There is an undirected connected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1 and n - 1 edges.
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums of length n where nums[i] represents the value of the ith node. You are also given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1 where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Remove two distinct edges of the tree to form three connected components. For a pair of removed edges, the following steps are defined:
- Get the XOR of all the values of the nodes for each of the three components respectively.
- The difference between the largest XOR value and the smallest XOR value is the score of the pair.
- For example, say the three components have the node values:
[4,5,7],[1,9], and[3,3,3]. The three XOR values are4 ^ 5 ^ 7 = 6,1 ^ 9 = 8, and3 ^ 3 ^ 3 = 3. The largest XOR value is8and the smallest XOR value is3. The score is then8 - 3 = 5.
Return the minimum score of any possible pair of edge removals on the given tree.
Example 1:
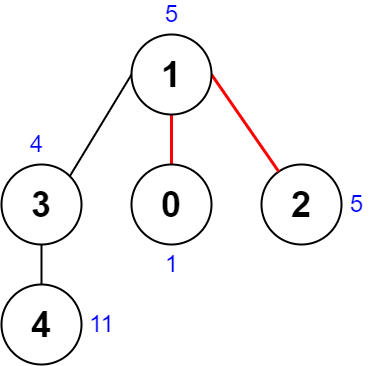
Input: nums = [1,5,5,4,11], edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[3,4]] Output: 9 Explanation: The diagram above shows a way to make a pair of removals. - The 1st component has nodes [1,3,4] with values [5,4,11]. Its XOR value is 5 ^ 4 ^ 11 = 10. - The 2nd component has node [0] with value [1]. Its XOR value is 1 = 1. - The 3rd component has node [2] with value [5]. Its XOR value is 5 = 5. The score is the difference between the largest and smallest XOR value which is 10 - 1 = 9. It can be shown that no other pair of removals will obtain a smaller score than 9.
Example 2:
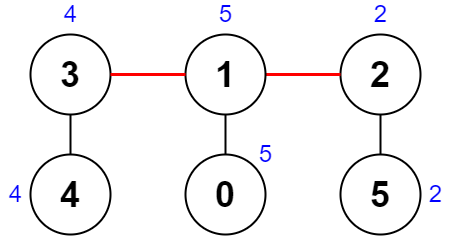
Input: nums = [5,5,2,4,4,2], edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[5,2],[4,3],[1,3]] Output: 0 Explanation: The diagram above shows a way to make a pair of removals. - The 1st component has nodes [3,4] with values [4,4]. Its XOR value is 4 ^ 4 = 0. - The 2nd component has nodes [1,0] with values [5,5]. Its XOR value is 5 ^ 5 = 0. - The 3rd component has nodes [2,5] with values [2,2]. Its XOR value is 2 ^ 2 = 0. The score is the difference between the largest and smallest XOR value which is 0 - 0 = 0. We cannot obtain a smaller score than 0.
Constraints:
n == nums.length3 <= n <= 10001 <= nums[i] <= 108edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != biedgesrepresents a valid tree.
class Solution:
def minimumScore(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def dfs(i, fa, x):
res = nums[i]
for j in g[i]:
if j != fa and j != x:
res ^= dfs(j, i, x)
return res
def dfs2(i, fa, x):
nonlocal s, s1, ans
res = nums[i]
for j in g[i]:
if j != fa and j != x:
a = dfs2(j, i, x)
res ^= a
b = s1 ^ a
c = s ^ s1
t = max(a, b, c) - min(a, b, c)
ans = min(ans, t)
return res
g = defaultdict(list)
for a, b in edges:
g[a].append(b)
g[b].append(a)
s = 0
for v in nums:
s ^= v
n = len(nums)
ans = inf
for i in range(n):
for j in g[i]:
s1 = dfs(i, -1, j)
dfs2(i, -1, j)
return ansclass Solution {
private int s;
private int s1;
private int n;
private int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private int[] nums;
private List<Integer>[] g;
public int minimumScore(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {
n = nums.length;
g = new List[n];
this.nums = nums;
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
for (int v : nums) {
s ^= v;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j : g[i]) {
s1 = dfs(i, -1, j);
dfs2(i, -1, j);
}
}
return ans;
}
private int dfs(int i, int fa, int x) {
int res = nums[i];
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (j != fa && j != x) {
res ^= dfs(j, i, x);
}
}
return res;
}
private int dfs2(int i, int fa, int x) {
int res = nums[i];
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (j != fa && j != x) {
int a = dfs2(j, i, x);
res ^= a;
int b = s1 ^ a;
int c = s ^ s1;
int t = Math.max(Math.max(a, b), c) - Math.min(Math.min(a, b), c);
ans = Math.min(ans, t);
}
}
return res;
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nums;
int s;
int s1;
int n;
int ans = INT_MAX;
vector<vector<int>> g;
int minimumScore(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
n = nums.size();
g.resize(n, vector<int>());
for (auto& e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
for (int& v : nums) s ^= v;
this->nums = nums;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j : g[i]) {
s1 = dfs(i, -1, j);
dfs2(i, -1, j);
}
}
return ans;
}
int dfs(int i, int fa, int x) {
int res = nums[i];
for (int j : g[i])
if (j != fa && j != x) res ^= dfs(j, i, x);
return res;
}
int dfs2(int i, int fa, int x) {
int res = nums[i];
for (int j : g[i])
if (j != fa && j != x) {
int a = dfs2(j, i, x);
res ^= a;
int b = s1 ^ a;
int c = s ^ s1;
int t = max(max(a, b), c) - min(min(a, b), c);
ans = min(ans, t);
}
return res;
}
};func minimumScore(nums []int, edges [][]int) int {
n := len(nums)
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
a, b := e[0], e[1]
g[a] = append(g[a], b)
g[b] = append(g[b], a)
}
s := 0
for _, v := range nums {
s ^= v
}
s1 := 0
ans := math.MaxInt32
var dfs func(int, int, int) int
var dfs2 func(int, int, int) int
dfs = func(i, fa, x int) int {
res := nums[i]
for _, j := range g[i] {
if j != fa && j != x {
res ^= dfs(j, i, x)
}
}
return res
}
dfs2 = func(i, fa, x int) int {
res := nums[i]
for _, j := range g[i] {
if j != fa && j != x {
a := dfs2(j, i, x)
res ^= a
b := s1 ^ a
c := s ^ s1
t := max(max(a, b), c) - min(min(a, b), c)
ans = min(ans, t)
}
}
return res
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for _, j := range g[i] {
s1 = dfs(i, -1, j)
dfs2(i, -1, j)
}
}
return ans
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}