- leetcode: Add Binary | LeetCode OJ
- lintcode: (408) Add Binary
Given two binary strings, return their sum (also a binary string).
For example,
a = "11"
b = "1"
Return "100".
用字符串模拟二进制的加法,加法操作一般使用自后往前遍历的方法,不同位大小需要补零。
public class Solution {
/**
* @param a a number
* @param b a number
* @return the result
*/
public String addBinary(String a, String b) {
if (a == null || a.length() == 0) return b;
if (b == null || b.length() == 0) return a;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int aLen = a.length(), bLen = b.length();
int carry = 0;
for (int ia = aLen - 1, ib = bLen - 1; ia >= 0 || ib >= 0; ia--, ib--) {
// replace with 0 if processed
int aNum = (ia < 0) ? 0 : a.charAt(ia) - '0';
int bNum = (ib < 0) ? 0 : b.charAt(ib) - '0';
int num = (aNum + bNum + carry) % 2;
carry = (aNum + bNum + carry) / 2;
sb.append(num);
}
if (carry == 1) sb.append(1);
// important!
sb.reverse();
String result = sb.toString();
return result;
}
}用到的技巧主要有两点,一是两个数位数大小不一时用0补上,二是最后需要判断最高位的进位是否为1。最后需要反转字符串,因为我们是从低位往高位迭代的。虽然可以使用 insert 避免最后的 reverse 操作,但如此一来时间复杂度就从 $$O(n)$$ 变为 $$O(n^2)$$ 了。
遍历两个字符串,时间复杂度 $$O(n)$$. reverse 操作时间复杂度 $$O(n)$$, 故总的时间复杂度 $$O(n)$$. 使用了 StringBuilder 作为临时存储对象,空间复杂度 $$O(n)$$.
- leetcode: Reverse Integer | LeetCode OJ
- lintcode: (413) Reverse Integer
Reverse digits of an integer. Returns 0 when the reversed integer overflows (signed 32-bit integer).
Given x = 123, return 321
Given x = -123, return -321
初看这道题觉得先将其转换为字符串然后转置以下就好了,但是仔细一想这种方法存在两种缺陷,一是负号需要单独处理,而是转置后开头的0也需要处理。另一种方法是将原数字逐个弹出,然后再将弹出的数字组装为新数字,咋看以为需要用到栈,实际上却是队列... 所以根本不需要辅助数据结构。关于正负号的处理,我最开始是单独处理的,后来看其他答案时才发现根本就不用分正负考虑。因为-1 / 10 = 0.
public class Solution {
/**
* @param n the integer to be reversed
* @return the reversed integer
*/
public int reverseInteger(int n) {
long result = 0;
while (n != 0) {
result = n % 10 + 10 * result;
n /= 10;
}
if (result < Integer.MIN_VALUE || result > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
return 0;
}
return (int)result;
}
}注意 lintcode 和 leetcode 的方法名不一样。使用 long 型保存中间结果,最后判断是否溢出。
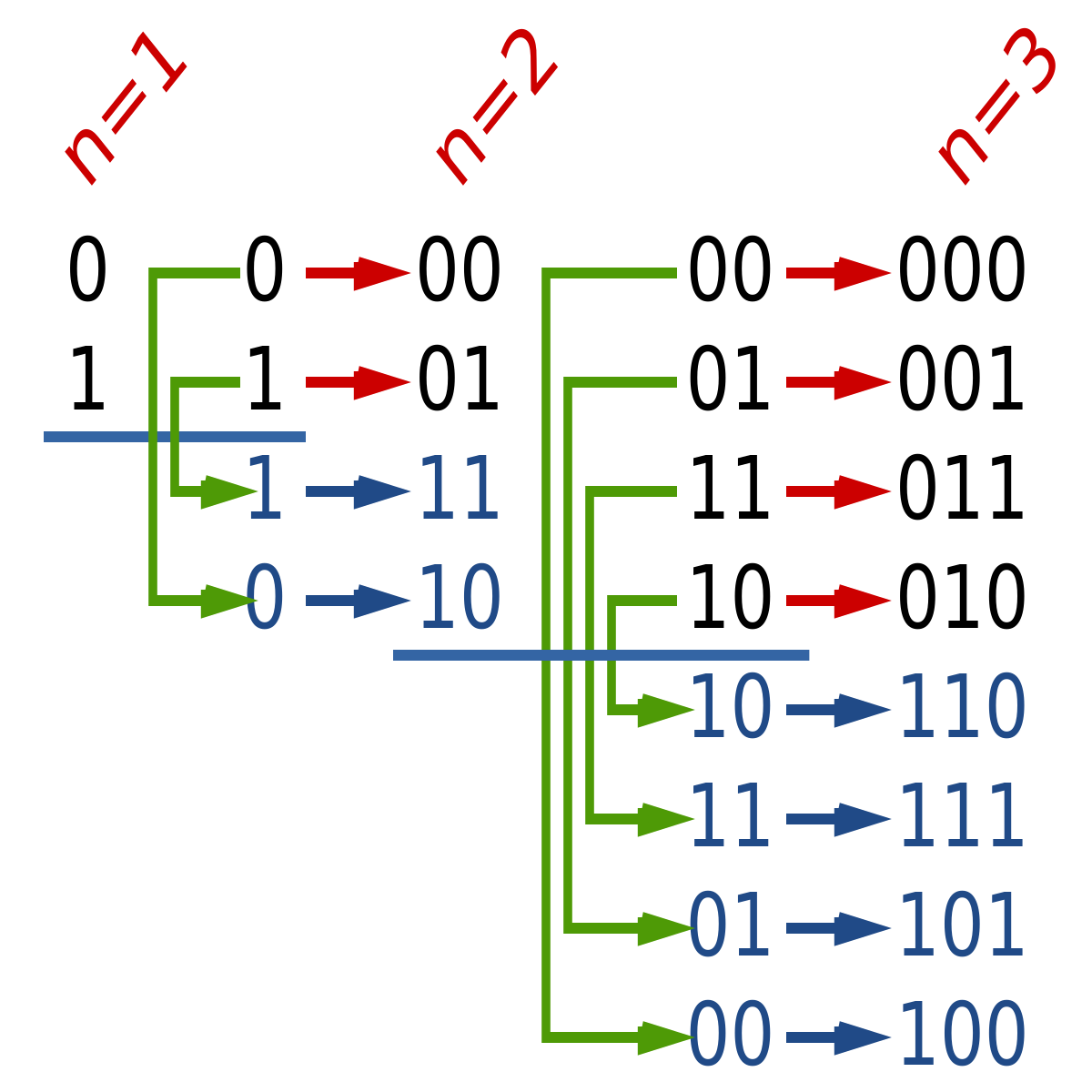
- leetcode: Gray Code | LeetCode OJ
- lintcode: (411) Gray Code
The gray code is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit.
Given a non-negative integer n representing the total number of bits in the code, find the sequence of gray code. A gray code sequence must begin with 0 and with cover all $$2^n$$ integers.
Given n = 2, return [0,1,3,2]. Its gray code sequence is:
00 - 0
01 - 1
11 - 3
10 - 2
For a given n, a gray code sequence is not uniquely defined.
[0,2,3,1] is also a valid gray code sequence according to the above definition.
$$O(2^n)$$ time.
第一次遇到这个题是在腾讯的在线笔试中,当时找到了规律,用的是递归,但是实现似乎有点问题... 直接从 n 位的格雷码分析不太好分析,比如题中n = 2的格雷码,我们不妨试试从小到大分析,以 n = 1 往后递推。
从图中我们可以看出n 位的格雷码可由 n-1位的格雷码递推,在最高位前顺序加0,逆序加1即可。实际实现时我们可以省掉在最高位加0的过程,因为其在数值上和前 n-1位格雷码相同。另外一点则是初始化的处理,图中为从1开始,但若从0开始可进一步简化程序。而且根据 格雷码 的定义,n=0时确实应该返回0.
public class Solution {
/**
* @param n a number
* @return Gray code
*/
public ArrayList<Integer> grayCode(int n) {
if (n < 0) return null;
ArrayList<Integer> currGray = new ArrayList<Integer>();
currGray.add(0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int msb = 1 << i;
// backward - symmetry
for (int j = currGray.size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
currGray.add(msb | currGray.get(j));
}
}
return currGray;
}
}加0 的那一部分已经在前一组格雷码中出现,故只需将前一组格雷码镜像后在最高位加1即可。第二重 for 循环中需要注意的是currGray.size() - 1并不是常量,只能用于给 j 初始化。本应该使用 $$2^n$$ 和上一组格雷码相加,这里考虑到最高位为1的特殊性,使用位运算模拟加法更好。
生成n 位的二进制码,时间复杂度 $$O(2^n)$$, 使用了msb代表最高位的值便于后续相加,空间复杂度 $$O(1)$$.
- Soulmachine 的 leetcode 题解
Given an array contains N numbers of 0 .. N, find which number doesn't exist in the array.
Given N = 3 and the array [0, 1, 3], return 2.
Do it in-place with $$O(1)$$ extra memory and $$O(n)$$ time.
和找单数的题类似,这里我们不妨试试位运算中异或的思路。最开始自己想到的是利用相邻项异或结果看是否会有惊喜,然而发现 a^(a+1) != a^a + a^1 之后眼泪掉下来... 如果按照找单数的做法,首先对数组所有元素异或,得到数x1, 现在的问题是如何利用x1得到缺失的数,由于找单数中其他数都是成对出现的,故最后的结果即是单数,这里每个数都是单数,怎么办呢?我们现在再来分析下如果没有缺失数的话会是怎样呢?假设所有元素异或得到数x2, 数x1和x2有什么差异呢?假设缺失的数是x0,那么容易知道x2 = x1 ^ x0, 相当于现在已知x1和x2,要求x0. 根据 Bit Manipulation 中总结的交换律,x0 = x1 ^ x2.
位运算的题往往比较灵活,需要好好利用常用等式变换。
public class Solution {
/**
* @param nums: an array of integers
* @return: an integer
*/
public int findMissing(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return -1;
// get xor from 0 to N excluding missing number
int x1 = 0;
for (int i : nums) {
x1 ^= i;
}
// get xor from 0 to N
int x2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= nums.length; i++) {
x2 ^= i;
}
// missing = x1 ^ x2;
return x1 ^ x2;
}
}略
遍历原数组和 N+1大小的数组,时间复杂度 $$O(n)$$, 空间复杂度 $$O(1)$$.
非常简单直观的想法——排序后检查缺失元素,但是此题中要求时间复杂度为 $$O(n)$$, 因此如果一定要用排序来做,那一定是使用非比较排序如桶排序或者计数排序。题中另一提示则是要求只使用 $$O(1)$$ 的额外空间,那么这就是在提示我们应该使用原地交换。根据题意,元素应无重复,可考虑使用桶排,索引和值一一对应即可。第一重 for 循环遍历原数组,内循环使用 while, 调整索引处对应的值,直至相等或者索引越界为止,for 循环结束时桶排结束。最后再遍历一次数组找出缺失元素。
初次接触这种题还是比较难想到使用桶排这种思想的,尤其是利用索引和值一一对应这一特性找出缺失元素,另外此题在实际实现时不容易做到 bug-free, while 循环处容易出现死循环。
public class Solution {
/**
* @param nums: an array of integers
* @return: an integer
*/
public int findMissing(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return -1;
bucketSort(nums);
// find missing number
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] != i) {
return i;
}
}
return nums.length;
}
private void bucketSort(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
while (nums[i] != i) {
// ignore nums[i] == nums.length
if (nums[i] == nums.length) {
break;
}
int nextNum = nums[nums[i]];
nums[nums[i]] = nums[i];
nums[i] = nextNum;
}
}
}
}难点一在于正确实现桶排,难点二在于数组元素中最大值 N 如何处理。N 有三种可能:
- N 不在原数组中,故最后应该返回 N
- N 在原数组中,但不在数组中的最后一个元素
- N 在原数组中且在数组最后一个元素
其中情况1在遍历桶排后的数组时无返回,最后返回 N.
其中2和3在 while 循环处均会遇到 break 跳出,即当前这个索引所对应的值要么最后还是 N,要么就是和索引相同的值。如果最后还是 N, 也就意味着原数组中缺失的是其他值,如果最后被覆盖掉,那么桶排后的数组不会出现 N, 且缺失的一定是 N 之前的数。
综上,这里的实现无论 N 出现在哪个索引都能正确返回缺失值。实现上还是比较巧妙的,所以说在没做过这类题时要在短时间内 bug-free 比较难,当然也可能是我比较菜...
另外一个难点在于如何保证或者证明 while 一定不会出现死循环,可以这么理解,如果 while 条件不成立且未出现nums.length这个元素,那么就一定会使得一个元素正确入桶,又因为没有重复元素出现,故一定不会出现死循环。
桶排时间复杂度 $$O(n)$$, 空间复杂度 $$O(1)$$. 遍历原数组找缺失数时间复杂度 $$O(n)$$. 故总的时间复杂度为 $$O(n)$$, 空间复杂度 $$O(1)$$.
- leetcode: Minimum Window Substring | LeetCode OJ
- lintcode: (32) Minimum Window Substring
Given a string source and a string target, find the minimum window in source which will contain all the characters in target.
source = "ADOBECODEBANC" target = "ABC" Minimum window is "BANC".
If there is no such window in source that covers all characters in target, return the emtpy string "".
If there are multiple such windows, you are guaranteed that there will always be only one unique minimum window in source.
Can you do it in time complexity O(n) ?
Should the characters in minimum window has the same order in target?
- Not necessary.
计算目标字符串的字符在给定字符串中出现的最小窗口。由于并不需要在给定字符串中有序出现,故只需要统计出现次数。这是典型的需要借助『哈希表』实现的题。题中字符串中的字符可以假定为 ascii 码,那么我们使用256个 ascii 码处理起来较为方便。那么接下来有两个难点,一就是在于怎么知道给定字符串中某一窗口长度已包含目标字符串中的全部字符(可能重复),二是在包含目标字符串中全部字符后如果再出现目标字符串中的其他字符串时如何处理?
其中第一个难点我们通过巧用目标字符串的长度来处理,遍历给定字符串,如果给定字符串中出现的字符次数小于目标字符串,我们就更新总的字符出现次数。第二个难题通过维护窗口起止索引(两根指针)来处理,在给定字符串中出现目标字符串中的全部字符时向前移动窗口起始处,若窗口长度小于之前的窗口长度则更新最终答案要求的窗口起始索引。
public class Solution {
/**
* @param source: A string
* @param target: A string
* @return: A string denote the minimum window
* Return "" if there is no such a string
*/
public String minWindow(String source, String target) {
if (source == null || target == null) return "";
if (source.length() < target.length()) return "";
final int ASCII_COUNT = 256;
int[] targetCount = new int[ASCII_COUNT];
int[] sourceCount = new int[ASCII_COUNT];
for (int i = 0; i < target.length(); i++) {
int ch2i = (int)target.charAt(i);
targetCount[ch2i]++;
}
// target string character appeared in source string
int winStart = 0, winMinStart = 0, winMin = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int occurence = 0;
for (int winEnd = 0; winEnd < source.length(); winEnd++) {
// convert character to integer
int ch2i = (int)source.charAt(winEnd);
sourceCount[ch2i]++;
// character occur in both source and target
if (targetCount[ch2i] > 0 && targetCount[ch2i] >= sourceCount[ch2i]) {
occurence++;
}
// adjust window size if all the target char occur in source
if (occurence == target.length()) {
// convert character to integer
int ch2i2 = (int)source.charAt(winStart);
while (sourceCount[ch2i2] > targetCount[ch2i2]) {
sourceCount[ch2i2]--;
winStart++;
ch2i2 = (int)source.charAt(winStart);
}
// update winMinStart
if (winMin > winEnd - winStart + 1) {
winMin = winEnd - winStart + 1;
winMinStart = winStart;
}
}
}
if (winMin == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
return "";
} else {
return source.substring(winMinStart, winMinStart + winMin);
}
}
}整个程序最为核心的即为题解中所提出的两大难点,窗口移动的方法使用贪心实现,在窗口长度变小时需要记录起始索引。
遍历给定字符串一次,外加更新窗口时可能需要遍历给定字符串一次,时间复杂度为 $$O(n)$$, 使用了几个额外变量,空间复杂度 $$O(1)$$.
- lintcode: (402) Continuous Subarray Sum
Given an integer array, find a continuous subarray where the sum of numbers is the biggest. Your code should return the index of the first number and the index of the last number. (If their are duplicate answer, return anyone)
Give [-3, 1, 3, -3, 4], return [1,4].
和题 Maximum Subarray 几乎一模一样,只是返回值要求不一样。由于需要返回区间索引值,那么显然需要额外变量记录区间起止处。若使用题解2中提到的sum - minSum的区间和更新方式,索引终止处容易得知是sum - minSum > maxSub时的i, 问题是索引起始处如何确定。容易得知索引起始处如果更新,必然在minSum > sum时,但问题在于满足此条件的可能不止一处,所以我们需要先记录这个索引值并在sum - minSum > maxSub时判定索引终止值是否大于索引起始值,不小于则更新。
此题难以一次 bug-free, 需要小心更新索引值。
public class Solution {
/**
* @param A an integer array
* @return A list of integers includes the index of the first number and the index of the last number
*/
public ArrayList<Integer> continuousSubarraySum(int[] A) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (A == null || A.length == 0) return result;
int sum = 0, minSum = 0, maxSub = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int first = 0, last = 0;
int first2 = 0; // candidate for first
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
if (minSum > sum) {
minSum = sum;
first2 = i;
}
sum += A[i];
if (sum - minSum > maxSub) {
maxSub = sum - minSum;
last = i;
// update first if valid
if (first2 <= last) first = first2;
}
}
result.add(first);
result.add(last);
return result;
}
}除了最后要求的first和last, 我们还需要引入first2作为first可能的候选变量值。
略
Given an integer array, find a continuous rotate subarray where the sum of numbers is the biggest. Your code should return the index of the first number and the index of the last number. (If their are duplicate answer, return anyone. The answer can be rorate array or non- rorate array)
Give [3, 1, -100, -3, 4], return [4,1].
题 Continuous Subarray Sum 的 follow up, 这道题 AC 率极低,真是磨人的小妖精。在上题的基础上容易想到可以将first和last分四种情况讨论,然后再逆向求大于0的最大和即可,但是这种想法忽略了一种情况——旋转后的最大值可能由两段子数组和构成,而这种情况如果用上题的解法则会被忽略。
所以这道题的正确解法不是分first和last四种情况讨论,而是利用旋转数组的特性。第一种情况,无论怎么拼接原数组中的数组和都无法大于最大的单一数组和;第二种情况则相反。所以现在问题的关键则转化为怎么求第二种情况。首先可以明确一点,最终得到的数组和索引必须连续(含首尾相接)。也就是说情况二一旦出现,则我们可以将原数组中挖空一小段,现在问题来了:到底要挖掉多少元素?
**我们的目标是使得挖掉后的元素值最大。**由于分段求解不容易(被隔开),但是被挖掉的元素索引是挨着的!正难则反!由于数组的总和是一定的,那么我们只要求得被挖掉部分元素的最小值即可得两边子数组的最大值!最后判断两个最大值孰大孰小就可以了。
public class Solution {
/**
* @param A an integer array
* @return A list of integers includes the index of the first number and the index of the last number
*/
public ArrayList<Integer> continuousSubarraySumII(int[] A) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (A == null || A.length == 0) return result;
// maximal subarray sum
ArrayList<Integer> sub1 = subSum(A, 1);
// minimal subarray sum
ArrayList<Integer> sub2 = subSum(A, -1);
int first = 0, last = 0;
if (sub1.get(3) - sub2.get(2) > sub1.get(2)) {
last = sub2.get(0) - 1;
first = sub2.get(1) + 1;
} else {
first = sub1.get(0);
last = sub1.get(1);
}
// corner case(all elements are negtive)
if (last == -1 && first == A.length) {
first = sub1.get(0);
last = sub1.get(1);
}
result.add(first);
result.add(last);
return result;
}
private ArrayList<Integer> subSum(int[] A, int sign) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// find the max/min subarray sum from [0...A.length]
int sum = 0, minSum = 0, maxSub = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (sign == -1) maxSub = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int first = 0, last = 0;
int first2 = 0; // candidate for first
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
if (sign * minSum > sign * sum) {
minSum = sum;
first2 = i;
}
sum += A[i];
if (sign * (sum - minSum) > sign * maxSub) {
maxSub = sum - minSum;
last = i;
// update first if valid
if (first2 <= last) first = first2;
}
}
result.add(first);
result.add(last);
result.add(maxSub);
result.add(sum);
return result;
}
}由于既需要求最大子数组和,也需要求最小子数组和,我们将这一部分写成一私有方法,并加入sign控制符号。如果两段子数组和大于一段子数组和时,新的first和last正好相反。且在数组全为负时需要排除,直接使用单一子数组和最大的情况。
遍历两次数组,时间复杂度 $$O(n)$$, 使用了部分额外 List, 空间复杂度 $$O(1)$$.
- leetcode: Longest Consecutive Sequence | LeetCode OJ
- lintcode: (124) Longest Consecutive Sequence
Given an unsorted array of integers, find the length of the longest consecutive elements sequence.
Given [100, 4, 200, 1, 3, 2],
The longest consecutive elements sequence is [1, 2, 3, 4]. Return its
length: 4.
Your algorithm should run in O(n) complexity.
首先看题要求,时间复杂度为 $$O(n)$$, 如果排序,基于比较的实现为 $$n \log n$$, 基数排序需要数据有特征。故排序无法达到复杂度要求。接下来可以联想空间换时间的做法,其中以哈希表为代表。这个题要求返回最长连续序列,不要求有序,非常符合哈希表的用法。**由于给定一个数其连续的数要么比它小1,要么大1,那么我们只需往左往右搜索知道在数组中找不到数为止。**结合哈希表查找为 $$O(1)$$ 的特性即可满足要求。
public class Solution {
/**
* @param nums: A list of integers
* @return an integer
*/
public int longestConsecutive(int[] num) {
if (num == null || num.length == 0) return 0;
// add number to hashset
Set<Integer> hashset = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int n : num) {
hashset.add(n);
}
int lcs = 0;
for (int n : num) {
int i = n, count = 1;
hashset.remove(n);
// i--
while (hashset.contains(--i)) {
count++;
hashset.remove(i);
}
// i++
i = n;
while (hashset.contains(++i)) {
count++;
hashset.remove(i);
}
// update lcs
lcs = Math.max(lcs, count);
}
return lcs;
}
}首先使用 HashSet 建哈希表,然后遍历数组,依次往左往右搜相邻数,搜到了就从 Set 中删除。末尾更新最大值。
时间复杂度和空间复杂度均为 $$O(n)$$.