-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 40
/
Copy pathREADME.Rmd
202 lines (131 loc) · 12.4 KB
/
README.Rmd
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
---
output: github_document
---
```{r, warning=FALSE, message=FALSE, echo = FALSE}
knitr::opts_chunk$set(
collapse = TRUE,
warning = FALSE,
message = FALSE,
fig.path = "README-",
comment = "#>"
)
options(knitr.kable.NA = "", digits = 2, width = 80)
```
# insight <img src='man/figures/logo.png' align="right" height="139" />
[](https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.01412)
[](https://cranlogs.r-pkg.org/) [](https://cranlogs.r-pkg.org/)
**Gain insight into your models!**
When fitting any statistical model, there are many useful pieces of information that are simultaneously calculated and stored beyond coefficient estimates and general model fit statistics. Although there exist some generic functions to obtain model information and data, many package-specific modelling functions do not provide such methods to allow users to access such valuable information.
**insight** is an R-package that fills this important gap by providing a suite of functions to support almost any model (see a list of the many models supported below in the **List of Supported Packages and Models** section). The goal of **insight**, then, is to provide tools to provide *easy*, *intuitive*, and *consistent* access to information contained in model objects. These tools aid applied research in virtually any field who fit, diagnose, and present statistical models by streamlining access to every aspect of many model objects via consistent syntax and output.
## Installation
[](https://cran.r-project.org/package=insight) [](https://easystats.r-universe.dev) [](https://github.com/easystats/insight/actions)
The *insight* package is available on CRAN, while its latest development version is available on R-universe (from _rOpenSci_) or GitHub.
Type | Source | Command
---|---|---
Release | CRAN | `install.packages("insight")`
Development | r-universe | `install.packages("insight", repos = "https://easystats.r-universe.dev")`
Development | GitHub | `remotes::install_github("easystats/insight")`
Once you have downloaded the package, you can then load it using:
```{r, eval=FALSE}
library("insight")
```
> **Tip**
>
> Instead of `library(insight)`, use `library(easystats)`. This will make all features of the easystats-ecosystem available.
>
> To stay updated, use `easystats::install_latest()`.
## Documentation
[](https://easystats.github.io/insight/)
[](https://easystats.github.io/blog/posts/)
[](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/index.html)
Built with non-programmers in mind, **insight** offers a broad toolbox for making model and data information easily accessible. While **insight** offers many useful functions for working with and understanding model objects (discussed below), we suggest users start with `model_info()`, as this function provides a clean and consistent overview of model objects (e.g., functional form of the model, the model family, link function, number of observations, variables included in the specification, etc.). With a clear understanding of the model introduced, users are able to adapt other functions for more nuanced exploration of and interaction with virtually any model object.Please visit [https://easystats.github.io/insight/](https://easystats.github.io/insight/) for documentation.
### Definition of Model Components
The functions from **insight** address different components of a model. In an effort to avoid confusion about specific "targets" of each function, in this section we provide a short explanation of **insight**'s definitions of regression model components.
#### Data
The dataset used to fit the model.
#### Parameters
Values estimated or learned from data that capture the relationship between variables. In regression models, these are usually referred to as *coefficients*.
#### Response and Predictors
* **response**: the outcome or response variable (dependent variable) of a regression model.
* **predictor**: independent variables of (the _fixed_ part of) a regression model. For mixed models, variables that are only in the _random effects_ part (i.e. grouping factors) of the model are not returned as predictors by default. However, these can be included using additional arguments in the function call, treating predictors are "unique". As such, if a variable appears as a fixed effect and a random slope, it is treated as one (the same) predictor.
#### Variables
Any unique variable names that appear in a regression model, e.g., response variable, predictors or random effects. A "variable" only relates to the unique occurence of a term, or the term name. For instance, the expression `x + poly(x, 2)` has only the variable `x`.
#### Terms
Terms themselves consist of variable and factor names separated by operators, or involve arithmetic expressions. For instance, the expression `x + poly(x, 2)` has _one_ variable `x`, but _two_ terms `x` and `poly(x, 2)`.
#### Random Effects
* **random slopes**: variables that are specified as random slopes in a mixed effects model.
* **random or grouping factors**: variables that are specified as grouping variables in a mixed effects model.
*Aren't the predictors, terms and parameters the same thing?*
In some cases, yes. But not in all cases. Find out more by [**clicking here to access the documentation**](https://easystats.github.io/insight/articles/insight.html).
### Functions
The package revolves around two key prefixes: `get_*` and `find_*`. The `get_*` prefix extracts *values* (or *data*) associated with model-specific objects (e.g., parameters or variables), while the `find_*` prefix *lists* model-specific objects (e.g., priors or predictors). These are powerful families of functions allowing for great flexibility in use, whether at a high, descriptive level (`find_*`) or narrower level of statistical inspection and reporting (`get_*`).
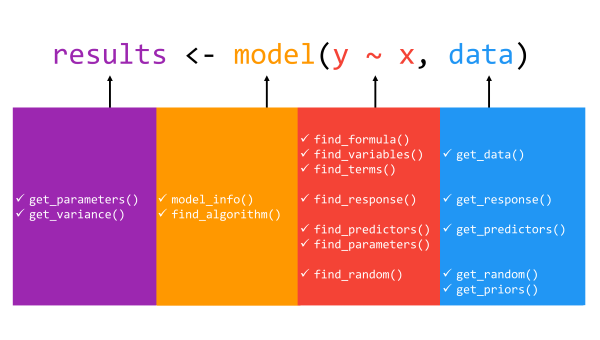
In total, the **insight** package includes 16 core functions: [get_data()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/get_data.html), [get_priors()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/get_priors.html), [get_variance()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/get_variance.html), [get_parameters()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/get_parameters.html), [get_predictors()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/get_predictors.html), [get_random()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/get_random.html), [get_response()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/get_response.html), [find_algorithm()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/find_algorithm.html), [find_formula()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/find_formula.html), [find_variables()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/find_variables.html), [find_terms()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/find_terms.html), [find_parameters()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/find_parameters.html), [find_predictors()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/find_predictors.html), [find_random()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/find_random.html), [find_response()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/find_response.html), and [model_info()](https://easystats.github.io/insight/reference/model_info.html). In all cases, users must supply at a minimum, the name of the model fit object. In several functions, there are additional arguments that allow for more targeted returns of model information. For example, the `find_terms()` function's `effects` argument allows for the extraction of "fixed effects" terms, "random effects" terms, or by default, "all" terms in the model object. We point users to the package documentation or the complementary package website, <https://easystats.github.io/insight/>, for a detailed list of the arguments associated with each function as well as the returned values from each function.
### Examples of Use Cases in R
We now would like to provide examples of use cases of the **insight** package. These examples probably do not cover typical real-world problems, but serve as illustration of the core idea of this package: The unified interface to access model information. **insight** should help both users and package developers in order to reduce the hassle with the many exceptions from various modelling packages when accessing model information.
#### Making Predictions at Specific Values of a Term of Interest
Say, the goal is to make predictions for a certain term, holding remaining co-variates constant. This is achieved by calling `predict()` and feeding the `newdata`-argument with the values of the term of interest as well as the "constant" values for remaining co-variates. The functions `get_data()` and `find_predictors()` are used to get this information, which then can be used in the call to `predict()`.
In this example, we fit a simple linear model, but it could be replaced by (m)any other models, so this approach is "universal" and applies to many different model objects.
```{r}
library(insight)
m <- lm(
Sepal.Length ~ Species + Petal.Width + Sepal.Width,
data = iris
)
dat <- get_data(m)
pred <- find_predictors(m, flatten = TRUE)
l <- lapply(pred, function(x) {
if (is.numeric(dat[[x]])) {
mean(dat[[x]])
} else {
unique(dat[[x]])
}
})
names(l) <- pred
l <- as.data.frame(l)
cbind(l, predictions = predict(m, newdata = l))
```
#### Printing Model Coefficients
The next example should emphasize the possibilities to generalize functions to many different model objects using **insight**. The aim is simply to print coefficients in a complete, human readable sentence.
The first approach uses the functions that are available for some, but obviously not for all models, to access the information about model coefficients.
```{r}
print_params <- function(model) {
paste0(
"My parameters are ",
toString(row.names(summary(model)$coefficients)),
", thank you for your attention!"
)
}
m1 <- lm(Sepal.Length ~ Petal.Width, data = iris)
print_params(m1)
# obviously, something is missing in the output
m2 <- mgcv::gam(Sepal.Length ~ Petal.Width + s(Petal.Length), data = iris)
print_params(m2)
```
As we can see, the function fails for *gam*-models. As the access to models depends on the type of the model in the R ecosystem, we would need to create specific functions for all models types. With **insight**, users can write a function without having to worry about the model type.
```{r}
print_params <- function(model) {
paste0(
"My parameters are ",
toString(insight::find_parameters(model, flatten = TRUE)),
", thank you for your attention!"
)
}
m1 <- lm(Sepal.Length ~ Petal.Width, data = iris)
print_params(m1)
m2 <- mgcv::gam(Sepal.Length ~ Petal.Width + s(Petal.Length), data = iris)
print_params(m2)
```
## Contributing and Support
In case you want to file an issue or contribute in another way to the package, please follow [this guide](https://github.com/easystats/insight/blob/master/.github/CONTRIBUTING.md). For questions about the functionality, you may either contact us via email or also file an issue.
## List of Supported Models by Class
Currently, about `r length(supported_models())` model classes are supported.
```{r, warning=FALSE, message=FALSE, eval=TRUE}
supported_models()
```
- **Didn't find a model?** [File an issue](https://github.com/easystats/insight/issues) and request additional model-support in _insight_!
## Citation
If this package helped you, please consider citing as follows:
Lüdecke D, Waggoner P, Makowski D. insight: A Unified Interface to Access Information from Model Objects in R. Journal of Open Source Software 2019;4:1412. doi: [10.21105/joss.01412](https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.01412)
## Code of Conduct
Please note that the insight project is released with a [Contributor Code of Conduct](https://contributor-covenant.org/version/2/1/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.html). By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.