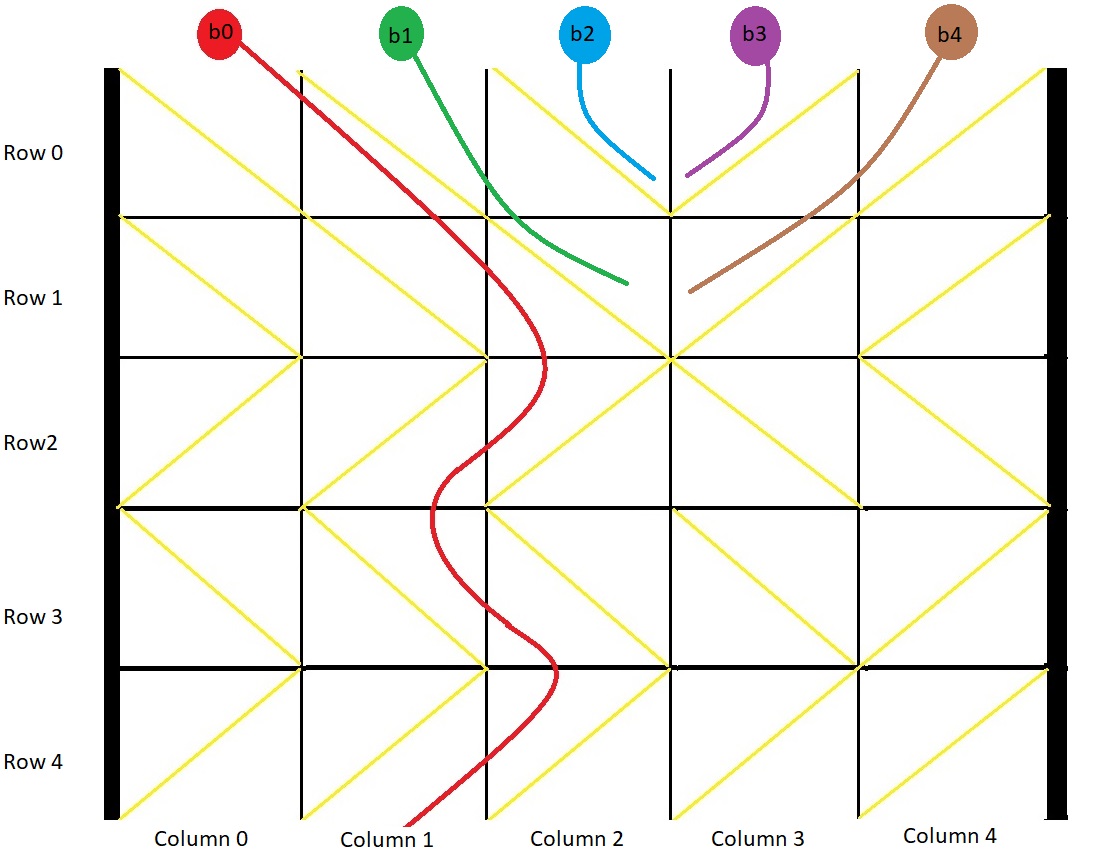
You have a 2-D grid of size m x n representing a box, and you have n balls. The box is open on the top and bottom sides.
Each cell in the box has a diagonal board spanning two corners of the cell that can redirect a ball to the right or to the left.
- A board that redirects the ball to the right spans the top-left corner to the bottom-right corner and is represented in the grid as 1.
- A board that redirects the ball to the left spans the top-right corner to the bottom-left corner and is represented in the grid as -1. We drop one ball at the top of each column of the box. Each ball can get stuck in the box or fall out of the bottom. A ball gets stuck if it hits a "V" shaped pattern between two boards or if a board redirects the ball into either wall of the box.
Return an array answer of size n where answer[i] is the column that the ball falls out of at the bottom after dropping the ball from the ith column at the top, or -1 if the ball gets stuck in the box.
Input: grid = [[1,1,1,-1,-1],[1,1,1,-1,-1],[-1,-1,-1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,-1],[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]]
Output: [1,-1,-1,-1,-1]
Code :
class Solution {
public int dfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j){
if(i==grid.length)
return j;
if(j<0 || j>=grid[0].length)
return -1;
if(grid[i][j]==1 && j+1<grid[0].length && grid[i][j+1]==1)
return dfs(grid,i+1,j+1);
else if(grid[i][j]==-1 && j-1>=0 && grid[i][j-1]==-1)
return dfs(grid,i+1,j-1);
return -1;
}
public int[] findBall(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid[0].length;
int[] ar = new int[m];
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
ar[j]=dfs(grid,0,j);
return ar;
}
}