-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 239
Home
Welcome to Medusa's wiki. Please use the sidebar to navigate to a section:
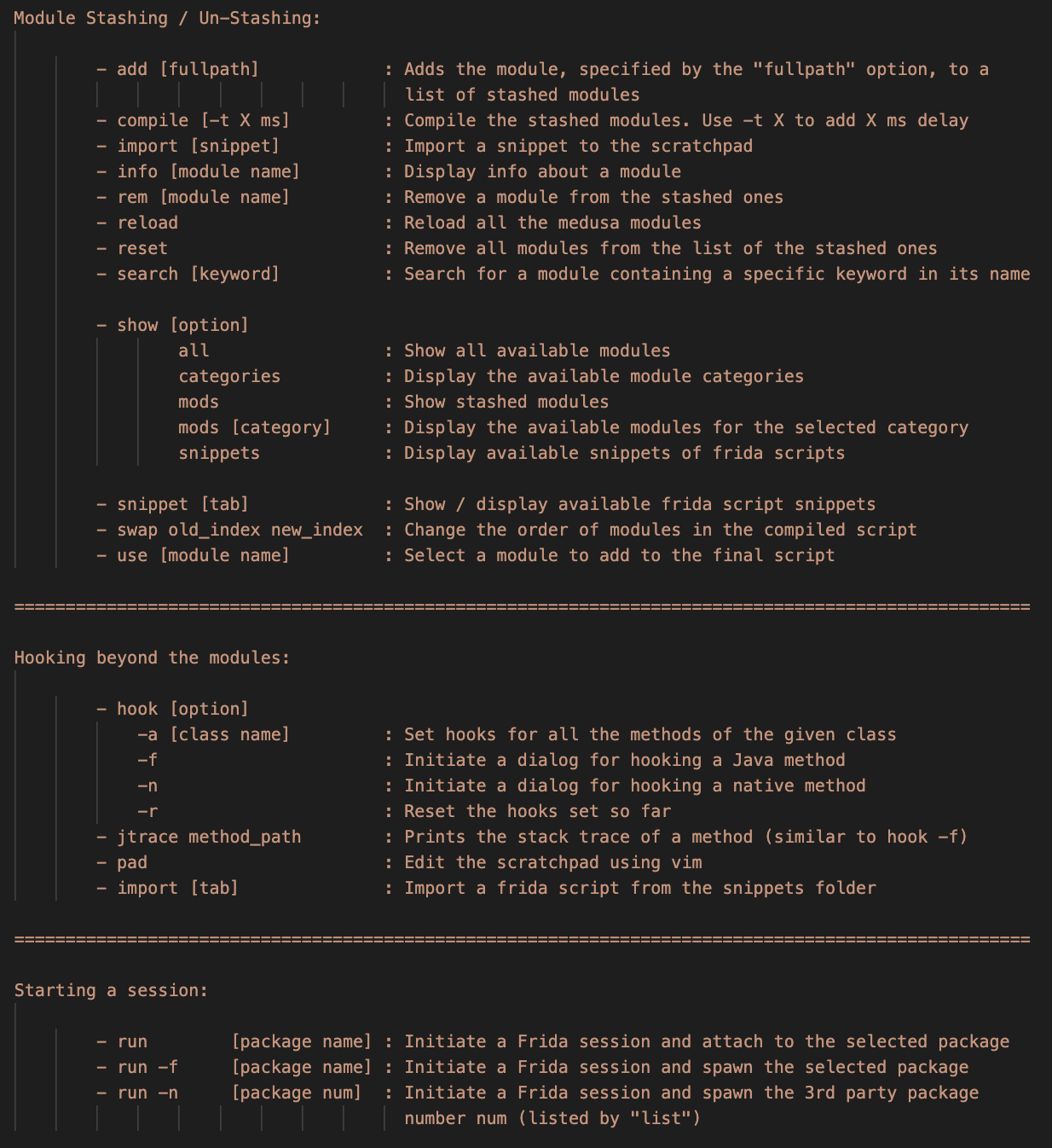
Use the show command, followed one of the following options:
- all to Display all available modules
- mods to Display stashed modules
- categories to Display the available module categories
- mods [category] to Display the available modules for the selected category
Use the info [module name]to get help about a specific module
- Use the
use [module name]to add a module to the stashed ones:
medusa> use http_communications/multiple_unpinner
- Use the
rem [module name]to remove a module to the stashed ones
medusa> rem http_communications/multiple_unpinner
- Use the
add [full-path-to-module]to stash modules saved out of the default directory
medusa> add /full/path/to/module.med
-
Use the
resetto empty the list of stashed modules and clear the unified script -
Use the
swapto change the compilation order of the stashed modules:
medusa> swap [index 1] [index 2]
- Use the
compileto compile your stashed modules to a unified one:
medusa> compile
- Use the
compile -t X(X is the delay value in milliseconds) to add a loading delay:
medusa> compile -t 1000
- Use the
run -f [package name]or torun -n [package number]to start or restart an application and attach to it (you can use thelistcommand to get the package number).
medusa> run -f com.foo.bar
- Use the
run [package name]to attach to an application.
[in-session] |c:clear |e:exit |r:reload | | rs:reset scratchpad |i:info |t:trace |?:help |:
While 'in session' you can use one of the following commands:
'c' (c)lear the sreen
'e' (e)xit the session
'r' (r)eload the script in case it changed
'rs' (r)e(s)et the scratchpad
'i' print (i)nformation about the application
't' (t)race a function and print the stack trace (e.g. t com.foo.bar.func)
'?' print this help message
- Use the
hookcommand followed by one of the options bellow to intercept methods which are not present in the currently available modules:
-a [class name] : Set hooks for all the methods of the given class. Example:
medusa> hook -a com.foo.bar.className
-f : Set hooks for a single method. Example
medusa> hook -f
Enter the full name of the method(s) class: com.foo.bar
Enter a method name (CTRL+C to Exit): fooMethod
Enable backtrace? (y/N) y
[+] Method: fooMethod hook added !
Enter a method name (CTRL+C to Exit):
Same result can be achieved with the jtrace command: medusa> jtrace full_path_to_method
-n : Set hooks for a native method. Example
medusa> hook -n
Library name (e.g.: libnative.so): libfoo.so
Imported or exported function? (i/e) e
Function name or offset (e.g.: 0x1234): 0x1234
Number of function arguments (0 to disable trace): 3
Enable backtrace? (y/N) y
Enable memory read? (y/N) y
Read Buffer size (0-1024): 128
Module scratchpad already added !
-r: Reset the hooks set so far
- Use the
padcommand to edit the scratchpad
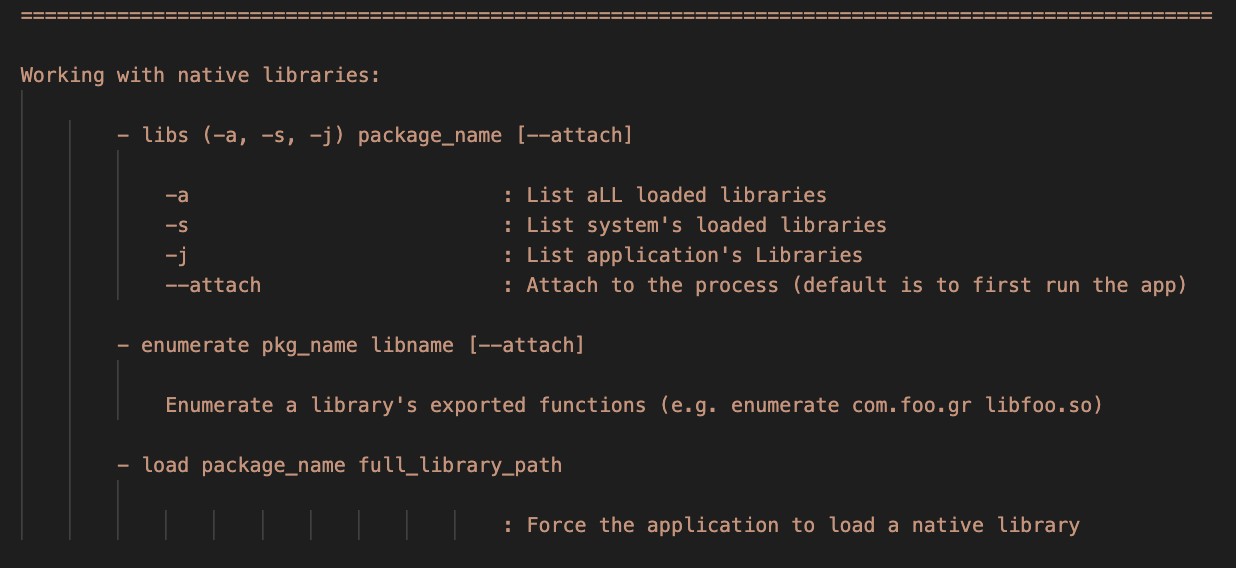
- Use the
libscommand followed by one of the options bellow to list the application's native libraries:
-a : List all the application's libraries.
-s : List only the system's libraries.
-j : List only the application's libraries.
Add the --attach to attach to an already running instance of the application (usually has better results)
Example:
medusa> libs -j com.foo.bar libnative.so --attach
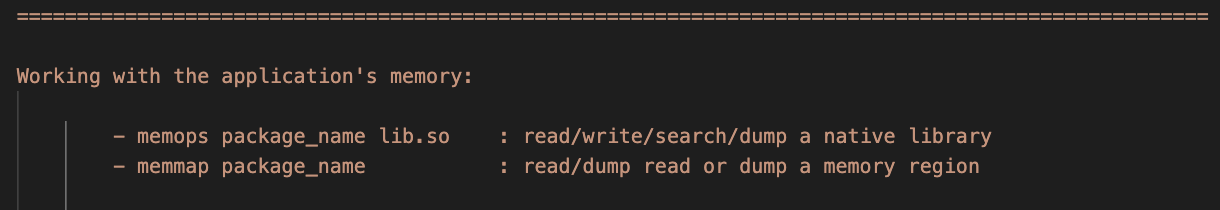
You can read/write/search/dump the application's memory by using the memops or memmap command. The former needs a library name to be attached to, while the later uses memory regions.
In both cases the application must already be running !
- memops example:
medusa> memops package_name libname.so
If the attachment is successful, medusa will start a session where you have the following options:
|(E)xit |r@offset |w@offset |⏎ |scan |(h)elp| dump|:
To get more details about the functionality of each option, please refer to the Basic Usage section
- memmap example:
medusa> memmap package_name
Then choose a memory region from the submenu.
If the attachment is successful, medusa will start a session where you have the following options:
|(E)xit |r@offset |dump |:
To get more details about the functionality of each option, please refer to the Basic Usage section
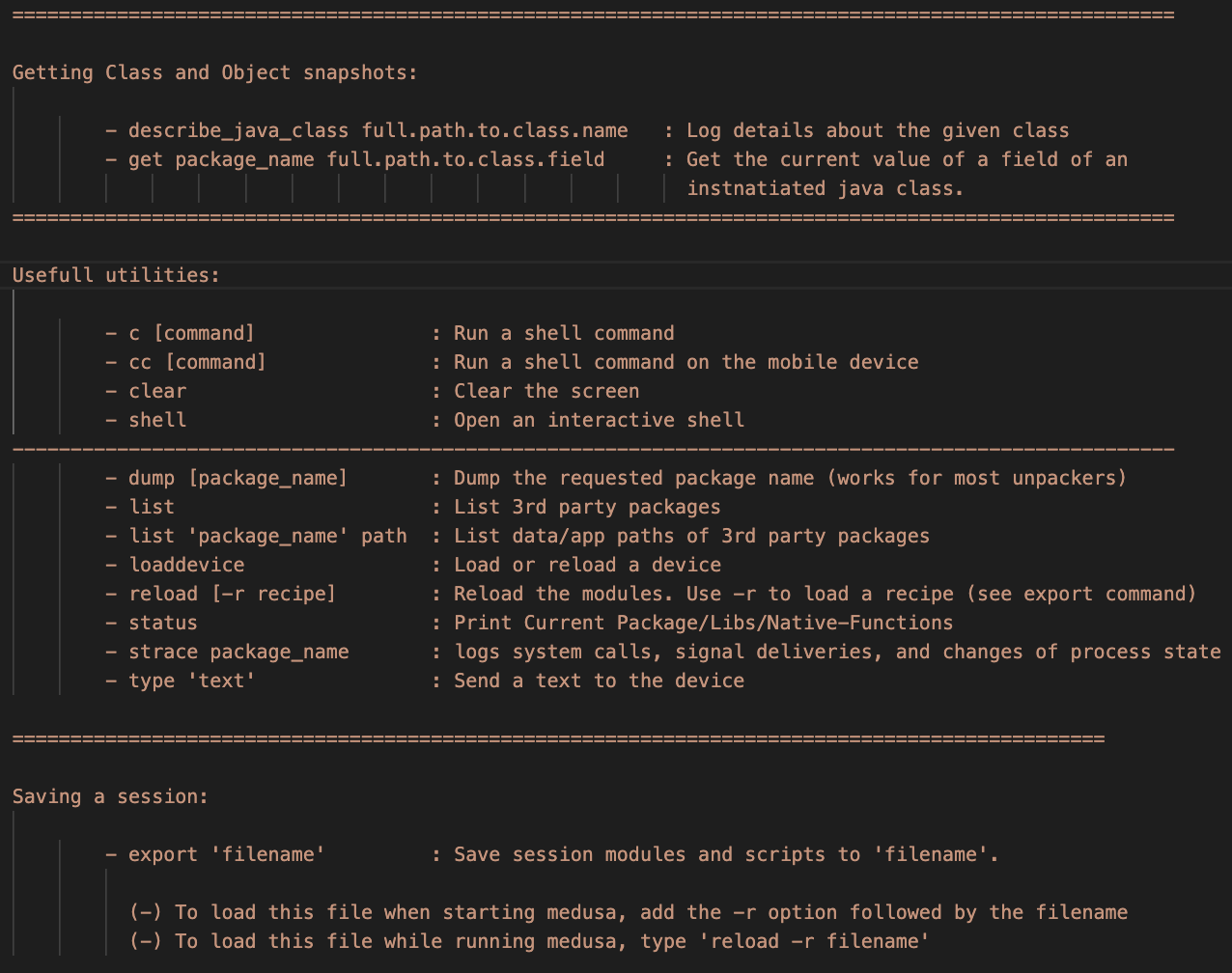
Use the describe_java_class to print a class's details, example:
medusa> describe_java_class full.path.to.class.name
Use the get to print the value of a field of a class, assuming that the class has been instantiated.
medusa> get package_name full.path.to.class.field
- Run a shell command
medusa> c ls -al
- Run a shell command to the connected device
medusa> cc ls -al
- Clear the screen
medusa> clear
- Open an interactive shell
medusa> clear
- Dump the dex files of an app
medusa> dump com.foo.bar
- List the installed packages
medusa> list
- List the paths of a package
medusa> list com.foo.bar path
- Load or reload a device:
medusa> loaddevice
- Reload the medusa modules. This option is useful in case you made a change to a medusa module.
medusa> reload
- Load a saved session
medusa> reload -r session-filename
- Print the current session status
medusa> status
- Log system calls
medusa> strace package_name
- Send text to the device
medusa> type 'text'
- Save the current session
medusa> export file-name
To load back this session use one of the following options:
-
./medusa -r file-name -
medusa> reload -r file-name
Medusa Wiki
Medusa Wiki
-
- Searching for the right module
- Getting info about a module
- Stashing / un-stashing
- Compiling
- Starting a session
- Hooking beyond the modules
- Importing Frida scripts
- Working with native libraries
- Working with the application's memory
- Getting Class and Object snapshots
- Useful utilities
- Saving a session (recipe)