APM 的全称是 Application performance management,即应用性能管理,通过对应用的可靠性、稳定性等方面的监控,进而达到快速修复问题、提高用户体验的目的。将在以下几个方面对数据进行监控,包括 CPU 占有率,内存使用情况,磁盘使用情况,FPS,冷启动时间,卡顿,闪退,闪退防护,HTTPDNS,网络流量等。
此仓库为 APM 数据采集调研产物,主要是对性能监控实现进行了统一封装。其中 SDK 为实现代码,Demo 为调用详情。
实现功能:
- 设备型号
- 设备系统名称
- 设备系统版本
- 设备启动时间
- 设备信息
通过设备机器名称(如“iPhone1,1”)硬编码方式输出相关数据。数据来自维基百科以及theiphonewiki。
实现功能:
- 设备名称
- CPU 名称
- CPU 频率
- 协处理器名称
- 电池容量
- 电池电压
- 屏幕尺寸
- 屏幕 PPI
实现功能:
- 磁盘总空间
- 磁盘使用空间
- 磁盘可用空间
- 文件大小
- 目录大小
任务(task)是一种容器(container)对象,虚拟内存空间和其他资源都是通过这个容器对象管理的,这些资源包括设备和其他句柄。严格地说,Mach 的任务并不是其他操作系统中所谓的进程,因为 Mach 作为一个微内核的操作系统,并没有提供“进程”的逻辑,而只是提供了最基本的实现。不过在 BSD 的模型中,这两个概念有1:1的简单映射,每一个 BSD 进程(也就是 OS X 进程)都在底层关联了一个 Mach 任务对象。
上面引用的是《OS X and iOS Kernel Programming》对 Mach task 的描述,Mach task 可以看作一个机器无关的 thread 执行环境的抽象一个 task 包含它的线程列表。内核提供了 task_threads API 调用获取指定 task 的线程列表,然后可以通过 thread_info API 调用来查询指定线程的信息。
task_threads 将 target_task 任务中的所有线程保存在 act_list 数组中,数组中包含 act_listCnt 个条目。
thread_info 查询 flavor 指定的 thread 信息,将信息返回到长度为 thread_info_outCnt 字节的 thread_info_out 缓存区中,
代码实现:
#import <mach/mach.h>
#import <assert.h>
+ (CGFloat)appCpuUsage {
kern_return_t kr;
task_info_data_t tinfo;
mach_msg_type_number_t task_info_count;
task_info_count = TASK_INFO_MAX;
kr = task_info(mach_task_self(), MACH_TASK_BASIC_INFO, (task_info_t)tinfo, &task_info_count);
if (kr != KERN_SUCCESS) {
return -1;
}
thread_array_t thread_list;
mach_msg_type_number_t thread_count;
thread_info_data_t thinfo;
mach_msg_type_number_t thread_info_count;
thread_basic_info_t basic_info_th;
// get threads in the task
kr = task_threads(mach_task_self(), &thread_list, &thread_count);
if (kr != KERN_SUCCESS) {
return -1;
}
long total_time = 0;
long total_userTime = 0;
CGFloat total_cpu = 0;
int j;
// for each thread
for (j = 0; j < (int)thread_count; j++) {
thread_info_count = THREAD_INFO_MAX;
kr = thread_info(thread_list[j], THREAD_BASIC_INFO,
(thread_info_t)thinfo, &thread_info_count);
if (kr != KERN_SUCCESS) {
return -1;
}
basic_info_th = (thread_basic_info_t)thinfo;
if (!(basic_info_th->flags & TH_FLAGS_IDLE)) {
total_time = total_time + basic_info_th->user_time.seconds + basic_info_th->system_time.seconds;
total_userTime = total_userTime + basic_info_th->user_time.microseconds + basic_info_th->system_time.microseconds;
total_cpu = total_cpu + basic_info_th->cpu_usage / (float)TH_USAGE_SCALE * kMaxPercent;
}
}
kr = vm_deallocate(mach_task_self(), (vm_offset_t)thread_list, thread_count * sizeof(thread_t));
assert(kr == KERN_SUCCESS);
return total_cpu;
}实现功能:
- CPU架构
- CPU核数
- 系统CPU使用率
- 当前应用CPU使用率
注意:由于安全性考虑,苹果已经禁止访问内核变量来获取 CPU 频率。现实现方法是通过硬编码方式获取 CPU 频率,新机发布需更新。
mach_task_basic_info 结构体存储了 Mach task 的内存使用信息,其中 resident_size 就是应用使用的物理内存大小,virtual_size 是虚拟内存大小。
与获取 CPU 占用率类似,在调用 task_info API 时,target_task 参数传入的是 mach_task_self(),表示获取当前的 Mach task,另外 flavor 参数传的是 MACH_TASK_BASIC_INFO,使用这个类型会返回 mach_task_basic_info 结构体,表示返回 target_task 的基本信息,比如 task 的挂起次数和驻留页面数量。
代码实现:
+ (unsigned long long)getAppRAMUsage {
struct mach_task_basic_info info;
mach_msg_type_number_t count = MACH_TASK_BASIC_INFO_COUNT;
kern_return_t kr = task_info(mach_task_self(), MACH_TASK_BASIC_INFO, (task_info_t)&info, &count);
if (kr != KERN_SUCCESS) {
return 0;
}
return info.resident_size;
}
+ (fs_system_ram_usage)getSystemRamUsageStruct {
vm_statistics64_data_t vmStats;
mach_msg_type_number_t infoCount = HOST_VM_INFO_COUNT;
kern_return_t kr = host_statistics(mach_host_self(),
HOST_VM_INFO,
(host_info_t)&vmStats,
&infoCount);
fs_system_ram_usage system_memory_usage = {0, 0, 0};
if (kr != KERN_SUCCESS) {
return system_memory_usage;
}
system_memory_usage.used_size = (vmStats.active_count + vmStats.wire_count + vmStats.inactive_count) * vm_kernel_page_size;
system_memory_usage.available_size = (vmStats.free_count) * vm_kernel_page_size;
system_memory_usage.total_size = [NSProcessInfo processInfo].physicalMemory;
return system_memory_usage;
}
实现功能:
- 系统总内存
- 系统使用内存
- 系统可用内存
- 当前应用内存使用量
t(App总启动时间) = t1(main()之前的加载时间)+ t2(main()之后的加载时间)
t1 = 系统先读取App的可执行文件(Mach-O 文件),从里面获得 dyld 的路径,加载 dyld,dyld 去初始化运行环境,开启缓存策略,加载程序相关依赖库(其中也包含我们的可执行文件),并对这些库进行链接,最后调用每个依赖库的初始化方法,在这一步, runtime 被初始化。当所有依赖库的初始化后,轮到最后一位(程序可执行文件)进行初始化,在这时 runtime 会对项目中所有类进行类结构初始化,然后调用所有的 load 方法。最后 dyld 返回 main 函数地址, main 函数被调用,我们便来到了熟悉的程序入口。可归纳以下几点:
-
系统先读取 App 的可执行文件(
Mach-O文件,自身 App 的所有.o文件的集合) -
加载dyld(动态链接编辑器)
-
Load dylibs: 加载动态库(包括所依赖的所有动态库)
-
Rebase && Bind
-
Objc SetUp: 初始化 Objective C Runtime
-
Initializers
t2 = main方法执行之后到
AppDelegate 类中的- (BOOL)Application:(UIApplication *)Application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions方法执行结束前这段时间,主要是构建第一个界面,并完成渲染展示。
因为类的
+ load方法在main函数执行之前调用,所以我们可以在+ load方法记录开始时间,同时监听UIApplicationDidFinishLaunchingNotification通知,收到通知时将时间相减作为应用启动时间,这样做有一个好处,不需要侵入到业务方的main函数去记录开始时间点。
代码实现:
static uint64_t loadTime;
static uint64_t applicationRespondedTime = -1;
static mach_timebase_info_data_t timebaseInfo;
static inline NSTimeInterval MachTimeToSeconds(uint64_t machTime) {
return ((machTime / 1e9) * timebaseInfo.numer) / timebaseInfo.denom;
}
@implementation XXStartupMeasurer
+ (void)load {
loadTime = mach_absolute_time();
mach_timebase_info(&timebaseInfo);
@autoreleasepool {
__block id<NSObject> obs;
obs = [[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserverForName:UIApplicationDidFinishLaunchingNotification
object:nil queue:nil
usingBlock:^(NSNotification *note) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
applicationRespondedTime = mach_absolute_time();
NSLog(@"StartupMeasurer: it took %f seconds until the app could respond to user interaction.", MachTimeToSeconds(applicationRespondedTime - loadTime));
});
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] removeObserver:obs];
}];
}
}注意:由于 load 方法执行时机问题,通过以上方式计算出的结果并不十分准确
FPS 是测量用于保存、显示动态视频的信息数量,每秒钟帧数愈多,所显示的动作就会愈流畅,一般应用只要保持 FPS 在 50-60,应用就会给用户流畅的感觉,反之,用户则会感觉到卡顿。
代码实现:
@implementation YYFPSLabel {
CADisplayLink *_link;
NSUInteger _count;
NSTimeInterval _lastTime;
}
- (id)init {
self = [super init];
if( self ){
_link = [CADisplayLink displayLinkWithTarget:[YYWeakProxy proxyWithTarget:self] selector:@selector(tick:)];
[_link addToRunLoop:[NSRunLoop mainRunLoop] forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes];
}
return self;
}
- (void)dealloc {
[_link invalidate];
}
- (void)tick:(CADisplayLink *)link {
if (_lastTime == 0) {
_lastTime = link.timestamp;
return;
}
_count++;
NSTimeInterval delta = link.timestamp - _lastTime;
if (delta < 1) return;
_lastTime = link.timestamp;
float fps = _count / delta;
_count = 0;
}由于 CADisplayLink 的
frameInterval值默认为 1,代表与帧刷新同步,这样可以通过 CADisplayLink 一个时间段内定时器方法刷新次数算出屏幕 FPS 值
注意:值得注意的是基于 CADisplayLink 实现的 FPS 在生产场景中只有指导意义,不能代表真实的 FPS,因为基于 CADisplayLink 实现的 FPS 无法完全检测出当前 Core Animation 的性能情况,它只能检测出当前 RunLoop 的帧率。
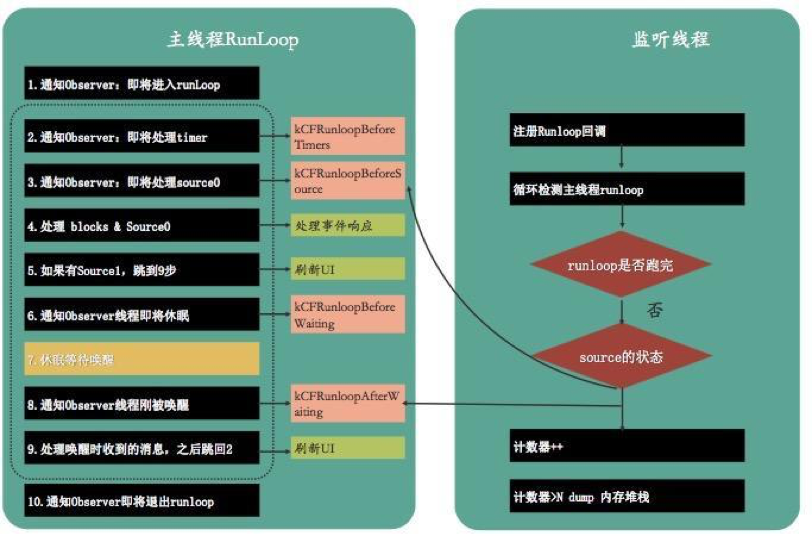
监控卡顿,最直接就是找到主线程。我们知道一个线程的消息事件处理都是依赖于 NSRunLoop 来驱动,所以要知道线程正在调用什么方法,就需要从 NSRunLoop 来入手。发现 NSRunLoop 调用方法主要就是在 kCFRunLoopBeforeSources 和kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting 之间,还有kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting 之后,也就是如果我们发现这两个时间内耗时太长,那么就可以判定出此时主线程卡顿。
代码实现:
static void runLoopObserverCallBack(CFRunLoopObserverRef observer, CFRunLoopActivity activity, void *info)
{
MyClass *object = (__bridge MyClass*)info;
// 记录状态值
object->activity = activity;
// 发送信号
dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore = moniotr->semaphore;
dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore);
}
- (void)registerObserver
{
CFRunLoopObserverContext context = {0,(__bridge void*)self,NULL,NULL};
CFRunLoopObserverRef observer = CFRunLoopObserverCreate(kCFAllocatorDefault,
kCFRunLoopAllActivities,
YES,
0,
&runLoopObserverCallBack,
&context);
CFRunLoopAddObserver(CFRunLoopGetMain(), observer, kCFRunLoopCommonModes);
// 创建信号
semaphore = dispatch_semaphore_create(0);
// 在子线程监控时长
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
while (YES)
{
// 假定连续5次超时50ms认为卡顿(当然也包含了单次超时250ms)
long st = dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore, dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, 50*NSEC_PER_MSEC));
if (st != 0)
{
if (activity==kCFRunLoopBeforeSources || activity==kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting)
{
if (++timeoutCount < 5)
continue;
NSLog(@"好像有点儿卡哦");
}
}
timeoutCount = 0;
}
});
}利用 Objective-C 语言的动态特性,采用 AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)面向切面编程的设计思想,做到无痕植入。能够自动在 app 运行时实时捕获导致 app 崩溃的破环因子,然后通过特定的技术手段去化解这些破坏因子,使 app 免于崩溃,照样可以继续正常运行,为 app 的持续运转保驾护航。
实现思路来自《大白健康系统--iOS APP运行时Crash自动修复系统》。
具体实现引用了JJException库以及其实现原理
实现功能:
- Unrecognized selector crash
- KVO crash
- NSNotification crash
- NSTimer crash
- Container crash(数组越界,插nil等)
- NSString crash (字符串操作的crash)
- Bad Access crash (野指针)
开发 iOS 应用,解决 Crash 问题始终是一个难题。Crash分为两种,一种是Mach Exception(系统异常),Mach异常最终会转化成Unix信号投递到出错的线程,原因可能是访问了不属于本进程的内存地址,有可能是访问已被释放的内存;另一种是未被捕获的 Objective-C 异常(NSException),导致程序向自身发送了 SIGABRT 信号而崩溃。
对于系统 Crash 而引起的程序异常退出,可以通过UncaughtExceptionHandler 机制捕获;也就是说在程序中 catch 以外的内容,被系统自带的错误处理而捕获。我们要做的就是用自定义的函数替代该 ExceptionHandler 即可。
代码实现:
/**
开启捕捉闪退handler
*/
void fs_installUncaughtCrashHandler() {
if (isSetUncaughtHandler) {
return;
}
isSetUncaughtHandler = YES;
oldUncaughtExceptionHandler = NSGetUncaughtExceptionHandler();
NSSetUncaughtExceptionHandler (p_uncaughtExceptionHandler);
signal(SIGABRT, p_uncaughtSignalHandler);
signal(SIGILL, p_uncaughtSignalHandler);
signal(SIGSEGV, p_uncaughtSignalHandler);
signal(SIGFPE, p_uncaughtSignalHandler);
signal(SIGBUS, p_uncaughtSignalHandler);
signal(SIGPIPE, p_uncaughtSignalHandler);
}
/**
异常处理回调
@param exception NSException
*/
- (void)p_uncaughtExceptionHandler:(NSException *)exception {
if (!_hashTable) {
return;
}
FSCrashInfo *info = [[FSCrashInfo alloc] init];
info.date = [NSDate date];
info.signal = kFSCrashException;
info.exception = exception;
info.name = exception.name;
info.reason = exception.reason;
info.callBackTrace = [exception.callStackSymbols componentsJoinedByString:@"\n"];
for (id<FSCrashMonitorDelegate> delegate in _hashTable) {
if ([delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(crashMonitor:didCatchExceptionInfo:)]) {
[delegate crashMonitor:self didCatchExceptionInfo:info];
}
}
}
/**
异常信号处理回调
@param signal 信号类型
*/
- (void)p_uncaughtSignalHandler:(int)signal {
if (!_hashTable) {
return;
}
NSMutableArray *callStackSymbols = [[NSThread callStackSymbols] mutableCopy];
if (callStackSymbols.count > 2) {
[callStackSymbols removeObjectsAtIndexes:[NSIndexSet indexSetWithIndexesInRange:NSMakeRange(0, 3)]];
}
FSCrashInfo *info = [[FSCrashInfo alloc]init];
info.date = [NSDate date];
info.signal = signal;
info.name = [self signalName:signal];
info.reason = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Signal %@ crash.",
[self signalName:signal]];
info.callBackTrace = [callStackSymbols componentsJoinedByString:@"\n"];
for (id<FSCrashMonitorDelegate>delegate in _hashTable) {
if ([delegate respondsToSelector:@selector(crashMonitor:didCatchExceptionInfo:)]) {
[delegate crashMonitor:self didCatchExceptionInfo:info];
}
}
[self stop];
kill(getpid(), SIGKILL);
}注意:此模块只是对未防护的闪退信息进行记录,用来定位问题,并不能屏蔽闪退
应用内自动解析 DNS,降低 DNS 请求带来的延迟,其次预防了 DNS 被劫持。应用将 DNS 映射文件打包到 APP 中,客户端启动时从服务器获取最新的 DNS 映射。此外客户端将自己的位置信息诸如 IP 地址,国家码等加入映射文件的请求参数中,服务器就可以根据客户端所处的位置不同,下发距离其物理位置最近的 Server IP 地址,从而减小整体网络请求的延迟,实现一定程度的服务器动态部署 DNS。当映射 IP 地址持续请求失败,上报失败 IP 地址。
实现功能:
- 移动网络 IP
- WIfi 网络 IP
在每一个 HTTP 请求开始时,URL 加载系统创建一个合适的 NSURLProtocol 对象处理对应的 URL 请求,而我们需要做的就是写一个继承自 NSURLProtocol 的类,并通过 - registerClass: 方法注册我们的协议类,然后 URL 加载系统就会在请求发出时使用我们创建的协议对象对该请求进行处理。我们在请求以及响应时记录数据从而实现了对网络流量的监控。
注意:需要注意的是 NSURLProtocol 只能拦截
UIURLConnection、NSURLSession 和 UIWebView 中的请求,对于 WKWebView 中发出的网络请求无能为力.
实现功能:
- 系统网络流量
- 应用网络流量
- 首包时间
- 响应时间
- 网络状态
- 上行流量
- 下行流量
- 本地日志记录
- 业务逻辑采集以及日志上传