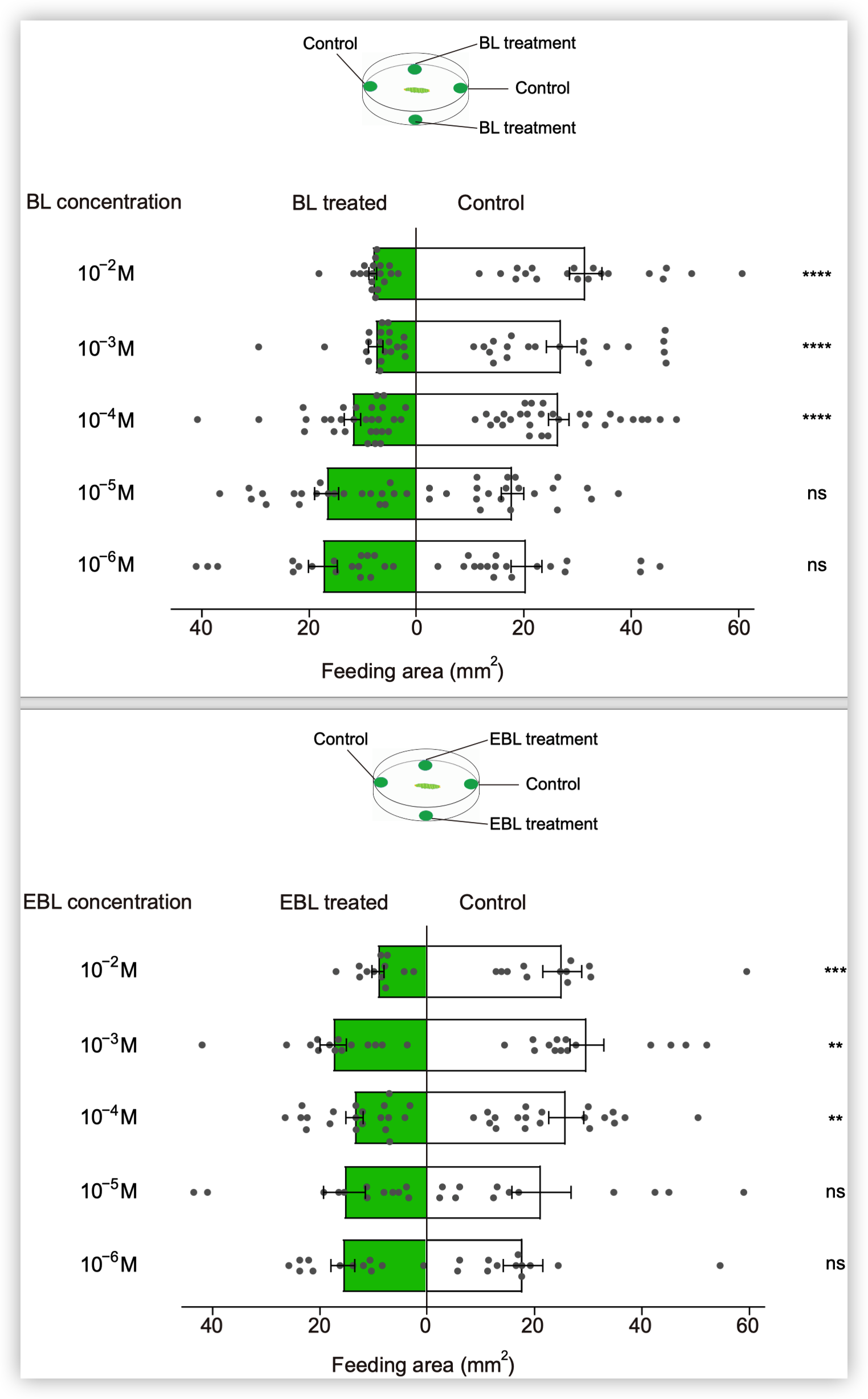
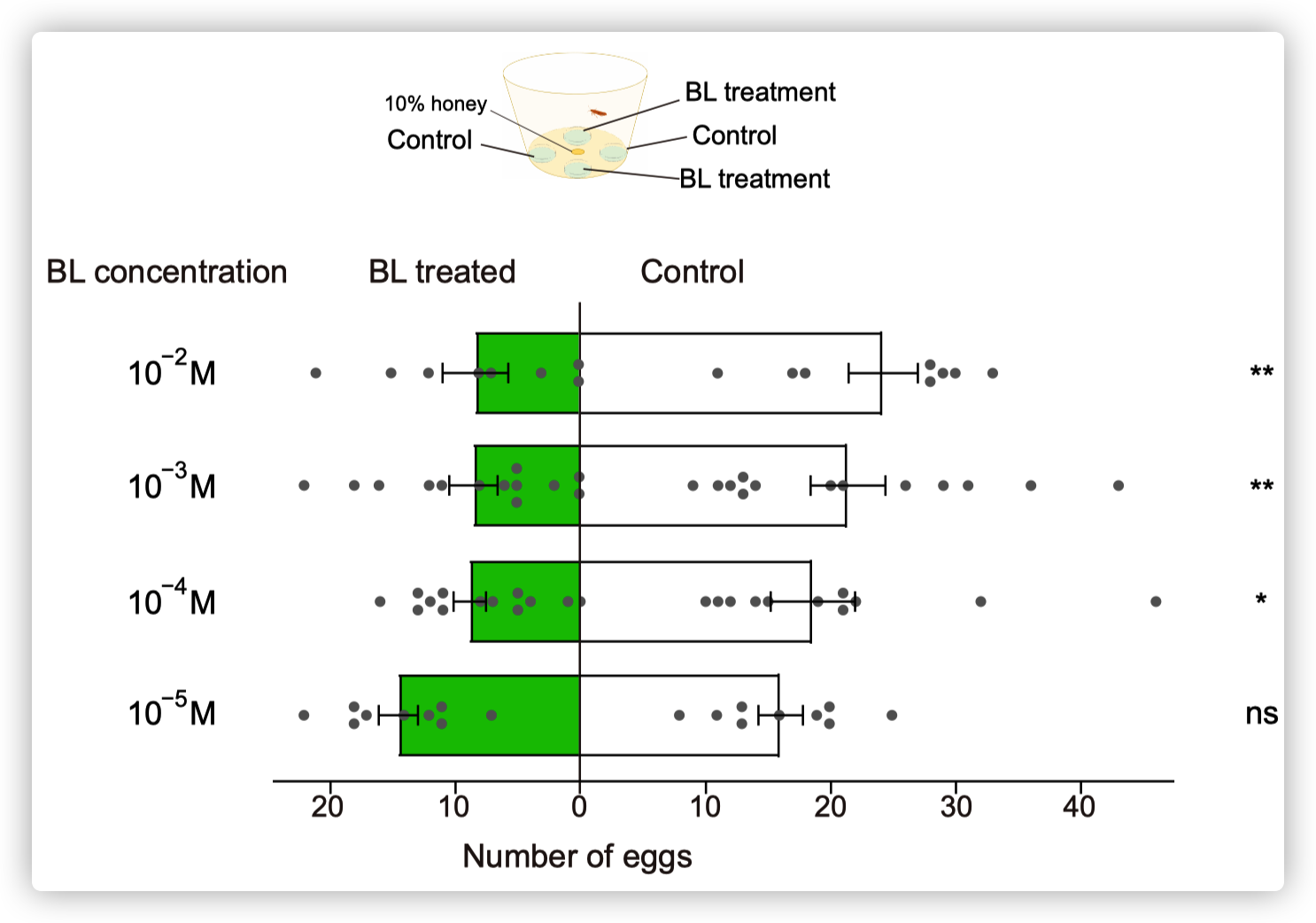
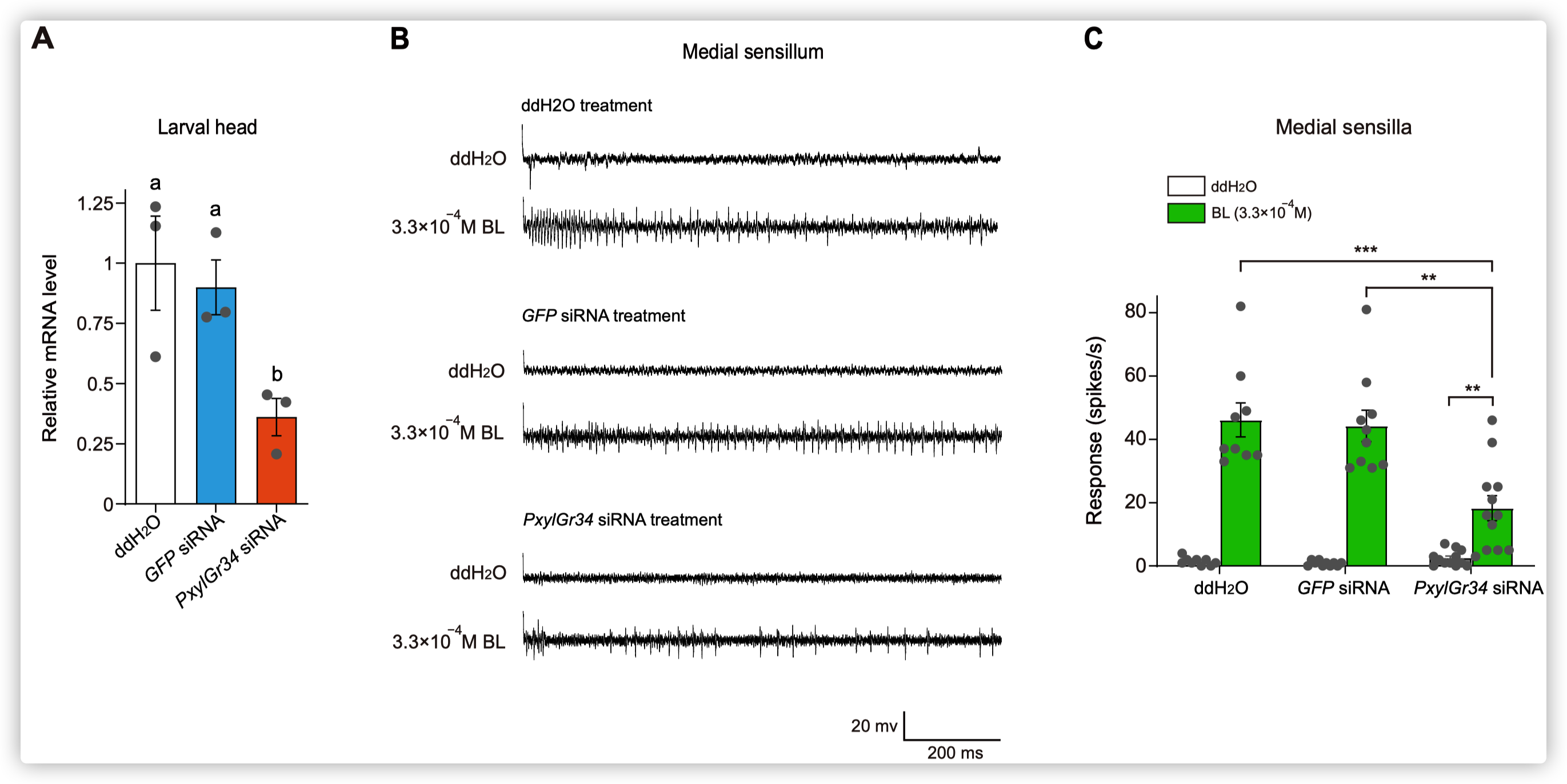
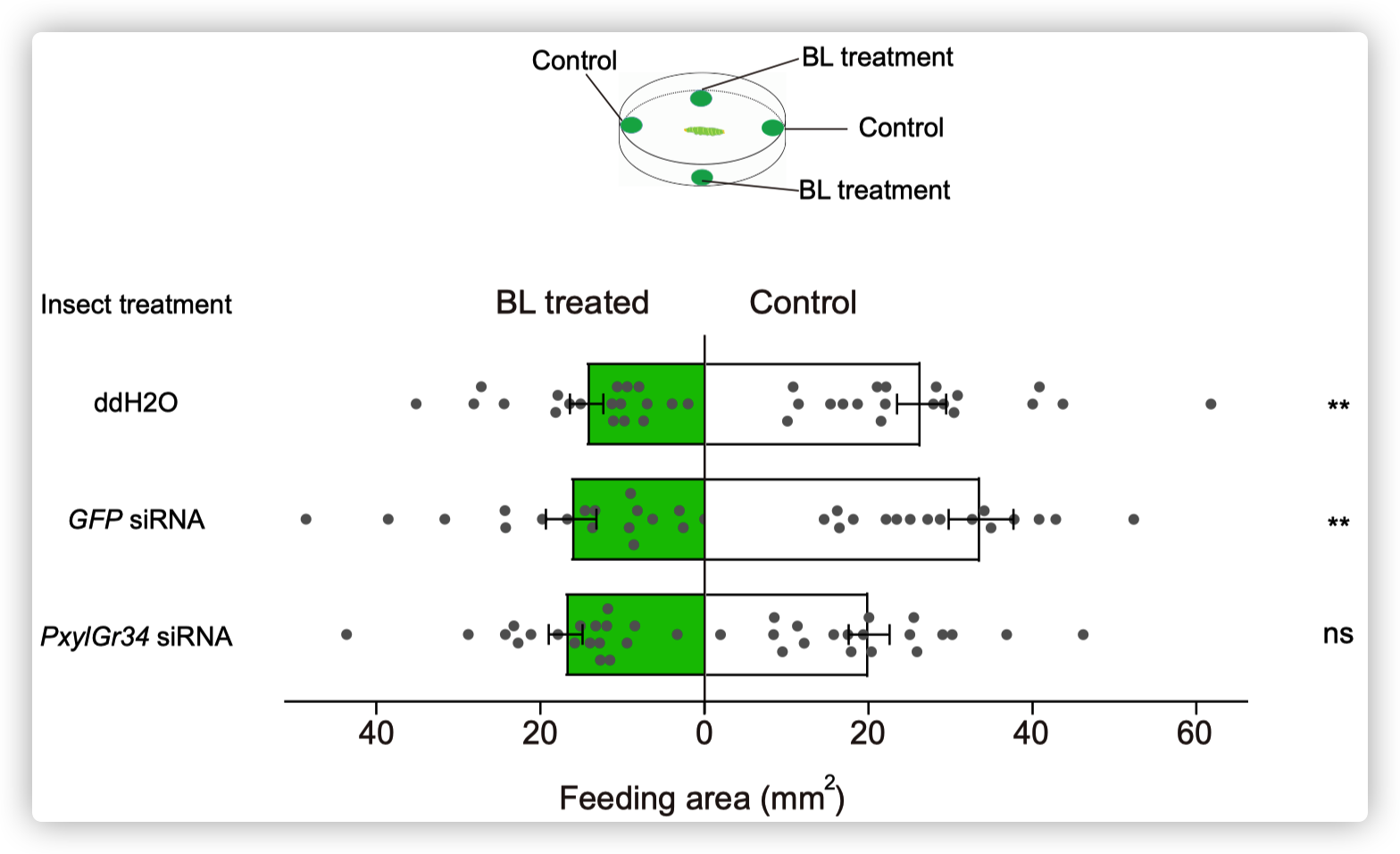
小菜蛾为鳞翅目菜蛾科昆虫,是世界性的大害虫,主要取食十字花科植物,每年造成4-5亿美元的损失。由于其生命周期短(14天),它已对常规杀虫剂产生了抗药性。其雌虫在产卵前用触角拍打叶表面,此行为可能与十字花科植物叶片中的某些化学成分有关,包括糖,糖醇,氨基酸,胺,硫代葡萄糖苷和植物激素等。在这些化合物中,黑芥子苷(sinigrin)和油菜素内酯(brassinolide)在十字花科植物中的浓度要比许多其他植物物种高。 前人的研究表明,Sinigrin是小菜蛾的取食/产卵兴奋剂。小菜蛾幼虫口器上中栓锥感器含有对黑芥子苷和其他芥子油苷化合物敏感的味觉受体神经元。取食和产卵抑制物可帮助植食性昆虫识别寄主植物,其味觉器官中含有苦味受体(GRs)。油菜素内酯是一种普遍存在的植物激素,已对其在植物生长和发育中的作用进行了广泛的研究,但对其植食性昆虫的影响知之甚少。为了揭示小菜蛾对食物/产卵刺激物和趋避物的化学感受分子基础,通过转录组分析和qPCR,我们鉴定了一种在幼虫头部和成虫触角中高表达的苦味味觉受体(PxylGr34)。使用非洲爪蟾卵母细胞表达系统和24种不同的植物化学物质进行的功能分析表明,PxylGr34可以调节经典的植物激素油菜素内酯(BL)和24-表油菜素内酯(EBL)。电生理分析表明,四龄幼虫的中栓锥感器对BL和EBL有反应。双向取食实验表明,BL抑制幼虫取食和雌虫产卵。 RNAi抑制PxylGr34减弱了对BL的味觉反应,并消除了BL诱导的取食抑制。
PxylGr34 siRNA-treated P. xylostella larvae show attenuated taste responses to BL and alleviated feeding deterrent effect of BL
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.64114
**行为生理与神经遗传学课题组主页:**http://www.ipm.ioz.cas.cn/kydw/yjz/wangchenzhu/bzjs/
**更多内容也可关注我们课题组网站:**https://www.moths.life/