本章主要总结图与搜索相关题目。
Find the number connected component in the undirected graph. Each node in the graph contains a label and a list of its neighbors. (a connected component (or just component) of an undirected graph is a subgraph in which any two vertices are connected to each other by paths, and which is connected to no additional vertices in the supergraph.)
Given graph:
A------B C
\ | |
\ | |
\ | |
\ | |
D E
Return {A,B,D}, {C,E}. Since there are two connected component which is
{A,B,D}, {C,E}
深搜加哈希表(因为有环,必须记录节点是否被访问过)
/**
* Definition for Undirected graph.
* class UndirectedGraphNode {
* int label;
* ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode> neighbors;
* UndirectedGraphNode(int x) { label = x; neighbors = new ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode>(); }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param nodes a array of Undirected graph node
* @return a connected set of a Undirected graph
*/
public List<List<Integer>> connectedSet(ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode> nodes) {
if (nodes == null || nodes.size() == 0) return null;
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
Set<UndirectedGraphNode> visited = new HashSet<UndirectedGraphNode>();
for (UndirectedGraphNode node : nodes) {
if (visited.contains(node)) continue;
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
dfs(node, visited, temp);
Collections.sort(temp);
result.add(temp);
}
return result;
}
private void dfs(UndirectedGraphNode node,
Set<UndirectedGraphNode> visited,
List<Integer> result) {
// add node into result
result.add(node.label);
visited.add(node);
// node is not connected, exclude by for iteration
// if (node.neighbors.size() == 0 ) return;
for (UndirectedGraphNode neighbor : node.neighbors) {
if (visited.contains(neighbor)) continue;
dfs(neighbor, visited, result);
}
}
}注意题目的输出要求,需要为 Integer 和有序。添加 node 至 result 和 visited 时放一起,且只在 dfs 入口,避免漏解和重解。
遍历所有节点和边一次,时间复杂度 $$O(V+E)$$, 记录节点是否被访问,空间复杂度 $$O(V)$$.
深搜容易爆栈,采用 BFS 较为安全。BFS 中记录已经访问的节点在入队前判断,可有效防止不重不漏。
/**
* Definition for Undirected graph.
* class UndirectedGraphNode {
* int label;
* ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode> neighbors;
* UndirectedGraphNode(int x) { label = x; neighbors = new ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode>(); }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param nodes a array of Undirected graph node
* @return a connected set of a Undirected graph
*/
public List<List<Integer>> connectedSet(ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode> nodes) {
if (nodes == null || nodes.size() == 0) return null;
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
// log visited node before push into queue
Set<UndirectedGraphNode> visited = new HashSet<UndirectedGraphNode>();
for (UndirectedGraphNode node : nodes) {
if (visited.contains(node)) continue;
List<Integer> row = bfs(node, visited);
result.add(row);
}
return result;
}
private List<Integer> bfs(UndirectedGraphNode node,
Set<UndirectedGraphNode> visited) {
List<Integer> row = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Queue<UndirectedGraphNode> q = new LinkedList<UndirectedGraphNode>();
q.offer(node);
visited.add(node);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
UndirectedGraphNode qNode = q.poll();
row.add(qNode.label);
for (UndirectedGraphNode neighbor : qNode.neighbors) {
if (visited.contains(neighbor)) continue;
q.offer(neighbor);
visited.add(neighbor);
}
}
Collections.sort(row);
return row;
}
}略
同题解一。
- lintcode: (176) Route Between Two Nodes in Graph
- Find if there is a path between two vertices in a directed graph - GeeksforGeeks
Given a directed graph, design an algorithm to find out whether there is a route between two nodes.
Given graph:
A----->B----->C
\ |
\ |
\ |
\ v
->D----->E
for s = B and t = E, return true
for s = D and t = C, return false
检测图中两点是否通路,图搜索的简单问题,DFS 或者 BFS 均可,注意检查是否有环即可。这里使用哈希表记录节点是否被处理较为方便。深搜时以起点出发,递归处理其邻居节点,需要注意的是处理邻居节点的循环时不是直接 return, 而只在找到路径为真时才返回 true, 否则会过早返回 false 而忽略后续可能满足条件的路径。
/**
* Definition for Directed graph.
* class DirectedGraphNode {
* int label;
* ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> neighbors;
* DirectedGraphNode(int x) {
* label = x;
* neighbors = new ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode>();
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param graph: A list of Directed graph node
* @param s: the starting Directed graph node
* @param t: the terminal Directed graph node
* @return: a boolean value
*/
public boolean hasRoute(ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> graph,
DirectedGraphNode s, DirectedGraphNode t) {
Set<DirectedGraphNode> visited = new HashSet<DirectedGraphNode>();
return dfs(graph, s, t, visited);
}
public boolean dfs(ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> graph,
DirectedGraphNode s, DirectedGraphNode t,
Set<DirectedGraphNode> visited) {
if (s == t) {
return true;
} else {
// corner cases
if (s == null || t == null) return false;
// flag visited node, avoid cylic
visited.add(s);
// compare unvisited neighbor nodes recursively
if (s.neighbors.size() > 0) {
for (DirectedGraphNode node : s.neighbors) {
if (visited.contains(node)) continue;
if (dfs(graph, node, t, visited)) return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}根据构造函数的实现,Java 中判断是否有邻居节点时使用.size,而不是null. 注意深搜前检测是否被处理过。行
if (dfs(graph, node, t, visited)) return true;中注意不是直接 return, 只在为 true 时返回。
遍历所有点及边,时间复杂度为 $$O(V+E)$$.
除了深搜处理邻居节点,我们也可以采用 BFS 结合队列处理,优点是不会爆栈,缺点是空间复杂度稍高和实现复杂点。
/**
* Definition for Directed graph.
* class DirectedGraphNode {
* int label;
* ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> neighbors;
* DirectedGraphNode(int x) {
* label = x;
* neighbors = new ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode>();
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param graph: A list of Directed graph node
* @param s: the starting Directed graph node
* @param t: the terminal Directed graph node
* @return: a boolean value
*/
public boolean hasRoute(ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> graph,
DirectedGraphNode s, DirectedGraphNode t) {
if (graph == null || s == null || t == null) return false;
Queue<DirectedGraphNode> q = new LinkedList<DirectedGraphNode>();
Set<DirectedGraphNode> visited = new HashSet<DirectedGraphNode>();
q.offer(s);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int qLen = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < qLen; i++) {
DirectedGraphNode node = q.poll();
visited.add(node);
if (node == t) return true;
// push neighbors into queue
if (node.neighbors.size() > 0) {
for (DirectedGraphNode n : node.neighbors) {
// avoid cylic
if (visited.contains(n)) continue;
q.offer(n);
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
}同题解一。
时间复杂度同题解一,也是 $$O(V+E)$$, 空间复杂度最坏情况下为两层多叉树,为 $$O(V+E)$$.
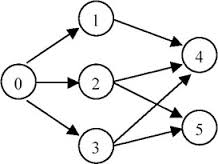
Given an directed graph, a topological order of the graph nodes is defined as follow:
For each directed edge A -> B in graph, A must before B in the order list.
The first node in the order can be any node in the graph with no nodes direct to it.
Find any topological order for the given graph.
Example For graph as follow:
The topological order can be:
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[0, 2, 3, 1, 5, 4]
...
Note
You can assume that there is at least one topological order in the graph.
Challenge
Can you do it in both BFS and DFS?
图搜索相关的问题较为常见的解法是用 DFS,这里结合 BFS 进行求解,分为三步走:
- 统计各定点的入度——只需统计节点在邻接列表中出现的次数即可知。
- 遍历图中各节点,找到入度为0的节点。
- 对入度为0的节点进行递归 DFS,将节点加入到最终返回结果中。
/**
* Definition for Directed graph.
* struct DirectedGraphNode {
* int label;
* vector<DirectedGraphNode *> neighbors;
* DirectedGraphNode(int x) : label(x) {};
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param graph: A list of Directed graph node
* @return: Any topological order for the given graph.
*/
vector<DirectedGraphNode*> topSort(vector<DirectedGraphNode*> graph) {
vector<DirectedGraphNode*> result;
if (graph.size() == 0) return result;
map<DirectedGraphNode*, int> indegree;
// get indegree of all DirectedGraphNode
indeg(graph, indegree);
// dfs recursively
for (int i = 0; i < graph.size(); ++i) {
if (indegree[graph[i]] == 0) {
dfs(indegree, graph[i], result);
}
}
return result;
}
private:
/** get indegree of all DirectedGraphNode
*
*/
void indeg(vector<DirectedGraphNode*> &graph,
map<DirectedGraphNode*, int> &indegree) {
for (int i = 0; i < graph.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < graph[i]->neighbors.size(); j++) {
if (indegree.find(graph[i]->neighbors[j]) == indegree.end()) {
indegree[graph[i]->neighbors[j]] = 1;
} else {
indegree[graph[i]->neighbors[j]] += 1;
}
}
}
}
void dfs(map<DirectedGraphNode*, int> &indegree, DirectedGraphNode *i,
vector<DirectedGraphNode*> &ret) {
ret.push_back(i);
indegree[i]--;
for (int j = 0; j < i->neighbors.size(); ++j) {
indegree[i->neighbors[j]]--;
if (indegree[i->neighbors[j]] == 0) {
dfs(indegree, i->neighbors[j], ret);
}
}
}
};C++中使用 unordered_map 可获得更高的性能,私有方法中使用引用传值。
以 V 表示顶点数,E 表示有向图中边的条数。
首先获得节点的入度数,时间复杂度为 $$O(V+E)$$, 使用了哈希表存储,空间复杂度为 $$O(V)$$. 遍历图求得入度为0的节点,时间复杂度为 $$O(V)$$. 仅在入度为0时调用 DFS,故时间复杂度为 $$O(V+E)$$.
需要注意的是这里的 DFS 不是纯 DFS,使用了 BFS 的思想进行了优化,否则一个节点将被遍历多次,时间复杂度可能恶化为指数级别。
综上,时间复杂度近似为 $$O(V+E)$$, 空间复杂度为 $$O(V)$$.
拓扑排序除了可用 DFS 求解外,也可使用 BFS, 具体方法为:
- 获得图中各节点的入度。
- BFS 首先遍历求得入度数为0的节点,入队,便于下一次 BFS。
- 队列不为空时,弹出队顶元素并对其邻接节点进行 BFS,将入度为0的节点加入到最终结果和队列中,重复此过程直至队列为空。
/**
* Definition for Directed graph.
* struct DirectedGraphNode {
* int label;
* vector<DirectedGraphNode *> neighbors;
* DirectedGraphNode(int x) : label(x) {};
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param graph: A list of Directed graph node
* @return: Any topological order for the given graph.
*/
vector<DirectedGraphNode*> topSort(vector<DirectedGraphNode*> graph) {
vector<DirectedGraphNode*> result;
if (graph.size() == 0) return result;
map<DirectedGraphNode*, int> indegree;
// get indegree of all DirectedGraphNode
indeg(graph, indegree);
queue<DirectedGraphNode*> q;
// bfs
bfs(graph, indegree, q, result);
return result;
}
private:
/** get indegree of all DirectedGraphNode
*
*/
void indeg(vector<DirectedGraphNode*> &graph,
map<DirectedGraphNode*, int> &indegree) {
for (int i = 0; i < graph.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < graph[i]->neighbors.size(); j++) {
if (indegree.find(graph[i]->neighbors[j]) == indegree.end()) {
indegree[graph[i]->neighbors[j]] = 1;
} else {
indegree[graph[i]->neighbors[j]] += 1;
}
}
}
}
void bfs(vector<DirectedGraphNode*> &graph, map<DirectedGraphNode*, int> &indegree,
queue<DirectedGraphNode *> &q, vector<DirectedGraphNode*> &ret) {
for (int i = 0; i < graph.size(); ++i) {
if (indegree[graph[i]] == 0) {
ret.push_back(graph[i]);
q.push(graph[i]);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
DirectedGraphNode *cur = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int j = 0; j < cur->neighbors.size(); ++j) {
indegree[cur->neighbors[j]]--;
if (indegree[cur->neighbors[j]] == 0) {
ret.push_back(cur->neighbors[j]);
q.push(cur->neighbors[j]);
}
}
}
}
};C++中在判断入度是否为0时将对 map 产生副作用,在求入度数时只有入度数大于等于1才会出现在 map 中,故不在 map 中时直接调用 indegree 方法将产生新的键值对,初始值为0,恰好满足此题需求。
同题解1 的分析,时间复杂度为 $$O(V+E)$$, 空间复杂度为 $$O(V)$$.
- leetcode: Word Ladder | LeetCode OJ
- lintcode: (120) Word Ladder
Given two words (start and end), and a dictionary, find the length of shortest transformation sequence from start to end, such that:
- Only one letter can be changed at a time
- Each intermediate word must exist in the dictionary
Given:
start = "hit"
end = "cog"
dict = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"]
As one shortest transformation is "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> "cog",
return its length 5.
- Return 0 if there is no such transformation sequence.
- All words have the same length.
- All words contain only lowercase alphabetic characters.
咋一看还以为是 Edit Distance 的变体,仔细审题后发现和动态规划没啥关系。题中有两大关键点:一次只能改动一个字符;改动的中间结果必须出现在词典中。那么大概总结下来共有四种情形:
- start 和 end 相等。
- end 在 dict 中,且 start 可以转换为 dict 中的一个单词。
- end 不在 dict 中,但可由 start 或者 dict 中的一个单词转化而来。
- end 无法由 start 转化而来。
由于中间结果也必须出现在词典中,故此题相当于图搜索问题,将 start, end, dict 中的单词看做图中的节点,节点与节点(单词与单词)可通过一步转化得到,可以转换得到的节点相当于边的两个节点,边的权重为1(都是通过1步转化)。到这里问题就比较明确了,相当于搜索从 start 到 end 两点间的最短距离,即 Dijkstra 最短路径算法。通过 BFS 和哈希表实现。
首先将 start 入队,随后弹出该节点,比较其和 end 是否相同;再从 dict 中选出所有距离为1的单词入队,并将所有与当前节点距离为1且未访问过的节点(需要使用哈希表)入队,方便下一层遍历时使用,直至队列为空。
public class Solution {
/**
* @param start, a string
* @param end, a string
* @param dict, a set of string
* @return an integer
*/
public int ladderLength(String start, String end, Set<String> dict) {
if (start == null && end == null) return 0;
if (start.length() == 0 && end.length() == 0) return 0;
assert(start.length() == end.length());
if (dict == null || dict.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int ladderLen = 1;
dict.add(end); // add end to dict, important!
Queue<String> q = new LinkedList<String>();
Set<String> hash = new HashSet<String>();
q.offer(start);
hash.add(start);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
ladderLen++;
int qLen = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < qLen; i++) {
String strTemp = q.poll();
for (String nextWord : getNextWords(strTemp, dict)) {
if (nextWord.equals(end)) return ladderLen;
// filter visited word in the dict
if (hash.contains(nextWord)) continue;
q.offer(nextWord);
hash.add(nextWord);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
private Set<String> getNextWords(String curr, Set<String> dict) {
Set<String> nextWords = new HashSet<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < curr.length(); i++) {
char[] chars = curr.toCharArray();
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) {
chars[i] = c;
String temp = new String(chars);
if (dict.contains(temp)) {
nextWords.add(temp);
}
}
}
return nextWords;
}
}首先分析给定单词curr并从 dict 中选出所有距离为1 的单词。常规的思路可能是将curr与 dict 中的单词逐个比较,并遍历每个字符串,返回距离为1的单词组。这种找距离为1的节点的方法复杂度为 $$l(length\ of\ word) \times n(size\ of\ dict)\times m(queue\ length) = O(lmn)$$. 在 dict 较长时会 TLE. 其实根据 dict 的数据结构特点,比如查找任一元素的时间复杂度可认为是 $$O(1)$$. 根据哈希表和单个单词长度通常不会太长这一特点,我们就可以根据给定单词构造到其距离为一的单词变体,然后查询其是否在 dict 中,这种实现的时间复杂度为 $$O(26(a\ to\ z) \times l \times m) = O(lm)$$, 与 dict 长度没有太大关系,大大优化了时间复杂度。
经验教训:根据给定数据结构特征选用合适的实现,遇到哈希表时多用其查找的 $$O(1)$$ 特性。
BFS 用作搜索,哈希表用于记录已经访问节点。在可以改变输入数据的前提下,需要将 end 加入 dict 中,否则对于不在 dict 中出现的 end 会有问题。
主要在于getNextWords方法的时间复杂度,时间复杂度 $$O(lmn)$$。使用了队列存储中间处理节点,空间复杂度平均条件下应该是常量级别,当然最坏条件下可能恶化为 $$O(n)$$, 即 dict 中某个点与其他点距离均为1.
- Word Ladder 参考程序 Java/C++/Python
- Java Solution using Dijkstra's algorithm, with explanation - Leetcode Discuss
时间限制:10000ms
单点时限:1000ms
内存限制:256MB
大家好,我是小Hi和小Ho的小伙伴Nettle,从这个星期开始由我来完成我们的Weekly。
新年回家,又到了一年一度大龄剩男剩女的相亲时间。Nettle去姑姑家玩的时候看到了一张姑姑写的相亲情况表,上面都是姑姑介绍相亲的剩男剩女们。每行有2个名字, 表示这两个人有一场相亲。由于姑姑年龄比较大了记性不是太好,加上相亲的人很多,所以姑姑一时也想不起来其中有些人的性别。因此她拜托我检查一下相亲表里面有没有错误 的记录,即是否把两个同性安排了相亲。
OK,让我们愉快的暴力搜索吧!
才怪咧。
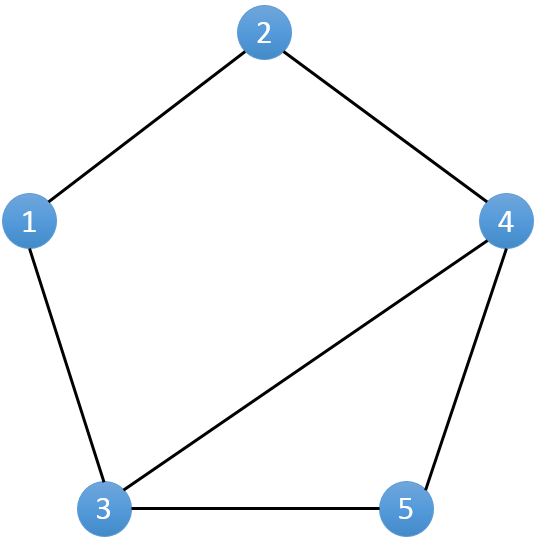
对于拿到的相亲情况表,我们不妨将其转化成一个图。将每一个人作为一个点**(编号1..N)**,若两个人之间有一场相亲,则在对应的点之间连接一条无向边。(如下图)
因为相亲总是在男女之间进行的,所以每一条边的两边对应的人总是不同性别。假设表示男性的节点染成白色,女性的节点染色黑色。对于得到的无向图来说,即每一条边的两端 一定是一白一黑。如果存在一条边两端同为白色或者黑色,则表示这一条边所表示的记录有误。
由于我们并不知道每个人的性别,我们的问题就转化为判定是否存在一个合理的染色方案,使得我们所建立的无向图满足每一条边两端的顶点颜色都不相同。
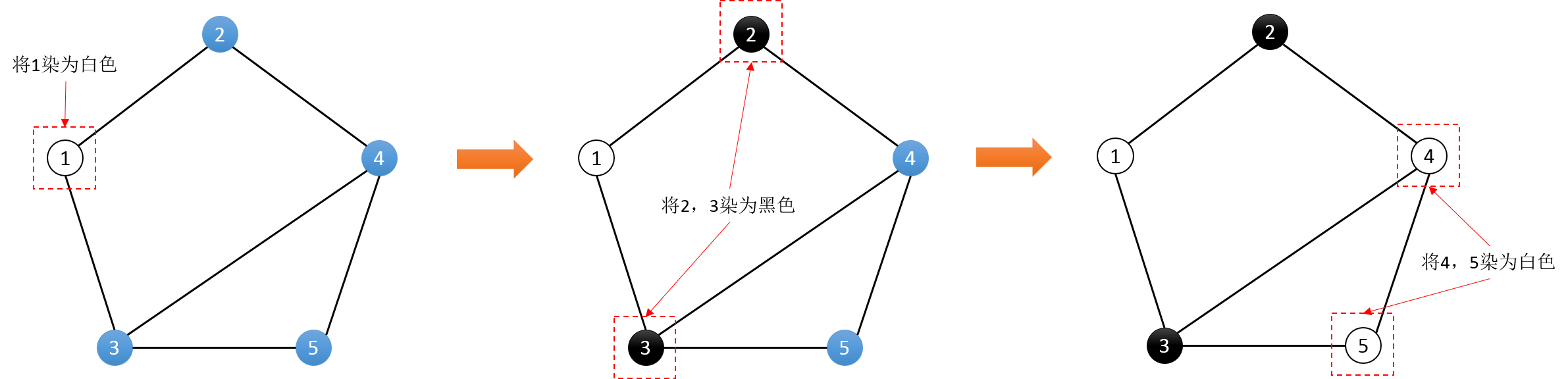
那么,我们不妨将所有的点初始为未染色的状态。随机选择一个点,将其染成白色。再以它为起点,将所有相邻的点染成黑色。再以这些黑色的点为起点,将所有与其相邻未染色 的点染成白色。不断重复直到整个图都染色完成。(如下图)
在染色的过程中,我们应该怎样发现错误的记录呢?相信你一定发现了吧。对于一个已经染色的点,如果存在一个与它相邻的已染色点和它的颜色相同,那么就一定存在一条错误 的记录。(如上图的4,5节点)
到此我们就得到了整个图的算法:
- 选取一个未染色的点u进行染色
- 遍历u的相邻节点v:若v未染色,则染色成与u不同的颜色,并对v重复第2步;若v已经染色,如果 u和v颜色相同,判定不可行退出遍历。
- 若所有节点均已染色,则判定可行。
接下来就动手写写吧!
第1行:1个正整数T(1≤T≤10)
接下来T组数据,每组数据按照以下格式给出:
第1行:2个正整数N,M(1≤N≤10,000,1≤M≤40,000)
第2..M+1行:每行两个整数u,v表示u和v之间有一条边
第1..T行:第i行表示第i组数据是否有误。如果是正确的数据输出”Correct”,否则输出”Wrong”
样例输入
2
5 5
1 2
1 3
3 4
5 2
1 5
5 5
1 2
1 3
3 4
5 2
3 5
样例输出
Wrong
Correct
二分图中最简单的题,思路原文中已提到,这里就不赘述了,简单实现的话可以使用二维数组,如果要模拟图的操作的话可以自定义类。
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Queue;
class UndirectedGraphNode {
int label;
int color;
ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode> neighbors;
UndirectedGraphNode(int x) {
this.label = x;
this.color = 0;
this.neighbors = new ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode>();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int T = in.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= T; i++) {
int N = in.nextInt();
int M = in.nextInt();
// initialize graph
List<UndirectedGraphNode> graph = new ArrayList<UndirectedGraphNode>();
for (int n = 1; n <= N; n++) {
graph.add(new UndirectedGraphNode(n));
}
// construct graph
for (int j = 1; j <= M; j++) {
int u = in.nextInt(), v = in.nextInt();
graph.get(u - 1).neighbors.add(graph.get(v - 1));
graph.get(v - 1).neighbors.add(graph.get(u - 1));
}
// solve
if (solve(graph)) {
System.out.println("Correct");
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong");
}
}
}
public static boolean solve(List<UndirectedGraphNode> graph) {
// 1 for white, -1 for black, 0 for uncolored
for (UndirectedGraphNode node : graph) {
if (node.color == 0) {
node.color = 1;
Queue<UndirectedGraphNode> q = new LinkedList<UndirectedGraphNode>();
q.offer(node);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int qSize = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < qSize; i++) {
UndirectedGraphNode qNode = q.poll();
for (UndirectedGraphNode neighbor : qNode.neighbors) {
if (neighbor.color == 0) {
neighbor.color = -1 * qNode.color;
q.offer(neighbor);
} else if (neighbor.color + qNode.color != 0) {
// the color of qNode is the same with neighbor
return false;
}
}
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}使用 BFS 不容易爆栈。
时间复杂度 $$O(V + E)$$.